J Korean Med Sci.
2017 Jan;32(1):155-159. 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.1.155.
Pregnancy and Delivery in a Generalized Dystonia Patient Treated with Internal Globus Pallidal Deep Brain Stimulation: a Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. paeksh@snu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Neurology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2417599
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.1.155
Abstract
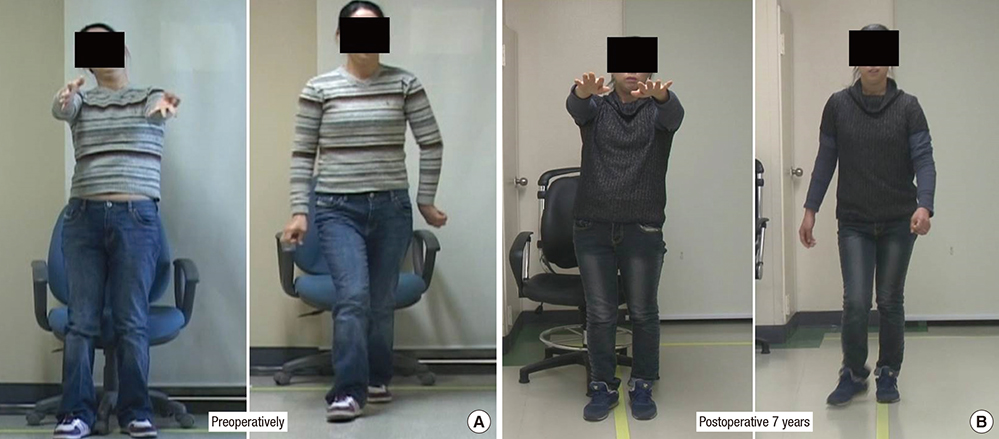
- Internal globus pallidus (GPi) deep brain stimulation (DBS) has been widely accepted as an effective treatment modality of medically refractory dystonia. However, there have been few studies regarding the safety issue of pregnancy and childbirth related with DBS. This report describes a female patient who was pregnant and delivered a baby after GPi DBS surgery. A 33-year-old female patient with acquired generalized dystonia underwent bilateral GPi DBS implantation. She obtained considerable improvement in both movement and disability after DBS implantation. Four years later, she was pregnant and the obstetricians consulted us about the safety of the delivery. At 38-weeks into pregnancy, a scheduled caesarian section was carried out under general anesthesia. After induction using thiopental and succinylcholine, intubation was done quickly, followed by DBS turn off. For hemostasis, only bipolar electrocautery was used. Before awakening from the anesthesia, DBS was turned on as the same parameters previously adjusted. After delivery, she could feed her baby by herself, because the dystonia of left upper extremity and hand was improved. Until now, she has been showing continual improvement and being good at housework, carrying for children, with no trouble in daily life. This observation indicates that the patients who underwent DBS could safely be pregnant and deliver a baby.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fahn S. Concept and classification of dystonia. Adv Neurol. 1988; 50:1–8.2. Albanese A, Bhatia K, Bressman SB, Delong MR, Fahn S, Fung VS, Hallett M, Jankovic J, Jinnah HA, Klein C, et al. Phenomenology and classification of dystonia: a consensus update. Mov Disord. 2013; 28:863–873.3. Toda H, Hamani C, Lozano A. Deep brain stimulation in the treatment of dyskinesia and dystonia. Neurosurg Focus. 2004; 17:E2.4. Meoni S, Zurowski M, Lozano AM, Hodaie M, Poon YY, Fallis M, Voon V, Moro E. Long-term neuropsychiatric outcomes after pallidal stimulation in primary and secondary dystonia. Neurology. 2015; 85:433–440.5. Krauss JK. Deep brain stimulation for cervical dystonia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2003; 74:1598.6. Coubes P, Vayssiere N, El Fertit H, Hemm S, Cif L, Kienlen J, Bonafe A, Frerebeau P. Deep brain stimulation for dystonia. Surgical technique. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2002; 78:183–191.7. Kupsch A, Benecke R, Müller J, Trottenberg T, Schneider GH, Poewe W, Eisner W, Wolters A, Müller JU, Deuschl G, et al. Pallidal deep-brain stimulation in primary generalized or segmental dystonia. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:1978–1990.8. Coubes P, Cif L, El Fertit H, Hemm S, Vayssiere N, Serrat S, Picot MC, Tuffery S, Claustres M, Echenne B, et al. Electrical stimulation of the globus pallidus internus in patients with primary generalized dystonia: long-term results. J Neurosurg. 2004; 101:189–194.9. Vidailhet M, Vercueil L, Houeto JL, Krystkowiak P, Benabid AL, Cornu P, Lagrange C, Tézenas du Montcel S, Dormont D, Grand S, et al. Bilateral deep-brain stimulation of the globus pallidus in primary generalized dystonia. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:459–467.10. Krauss JK, Loher TJ, Weigel R, Capelle HH, Weber S, Burgunder JM. Chronic stimulation of the globus pallidus internus for treatment of non-dYT1 generalized dystonia and choreoathetosis: 2-year follow up. J Neurosurg. 2003; 98:785–792.11. Vidailhet M, Jutras MF, Grabli D, Roze E. Deep brain stimulation for dystonia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2013; 84:1029–1042.12. Lee JY, Deogaonkar M, Rezai A. Deep brain stimulation of globus pallidus internus for dystonia. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2007; 13:261–265.13. FitzGerald JJ, Rosendal F, de Pennington N, Joint C, Forrow B, Fletcher C, Green AL, Aziz TZ. Long-term outcome of deep brain stimulation in generalised dystonia: a series of 60 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2014; 85:1371–1376.14. Vercueil L, Pollak P, Fraix V, Caputo E, Moro E, Benazzouz A, Xie J, Koudsie A, Benabid AL. Deep brain stimulation in the treatment of severe dystonia. J Neurol. 2001; 248:695–700.15. Speelman JD, Contarino MF, Schuurman PR, Tijssen MA, de Bie RM. Deep brain stimulation for dystonia: patient selection and outcomes. Eur J Neurol. 2010; 17:Suppl 1. 102–106.16. Bour LJ, Contarino MF, Foncke EM, de Bie RM, van den Munckhof P, Speelman JD, Schuurman PR. Long-term experience with intraoperative microrecording during DBS neurosurgery in STN and GPi. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2010; 152:2069–2077.17. Paluzzi A, Bain PG, Liu X, Yianni J, Kumarendran K, Aziz TZ. Pregnancy in dystonic women with in situ deep brain stimulators. Mov Disord. 2006; 21:695–698.18. Gwinn-Hardy KA, Adler CH, Weaver AL, Fish NM, Newman SJ. Effect of hormone variations and other factors on symptom severity in women with dystonia. Mayo Clin Proc. 2000; 75:235–240.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Deep Brain Stimulation of the Globus Pallidus in a 7-Year-Old Girl with DYT1 Generalized Dystonia
- Successful Pallidal Stimulation in a Patient with KMT2B-Related Dystonia
- A case report of deleterious SGCE myoclonus: dystonia successfully treated with pallidal deep brain stimulation
- Outcomes of Intrathecal Baclofen Therapy Compared With Deep Brain Stimulation in a Patient With Dystonic Cerebral Palsy: A Case Report
- Dual Pallidal and Thalamic Deep Brain Stimulation for Complex Ipsilateral Dystonia