Korean J Urol.
2010 Feb;51(2):94-100.
Expression of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 3 in the Recurrence of Non-Muscle-Invasive Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, School of Medicine, Jeju National University, Jeju, Korea.
- 2Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, Jeju National University, Jeju, Korea.
- 3Department of Urology, School of Medicine, Jeju National University, Jeju, Korea. urohjs@jejunu.ac.kr
Abstract
-
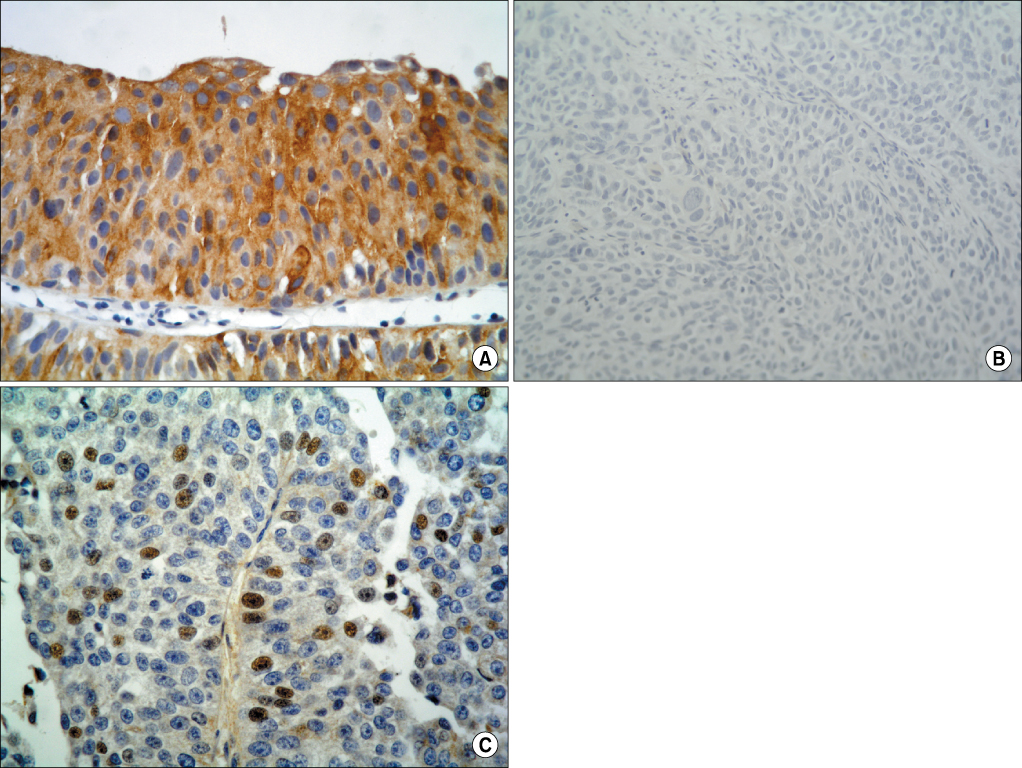
PURPOSE: The fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) gene is known to be frequently mutated in noninvasive urothelial carcinomas of the bladder. In this study, we investigated the expression of FGFR3, Ki-67, and p53 in bladder cancers and the effects of expression on tumor recurrence.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fifty-five cases of primary bladder cancer were examined by immunohistochemistry. The relationship of these markers with various clinicopathological factors, including recurrence, was assessed.
RESULTS
Positivity for cytoplasmic FGFR3 (FGFR3-c) was associated with a lower cancer grade (p=0.022) and stage (p=0.011). Recurrence was more frequent in patients with a higher stage, negative FGFR3-c, and high Ki-67 expression. According to univariate analysis, predictors of recurrence-free survival included the following: age, stage, FGFR-c, Ki-67, and p53. However, none of these was independent from the other parameters in multivariate studies.
CONCLUSIONS
The immunohistochemical expression of FGFR3 is not only one of the characteristic features of lower-grade and lower-stage urothelial carcinoma but also a possible marker in predicting disease recurrence.
