J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2017 Dec;25(4):124-130. 10.4250/jcu.2017.25.4.124.
Clinical Utility of Echocardiography for Early and Late Pulmonary Hypertension in Preterm Infants: Relation with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. joung756@dsmc.or.kr
- KMID: 2399413
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2017.25.4.124
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
We evaluated early and late pulmonary hypertension (PH) in preterm infants and its relation with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD).
METHODS
Sixty-seven preterm infants < 30 weeks' gestation underwent echocardiography within 14 days after birth for early PH and over 28 days after birth for late PH. We measured tricuspid regurgitation (TR) peak velocity, pulse Doppler-derived myocardial performance index (MPI) of right ventricle (RV) (RV MPI), eccentricity index (EI), and tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE).
RESULTS
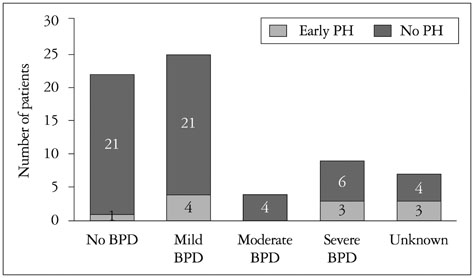
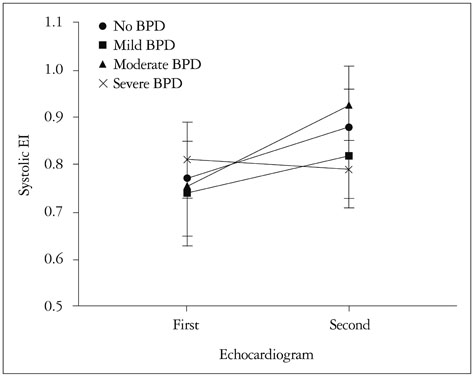
The median gestation age of patients was 27 weeks (range, 23-30 weeks) and median birth weight was 1030 g (range, 450-1780 g). TR peak velocity was measured only in 19 patients (28.4%). Patients with symptomatic early PH (n = 11) showed a significantly lower systolic EI and a significantly higher incidence of RV MPI > 0.38 and TAPSE < 0.5 cm than patients without PH. The incidence of symptomatic early PH was highest in severe BPD, although this was not statistically significant. Early echocardiographic parameters are not associated with BPD development. Patients with severe BPD showed a significantly higher RV MPI and a significantly higher incidence of RV MPI > 0.38 than patients with mild BPD, and a significantly lower systolic EI and a significantly higher incidence of systolic EI < 0.81 than patients without BPD.
CONCLUSION
Systolic EI, RV MPI, and TAPSE were well represented symptomatic early PH, while systolic EI and RV MPI could be useful parameters for identifying late PH in preterm infants with BPD, even if they did not present PH symptoms.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Issues on Estimated Pulmonary Artery Pressure in Liver Transplant Candidates
Chi Young Shim
J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018;26(2):61-62. doi: 10.4250/jcvi.2018.26.e7.
Reference
-
1. Walther FJ, Benders MJ, Leighton JO. Persistent pulmonary hypertension in premature neonates with severe respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatrics. 1992; 90:899–904.2. Mirza H, Ziegler J, Ford S, Padbury J, Tucker R, Laptook A. Pulmonary hypertension in preterm infants: prevalence and association with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr. 2014; 165:909–914.e1.3. Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Bell EF, Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Walsh MC, Hale EC, Newman NS, Schibler K, Carlo WA, Kennedy KA, Poindexter BB, Finer NN, Ehrenkranz RA, Duara S, Sánchez PJ, O'Shea TM, Goldberg RN, Van Meurs KP, Faix RG, Phelps DL, Frantz ID 3rd, Watterberg KL, Saha S, Das A, Higgins RD. Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. Neonatal outcomes of extremely preterm infants from the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics. 2010; 126:443–456.4. Gill AB, Weindling AM. Pulmonary artery pressure changes in the very low birthweight infant developing chronic lung disease. Arch Dis Child. 1993; 68(3 Spec No):303–307.5. Abman SH, Hansmann G, Archer SL, Ivy DD, Adatia I, Chung WK, Hanna BD, Rosenzweig EB, Raj JU, Cornfield D, Stenmark KR, Steinhorn R, Thébaud B, Fineman JR, Kuehne T, Feinstein JA, Friedberg MK, Earing M, Barst RJ, Keller RL, Kinsella JP, Mullen M, Deterding R, Kulik T, Mallory G, Humpl T, Wessel DL. American Heart Association Council on Cardiopulmonary, Critical Care, Perioperative and Resuscitation. Council on Clinical Cardiology. Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young. Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention. Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia. American Thoracic Society. Pediatric pulmonary hypertension: guidelines from the American Heart Association and American Thoracic Society. Circulation. 2015; 132:2037–2099.6. Nagiub M, Lee S, Guglani L. Echocardiographic assessment of pulmonary hypertension in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia: systematic review of literature and a proposed algorithm for assessment. Echocardiography. 2015; 32:819–833.7. Jobe AH, Bancalari E. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001; 163:1723–1729.8. Tei C, Dujardin KS, Hodge DO, Bailey KR, McGoon MD, Tajik AJ, Seward SB. Doppler echocardiographic index for assessment of global right ventricular function. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1996; 9:838–847.9. Aggarwal S, Stockmann P, Klein MD, Natarajan G. Echocardiographic measures of ventricular function and pulmonary artery size: prognostic markers of congenital diaphragmatic hernia? J Perinatol. 2011; 31:561–566.10. Koestenberger M, Nagel B, Ravekes W, Urlesberger B, Raith W, Avian A, Halb V, Cvirn G, Fritsch P, Gamillscheg A. Systolic right ventricular function in preterm and term neonates: reference values of the tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE) in 258 patients and calculation of Z-score values. Neonatology. 2011; 100:85–92.11. An HS, Bae EJ, Kim GB, Kwon BS, Beak JS, Kim EK, Kim HS, Choi JH, Noh CI, Yun YS. Pulmonary hypertension in preterm infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Korean Circ J. 2010; 40:131–136.12. Slaughter JL, Pakrashi T, Jones DE, South AP, Shah TA. Echocardiographic detection of pulmonary hypertension in extremely low birth weight infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia requiring prolonged positive pressure ventilation. J Perinatol. 2011; 31:635–640.13. Khemani E, McElhinney DB, Rhein L, Andrade O, Lacro RV, Thomas KC, Mullen MP. Pulmonary artery hypertension in formerly premature infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia: clinical features and outcomes in the surfactant era. Pediatrics. 2007; 120:1260–1269.14. Mirza H, Ziegler J, Ford S, Padbury J, Tucker R, Laptook A. Temporal profile of early pulmonary hypertension in preterm infants. Am J Perinatol. 2016; 33:903–909.15. Mourani PM, Sontag MK, Younoszai A, Miller JI, Kinsella JP, Baker CD, Poindexter BB, Ingram DA, Abman SH. Early pulmonary vascular disease in preterm infants at risk for bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015; 191:87–95.16. Kumar VH, Hutchison AA, Lakshminrusimha S, Morin FC 3rd, Wynn RJ, Ryan RM. Characteristics of pulmonary hypertension in preterm neonates. J Perinatol. 2007; 27:214–219.17. Mourani PM, Sontag MK, Younoszai A, Ivy DD, Abman SH. Clinical utility of echocardiography for the diagnosis and management of pulmonary vascular disease in young children with chronic lung disease. Pediatrics. 2008; 121:317–325.18. Abman SH. Pulmonary vascular disease and bronchopulmonary dysplasia: evaluation and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. NeoReviews. 2011; 12:e645–e651.19. Mourani PM, Mullen M, Abman SH. Pulmonary hypertension in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Prog Pediatr Cardiol. 2009; 27:43–48.20. Stuart BD, Sekar P, Coulson JD, Choi SE, McGrath-Morrow SA, Collaco JM. Health-care utilization and respiratory morbidities in preterm infants with pulmonary hypertension. J Perinatol. 2013; 33:543–547.21. McCrary AW, Malowitz JR, Hornick CP, Hill KD, Cotten CM, Tatum GH, Barker PC. Differences in eccentricity index and systolic-diastolic ratio in extremely low-birth-weight infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia at risk of pulmonary hypertension. Am J Perinatol. 2016; 33:57–62.22. Tei C, Ling LH, Hodge DO, Bailey KR, Oh JK, Rodeheffer RJ, Tajik AJ, Seward JB. New index of combined systolic and diastolic myocardial performance: a simple and reproducible measure of cardiac function--a study in normals and dilated cardiomyopathy. J Cardiol. 1995; 26:357–366.23. Yates AR, Welty SE, Gest AL, Cua CL. Myocardial tissue Doppler changes in patients with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr. 2008; 152:766–770.24. Sehgal A, Malikiwi A, Paul E, Tan K, Menahem S. Right ventricular function in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia: association with respiratory sequelae. Neonatology. 2016; 109:289–296.25. Zakaria D, Sachdeva R, Gossett JM, Tang X, O'Connor MJ. Tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion is reduced in infants with pulmonary hypertension. Echocardiography. 2015; 32:834–838.26. Czernik C, Rhode S, Metze B, Schmalisch G, Bührer C. Persistently elevated right ventricular index of myocardial performance in preterm infants with incipient bronchopulmonary dysplasia. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e38352.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pathophysiology and Risk Factors of Pulmonary Hypertension in Infants with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
- Use of Inhaled Iloprost in an Infant With Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Pulmonary Artery Hypertension
- Clinical Characteristics, Presentation, and Outcomes of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia-Associated Pulmonary Hypertension
- Pulmonary hypertension in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- Survival of the Infants with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Congenital Heart Disease