Tuberc Respir Dis.
2009 Jun;66(6):477-481.
A Case of Interstitial Pneumonitis in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Leflunomide
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Daejeon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Daejeon, Korea. kohj8804@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Daejeon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Daejeon, Korea.
Abstract
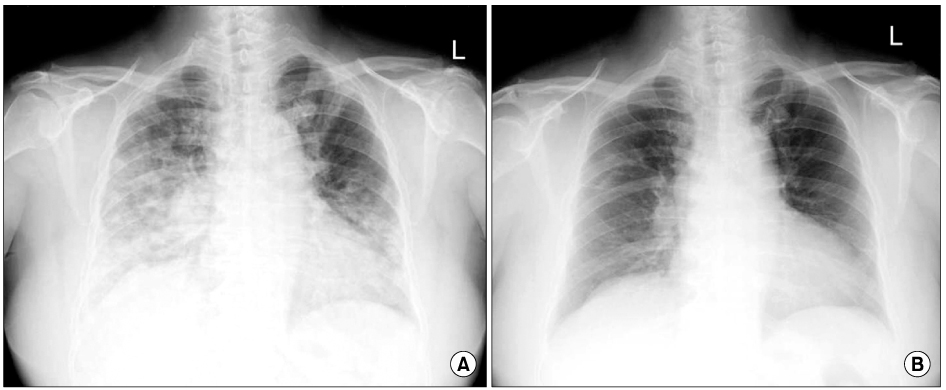
- Leflunomide, a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis has been available in Korea since 2003. Leflunomide-associated interstitial pneumonitis has been appearing recently. A 25-year-old woman with a 12-month history of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis (RA) presented with acute respiratory insufficiency. She developed fever, dyspnea, and non-productive cough. Her medication history included methotrexate (15 mg/week. commencing 1 year prior) and leflunomide (20 mg/day, no loading dose, commencing 4 months prior). She was diagnosed with leflunomide-associated interstitial pneumonitis based on history, physical examination, laboratory and radiologic findings. She recovered quickly after leflunomide was withdrawn and steroids and cholestyramine were initiated quickly. We report a case of leflunomide-associated interstitial pneumonitis treated successfully with intravenous high-dose steroid and cholestyramine.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Park YB, Lee SK. Leflunomide: a new disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2000. 7:323–332.2. Kalden JR, Schattenkirchner M, Sörensen H, Emery P, Deighton C, Rozman B, et al. The efficacy and safety of leflunomide in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: a five-year followup study. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. 48:1513–1520.3. Chikura B, Lane S, Dawson JK. Clinical expression of leflunomide-induced pneumonitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). Forthcoming 2009.4. Savage RL, Highton J, Boyd IW, Chapman P. Pneumonitis associated with leflunomide: a profile of New Zealand and Australian reports. Intern Med J. 2006. 36:162–169.5. Lee JH, Cheon WS, Seo YI, Eom KS, Jang SH, Bahn JW, et al. A case of interstitial pneumonitis caused by leflunomide. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2005. 58:83–88.6. Sheen DH, Lim MK, Shim SC, Lee SO, Kang SW, Song JK, et al. Successful treatment of interstitial pneumonitis induced by leflunomide. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2007. 14:268–273.7. Breedveld FC, Dayer JM. Leflunomide: mode of action in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000. 59:841–849.8. Bartlett RR, Brendel S, Zielinski T, Schorlemmer HU. Leflunomide, an immunorestoring drug for the therapy of autoimmune disorders, especially rheumatoid arthritis. Transplant Proc. 1996. 28:3074–3078.9. McCurry J. Japan deaths spark concerns over arthritis drug. Lancet. 2004. 363:461.10. Searles G, McKendry RJ. Methotrexate pneumonitis in rheumatoid arthritis: potential risk factors. Four case reports and a review of the literature. J Rheumatol. 1987. 14:1164–1171.11. Suissa S, Hudson M, Ernst P. Leflunomide use and the risk of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. 54:1435–1439.12. Kremer J, Genovese M, Cannon GW, Caldwell J, Cush J, Furst DE, et al. Combination leflunomide and methotrexate (MTX) therapy for patients with active rheumatoid arthritis failing MTX monotherapy: open-label extension of a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled trial. J Rheumatol. 2004. 31:1521–1531.13. Vallbracht II, Popper HH, Rieber J, Nowak F, Gallenberger S, Piper B, et al. Lethal pneumonitis under leflunomide therapy. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005. 44:1580–1581.14. Chikura B, Sathi N, Lane S, Dawson JK. Variation of immunological response in methotrexate-induced pneumonitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008. 47:1647–1650.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Successful Treatment of Interstitial Pneumonitis Induced by Leflunomide
- A Case of Interstitial Pneumonitis Caused by Leflunomide
- A Case of Peripheral Neuropathy in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Leflunomide
- Leflunomide-induced Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- A Case of Methotrexate: Associated Interstitial Pneumonitis in Rheumatoid Arthritis