Investig Clin Urol.
2019 Jan;60(1):14-20. 10.4111/icu.2019.60.1.14.
Prognostic significance of preoperative and follow-up neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with non-metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Ajou University Hospital, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. sikimuro@gmail.com
- KMID: 2434620
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/icu.2019.60.1.14
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the significance of preoperative and follow-up neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) as prognostic factors for recurrence in patients with non-metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (NMCCRCC).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 309 patients with NMCCRCC who underwent radical or partial nephrectomy. The prognostic significance of various clinicopathological variables, preoperative NLR (pNLR) and PLR (pPLR), and NLR and PLR at recurrence or quasi-recurrence (rNLR and rPLR) for recurrence-free survival (RFS) was analyzed.
RESULTS
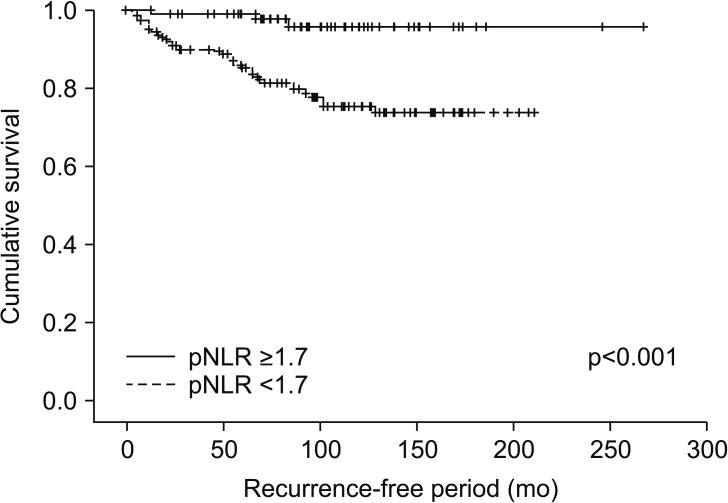
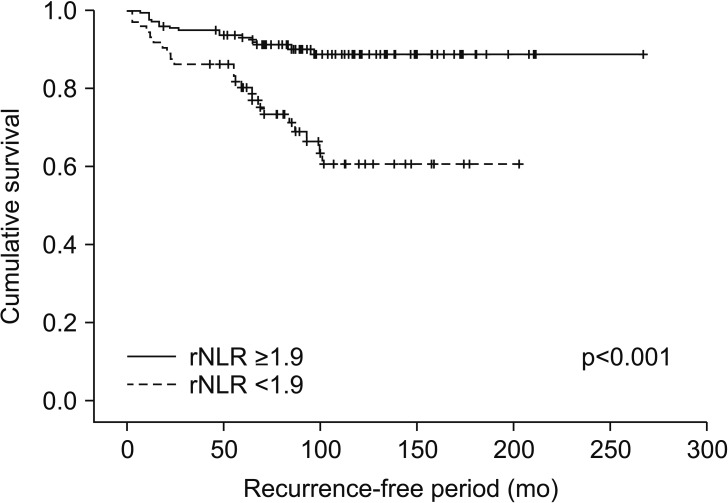
At mean follow-up of 93 months, 44 patients (14.2%) developed recurrence. In the univariate analysis, clinical presentation, tumor size, pathologic tumor stage, Fuhrman grade, pNLR, pPLR and rNLR were significant prognostic factors for RFS. In the multivariate analysis using pNLR and pPLR as continuous variables, tumor size, pathologic tumor stage and pPLR were independent prognostic factors for RFS. In the multivariate analysis using pNLR and pPLR as dichotomous variables, tumor size, pathologic tumor stage, Fuhrman grade and pNLR ≥1.7 were independent prognostic factors for RFS. In multivariate analyses using rNLR and rPLR, only tumor size and pathologic tumor stage were independent prognostic factors for RFS. In a subset of patients with recurrence or at least 42 months follow-up without recurrence, rNLR ≥1.9 was significantly associated with worse RFS, albeit without independent significance.
CONCLUSIONS
pNLR and pPLR are independent prognostic factors for RFS in patients with NMCCRCC. We propose that postoperative follow-up NLR of 1.9 and higher with one or more adverse clinicopathological factors should prompt radiologic evaluation for possible metastasis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Methylation Signature for Prediction of Progression Free Survival in Surgically Treated Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Ho Won Kang, Hongyong Park, Sung Pil Seo, Young Joon Byun, Xuan-Mei Piao, Sung Min Kim, Won Tae Kim, Seok-Joong Yun, Wooyeong Jang, Ho Sun Shon, Keun Ho Ryu, Sang-Cheol Lee, Wun-Jae Kim, Yong-June Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2019;34(19):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e144.Letter to the editor: Prognostic significance of preoperative and follow-up neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with non-metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Beuy Joob, Viroj Wiwaniitkit
Investig Clin Urol. 2019;60(4):331-332. doi: 10.4111/icu.2019.60.4.331.
Reference
-
1. Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010; 127:2893–2917. PMID: 21351269.
Article2. Lipworth L, Tarone RE, McLaughlin JK. The epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2006; 176:2353–2358. PMID: 17085101.3. Pichler M, Hutterer GC, Chromecki TF, Jesche J, Kampel-Kettner K, Pummer K, et al. Renal cell carcinoma stage migration in a single European centre over 25 years: effects on 5- and 10-year metastasis-free survival. Int Urol Nephrol. 2012; 44:997–1004. PMID: 22456765.4. Janzen NK, Kim HL, Figlin RA, Belldegrun AS. Surveillance after radical or partial nephrectomy for localized renal cell carcinoma and management of recurrent disease. Urol Clin North Am. 2003; 30:843–852. PMID: 14680319.
Article5. Eggener SE, Yossepowitch O, Pettus JA, Snyder ME, Motzer RJ, Russo P. Renal cell carcinoma recurrence after nephrectomy for localized disease: predicting survival from time of recurrence. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:3101–3106. PMID: 16809736.
Article6. Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 2008; 454:436–444. PMID: 18650914.
Article7. Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 2010; 140:883–899. PMID: 20303878.
Article8. Wojtukiewicz MZ, Sierko E, Hempel D, Tucker SC, Honn KV. Platelets and cancer angiogenesis nexus. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017; 36:249–262. PMID: 28681240.
Article9. Kaynar M, Yıldırım ME, Badem H, Caviş M, Tekinarslan E, Istanbulluoğlu MO, et al. Bladder cancer invasion predictability based on preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio. Tumour Biol. 2014; 35:6601–6605. PMID: 24696263.
Article10. Kemal Y, Yucel I, Ekiz K, Demirag G, Yilmaz B, Teker F, et al. Elevated serum neutrophil to lymphocyte and platelet to lymphocyte ratios could be useful in lung cancer diagnosis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014; 15:2651–2654. PMID: 24761879.
Article11. Lorente D, Mateo J, Templeton AJ, Zafeiriou Z, Bianchini D, Ferraldeschi R, et al. Baseline neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is associated with survival and response to treatment with second-line chemotherapy for advanced prostate cancer independent of baseline steroid use. Ann Oncol. 2015; 26:750–755. PMID: 25538172.
Article12. Ohno Y, Nakashima J, Ohori M, Hatano T, Tachibana M. Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as an independent predictor of recurrence in patients with nonmetastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2010; 184:873–878. PMID: 20643463.
Article13. Semeniuk-Wojtaś A, Lubas A, Stec R, Syryło T, Niemczyk S, Szczylik C. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-tolymphocyte ratio, and C-reactive protein as new and simple prognostic factors in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2018; 16:e685–e693. PMID: 29454639.14. Pichler M, Hutterer GC, Stoeckigt C, Chromecki TF, Stojakovic T, Golbeck S, et al. Validation of the pre-treatment neutrophillymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor in a large European cohort of renal cell carcinoma patients. Br J Cancer. 2013; 108:901–907. PMID: 23385728.
Article15. de Martino M, Pantuck AJ, Hofbauer S, Waldert M, Shariat SF, Belldegrun AS, et al. Prognostic impact of preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in localized nonclear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2013; 190:1999–2004. PMID: 23831313.
Article16. Viers BR, Houston Thompson R, Boorjian SA, Lohse CM, Leibovich BC, Tollefson MK. Preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio predicts death among patients with localized clear cell renal carcinoma undergoing nephrectomy. Urol Oncol. 2014; 32:1277–1284. PMID: 25017696.
Article17. Lucca I, de Martino M, Hofbauer SL, Zamani N, Shariat SF, Klatte T. Comparison of the prognostic value of pretreatment measurements of systemic inflammatory response in patients undergoing curative resection of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. World J Urol. 2015; 33:2045–2052. PMID: 25894368.
Article18. Huang J, Dahl DM, Dong L, Liu Q, Cornejo K, Wang Q, et al. Preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and neutrophilia are independent predictors of recurrence in patients with localized papillary renal cell carcinoma. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:891045. PMID: 26448948.
Article19. Wen RM, Zhang YJ, Ma S, Xu YL, Chen YS, Li HL, et al. Preoperative neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor in patients with non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015; 16:3703–3708. PMID: 25987025.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Letter to the editor: Prognostic significance of preoperative and follow-up neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with non-metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Incorporating Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-to-lymphocyte Ratio in Place of Neutrophil Count and Platelet Count Improves Prognostic Accuracy of the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium Model
- Prognostic Significance of the Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-Lymphocyte Ratio in Neuroendocrine Carcinoma
- Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in early-stage ovarian clear-cell carcinoma
- Clinical Significance of Preoperative Inflammatory Parameters in Gastric Cancer Patients