Cancer Res Treat.
2016 Apr;48(2):859-863. 10.4143/crt.2014.334.
Extranodal Marginal Zone B-Cell Lymphoma of Mucosa-Associated Tissue Type Involving the Dura
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. mednsh@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Pathology, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2454367
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2014.334
Abstract
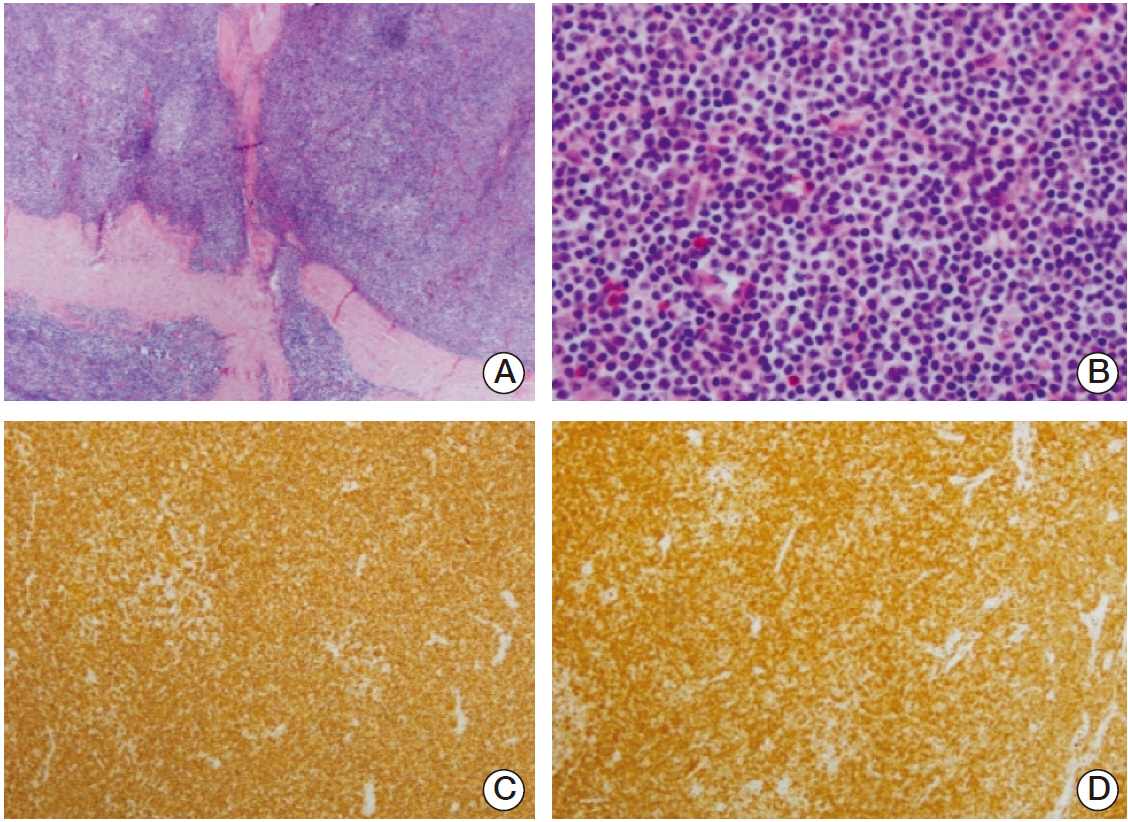
- Primary central nervous system marginal zone B-cell lymphoma (MZBCL) is very rare, with only a few reported cases worldwide. It has an indolent disease course with high cure potential. We experienced a rare case of dural MZBCL of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) in a 69-year-old man who presented with headache. A magnetic resonance imaging scan of brain showed a 1.9×3.6-cm-sized extra-axial mass with a broad based dural attachment to the anterosuperior aspect of the falx cerebri, radiographically consistent with meningioma. Surgical resection yielded a MZBCL of the MALT type. Histopathology revealed a lymphoplasmacytic infiltration of the dura, and immunohistochemical study showed a B-cell phenotype with CD20, bcl-2, MUM-1, Ki-67 positive. He was treated with chemotherapy after complete surgical resection and remained free of disease at 30 months after chemotherapy. MALT lymphoma must be considered in the differential diagnosis in patients presenting radiographically with meningioma.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Park I, Huh J, Kim JH, Lee SW, Ryu MH, Kang YK. Primary central nervous system marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of the Basal Ganglia mimicking low-grade glioma: a case report and review of the literature. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma. 2008; 8:305–8.