MeSH Terms
-
Carcinoma, Transitional Cell
Cytoplasm
Fibroblast Growth Factors
Fibroblasts
Genes, p53
Humans
Immunohistochemistry
Receptor, Fibroblast Growth Factor, Type 3
Receptors, Fibroblast Growth Factor
Recurrence
Urinary Bladder
Urinary Bladder Neoplasms
Fibroblast Growth Factors
Receptor, Fibroblast Growth Factor, Type 3
Receptors, Fibroblast Growth Factor
Figure
Reference
-
1. Holm C, Rayala S, Jirström K, Stal O, Kumar R, Landberg G. Association between Pak1 expression and subcellular localization and tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006. 98:671–680.2. Sylvester RJ, van der Meijden AP, Oosterlinck W, Witjes JA, Bouffioux C, Denis L, et al. Predicting recurrence and progression in individual patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: a combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur Urol. 2006. 49:466–475.3. L'Hote CG, Knowles MA. Cell responses to FGFR3 signalling: growth, differentiation and apoptosis. Exp Cell Res. 2005. 304:417–431.4. Barbisan F, Santinelli A, Mazzucchelli R, Lopez-Beltran A, Cheng L, Scarpelli M, et al. Strong immunohistochemical expression of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3, superficial staining pattern of cytokeratin 20, and low proliferative activity define those papillary urothelial neoplasms of low malignant potential that do not recur. Cancer. 2008. 112:636–644.5. Burger M, van der Aa MN, van Oers JM, Brinkmann A, van der Kwast TH, Steyerberg EC, et al. Prediction of progression of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer by WHO 1973 and 2004 grading and by FGFR3 mutation status: a prospective study. Eur Urol. 2008. 54:835–843.6. Tomlinson DC, Baldo O, Harnden P, Knowles MA. FGFR3 protein expression and its relationship to mutation status and prognostic variables in bladder cancer. J Pathol. 2007. 213:91–98.7. van Rhijn BW, Lurkin I, Radvanyi F, Kirkels WJ, van der Kwast TH, Zwarthoff EC. The fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) mutation is a strong indicator of superficial bladder cancer with low recurrence rate. Cancer Res. 2001. 61:1265–1268.8. Gómez-Román JJ, Saenz P, Molina M, Cuevas González J, Escuredo K, Santa Cruz S, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 3 is overexpressed in urinary tract carcinomas and modulates the neoplastic cell growth. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. 11:459–465.9. George B, Datar RH, Wu L, Cai J, Patten N, Beil SJ, et al. p53 gene and protein status: the role of p53 alterations in predicting outcome in patients with bladder cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007. 25:5352–5358.10. Salinas-Sánchez AS, Lorenzo-Romero JG, Giménez-Bachs JM, Sánchez-Sánchez F, Donate-Moreno MJ, Rubio-Del-Campo A, et al. Implications of p53 gene mutations on patient survival in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder: a long-term study. Urol Oncol. 2008. 26:620–626.11. Chatterjee SJ, Datar R, Youssefzadeh D, George B, Goebell PJ, Stein JP, et al. Combined effects of p53, p21, and pRb expression in the progression of bladder transitional cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2004. 22:1007–1013.12. Shim JW, Cho KS, Choi YD, Park YW, Lee DW, Han WS, et al. Diagnostic algorithm for papillary urothelial tumors in the urinary bladder. Virchows Arch. 2008. 452:353–362.13. Theodoropoulos VE, Lazaris AC, Kastriotis I, Spiliadi C, Theodoropoulos GE, Tsoukala V, et al. Evaluation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha overexpression as a predictor of tumour recurrence and progression in superficial urothelial bladder carcinoma. BJU Int. 2005. 95:425–431.14. van Rhijn BW, Vis AN, van der Kwast TH, Kirkels WJ, Radvanyi F, Ooms EC, et al. Molecular grading of urothelial cell carcinoma with fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 and MIB-1 is superior to pathologic grade for the prediction of clinical outcome. J Clin Oncol. 2003. 21:1912–1921.15. Cappellen D, De Oliveira C, Ricol D, de Medina S, Bourdin J, Sastre-Garau X, et al. Frequent activating mutations of FGFR3 in human bladder and cervix carcinomas. Nat Genet. 1999. 23:18–20.16. Chesi M, Brents LA, Ely SA, Bais C, Robbiani DF, Mesri EA, et al. Activated fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 is an oncogene that contributes to tumor progression in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2001. 97:729–736.17. van Rhijn BW, van Tilborg AA, Lurkin I, Bonaventure J, de Vries A, Thiery JP, et al. Novel fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) mutations in bladder cancer previously identified in non-lethal skeletal disorders. Eur J Hum Genet. 2002. 10:819–824.18. Matsumoto M, Ohtsuki Y, Ochii K, Seike Y, Iseda N, Sasaki T, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 protein expression in urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder, exhibiting no association with low-grade and/or non-invasive lesions. