Ann Lab Med.
2015 Jan;35(1):159-161. 10.3343/alm.2015.35.1.159.
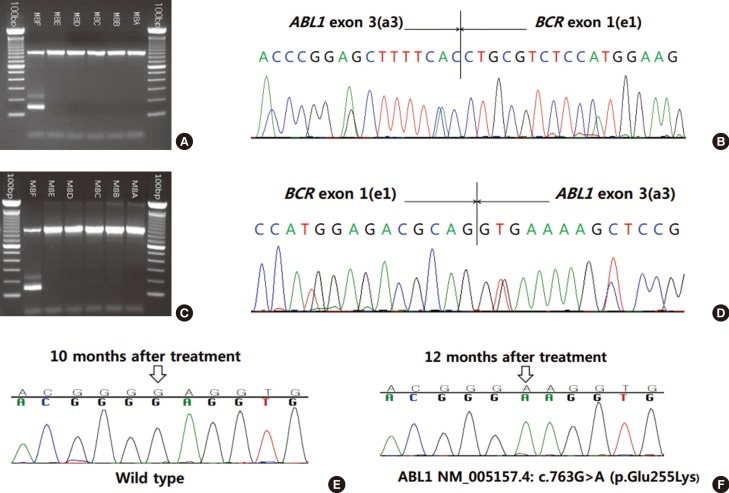
Two Cases of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with an e1a3 BCR-ABL1 Fusion Transcript
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine & Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. nb.seungtae.lee@icloud.com, sunnyhk@skku.edu
- 2Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2363168
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.1.159
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
-
Antineoplastic Agents/therapeutic use
Base Sequence
DNA/chemistry/genetics/metabolism
DNA Mutational Analysis
Fusion Proteins, bcr-abl/*genetics
Genotype
Humans
Imatinib Mesylate/therapeutic use
Karyotyping
Male
Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction
Mutation
Precursor Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia-Lymphoma/*diagnosis/drug therapy/*genetics
Antineoplastic Agents
DNA
Fusion Proteins, bcr-abl
Imatinib Mesylate
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The e1a3
BCR-ABL1 Fusion Transcript in Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Stephen E. Langabeer
Ann Lab Med. 2015;35(5):540-541. doi: 10.3343/alm.2015.35.5.540.
Reference
-
1. Fujisawa S, Nakamura S, Naito K, Kobayashi M, Ohnishi K. A variant transcript, e1a3, of the minor BCR-ABL fusion gene in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: case report and review of the literature. Int J Hematol. 2008; 87:184–188. PMID: 18253707.
Article2. Burmeister T, Schwartz S, Taubald A, Jost E, Lipp T, Schneller F, et al. Atypical BCR-ABL mRNA transcripts in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. 2007; 92:1699–1702. PMID: 18055996.
Article3. Soekarman D, van Denderen J, Hoefsloot L, Moret M, Meeuwsen T, van Baal J, et al. A novel variant of the bcr-abl fusion product in Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 1990; 4:397–403. PMID: 2193202.4. Iwata S, Mizutani S, Nakazawa S, Yata J. Heterogeneity of the breakpoint in the ABL gene in cases with BCR/ABL transcript lacking ABL exon a2. Leukemia. 1994; 8:1696–1702. PMID: 7934165.5. Wilson GA, Vandenberghe EA, Pollitt RC, Rees DC, Goodeve AC, Peake IR, et al. Are aberrant BCR-ABL transcripts more common than previously thought? Br J Haematol. 2000; 111:1109–1111. PMID: 11167748.
Article6. Roman J, Jimenez A, Barrios M, Castillejo JA, Maldonado J, Torres A. E1A3 as a unique, naturally occurring BCR-ABL transcript in an indolent case of chronic myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2001; 114:635–637. PMID: 11552990.
Article7. Schultheis B, Wang L, Clark RE, Melo JV. BCR-ABL with an e6a2 fusion in a CML patient diagnosed in blast crisis. Leukemia. 2003; 17:2054–2055. PMID: 14513059.
Article8. Burmeister T, Reinhardt R. A multiplex PCR for improved detection of typical and atypical BCR-ABL fusion transcripts. Leuk Res. 2008; 32:579–585. PMID: 17928051.
Article9. Goh HG, Hwang JY, Kim SH, Lee YH, Kim YL, Kim DW. Comprehensive analysis of BCR-ABL transcript types in Korean CML patients using a newly developed multiplex RT-PCR. Transl Res. 2006; 148:249–256. PMID: 17145570.
Article10. Kim HJ, Oh HJ, Lee JW, Jang PS, Chung NG, Kim M, et al. Utility of a multiplex reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction assay (HemaVision) in the evaluation of genetic abnormalities in Korean children with acute leukemia: a single institution study. Korean J Pediatr. 2013; 56:247–253. PMID: 23807891.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The e1a3 BCR-ABL1 Fusion Transcript in Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- Erratum: Two Cases of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with an e1a3 BCR-ABL1 Fusion Transcript
- A Case of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia with Co-existence of BCR-ABL1 and PML-RARA Rearrangements Detected by PCR
- The e8a2 fusion transcript in B lymphoblastic leukemia with BCR-ABL1 rearrangement
- Genomic Profiling of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia: Basic and Clinical Approach