Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2017 Dec;20(4):259-262. 10.5223/pghn.2017.20.4.259.
Alpers-Huttenlocher Syndrome First Presented with Hepatic Failure: Can Liver Transplantation Be Considered as Treatment Option?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Department of Pediatrics, Severance Children's Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. khong@yuhs.ac
- 2Division of Neurology, Department of Pediatrics, Severance Children's Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Division of Clinical Genetics, Department of Pediatrics, Severance Children's Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2398908
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2017.20.4.259
Abstract
- Mitochondria play essential role in eukaryotic cells including in the oxidative phosphorylation and generation of adenosine triphosphate via the electron-transport chain. Therefore, defects in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) can result in mitochondrial dysfunction which leads to various mitochondrial disorders that may present with various neurologic and non-neurologic manifestations. Mutations in the nuclear gene polymerase gamma (POLG) are associated with mtDNA depletions, and Alpers-Huttenlocher syndrome is one of the most severe manifestations of POLG mutation characterized by the clinical triad of intractable seizures, psychomotor regression, and liver failure. The hepatic manifestation usually occurs late in the disease's course, but in some references, hepatitis was reportedly the first manifestation. Liver transplantation was considered contraindicated in Alpers-Huttenlocher syndrome due to its poor prognosis. We acknowledged a patient with the first manifestation of the disease being hepatic failure who eventually underwent liver transplantation, and whose neurological outcome improved after cocktail therapy.
MeSH Terms
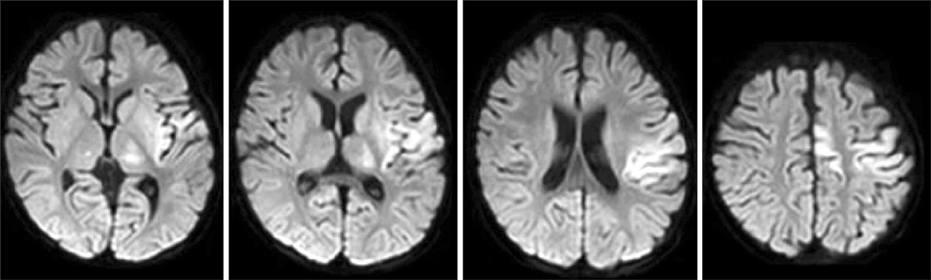
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Valproate Is Contraindicated in POLG1 Mutations
Josef Finsterer
Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2019;22(1):105-106. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2019.22.1.105.
Reference
-
1. Alpers BJ. Diffuse progressive degeneration of the gray matter of the cerebrum. Arch Neur Psych. 1931; 25:469–505.
Article2. Huttenlocher PR, Solitare GB, Adams G. Infantile diffuse cerebral degeneration with hepatic cirrhosis. Arch Neurol. 1976; 33:186–192.
Article3. Harding BN. Progressive neuronal degeneration of childhood with liver disease (Alpers-Huttenlocher syndrome): a personal review. J Child Neurol. 1990; 5:273–287.
Article4. Naviaux RK, Nyhan WL, Barshop BA, Poulton J, Markusic D, Karpinski NC, et al. Mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma deficiency and mtDNA depletion in a child with Alpers' syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1999; 45:54–58.
Article5. Saneto RP, Cohen BH, Copeland WC, Naviaux RK. Alpers-Huttenlocher syndrome. Pediatr Neurol. 2013; 48:167–178.
Article6. Hynynen J, Komulainen T, Tukiainen E, Nordin A, Arola J, Kälviäinen R, et al. Acute liver failure after valproate exposure in patients with POLG1 mutations and the prognosis after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2014; 20:1402–1412.
Article7. Cohen BH, Naviaux RK. The clinical diagnosis of POLG disease and other mitochondrial DNA depletion disorders. Methods. 2010; 51:364–373.
Article8. Avula S, Parikh S, Demarest S, Kurz J, Gropman A. Treatment of mitochondrial disorders. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2014; 16:292.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Hepatic Failure Associated with Stevens-Johnson Syndrome Induced by Carbamazepine Treatment in a Patient with Transverse Myelitis
- Indication and Prognosis of Liver Transplantation
- A Case of Fulminant Hepatic Failure Who Recovered during Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
- Hepatic failure caused by acute fatty liver of pregnancy treated by orthotopic liver transplantation: A case report
- Fatal neurological complication after liver transplantation in acute hepatic failure patient with hepatic encephalopathy