Article2. Bayraktar S, Stefanovic A, Montague N, Davis J, Murray T, Lossos IS. Central nervous system manifestations of marginal zone B-cell lymphoma. Ann Hematol. 2010; 89:1003–9.
Article3. Jaffe ES. The 2008 WHO classification of lymphomas: implications for clinical practice and translational research. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2009; 523–31.
Article4. Terada T. Extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT lymphoma) in ulcerative colitis. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:319–22.
Article5. Bhagavathi S, Greiner TC, Kazmi SA, Fu K, Sanger WG, Chan WC. Extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of the dura mater with IgH/MALT1 translocation and review of literature. J Hematop. 2008; 1:131–7.
Article6. Abbi KK, Muzaffar M, Gaudin D, Booth RL Jr, Feldmeier JJ, Skeel RT. Primary CNS lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma: a case report and review of literature. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2013; 6:76–8.
Article7. Giannini C, Dogan A, Salomao DR. CNS lymphoma: a practical diagnostic approach. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2014; 73:478–94.8. Sacho RH, Kogels M, du Plessis D, Jowitt S, Josan VA. Primary diffuse large B-cell central nervous system lymphoma presenting as an acute space-occupying subdural mass. J Neurosurg. 2010; 113:384–7.
Article9. Kamoshima Y, Sawamura Y, Sugiyama T, Yamaguchi S, Houkin K, Kubota K. Primary central nervous system mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma: case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2011; 51:527–30.10. Shaia J, Kerr PB, Saini A, Roberti F, Kapil J, Jones R, et al. Mucosa-associated lymphoma tissue of the dura presenting as meningioma. South Med J. 2010; 103:950–2.
Article11. Tu PH, Giannini C, Judkins AR, Schwalb JM, Burack R, O'Neill BP, et al. Clinicopathologic and genetic profile of intracranial marginal zone lymphoma: a primary low-grade CNS lymphoma that mimics meningioma. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:5718–27.
Article12. Iwamoto FM, DeAngelis LM, Abrey LE. Primary dural lymphomas: a clinicopathologic study of treatment and outcome in eight patients. Neurology. 2006; 66:1763–5.
Article13. Kumar S, Kumar D, Kaldjian EP, Bauserman S, Raffeld M, Jaffe ES. Primary low-grade B-cell lymphoma of the dura: a mucosa associated lymphoid tissue-type lymphoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997; 21:81–7.14. Sanjeevi A, Krishnan J, Bailey PR, Catlett J. Extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of malt type involving the cavernous sinus. Leuk Lymphoma. 2001; 42:1133–7.
Article15. Lehman NL, Horoupian DS, Warnke RA, Sundram UN, Peterson K, Harsh GR 4th. Dural marginal zone lymphoma with massive amyloid deposition: rare low-grade primary central nervous system B-cell lymphoma. Case report. J Neurosurg. 2002; 96:368–72.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Primary Pulmonary Extranodal Marginal Zone B-Cell Lymphoma of the MALT Type
- A Case of Synchronous Lung Adenocarcinoma and Extranodal Marginal Zone B-Cell Lymphoma of Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT) Type
- Endoscopic Findings of Gastric Extranodal Marginal Zone B-Cell Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma
- A Case of Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma in Nasopharynx and Thyroid Gland
- A Case of Primary Cutaneous Marginal Zone B-cell Lymphoma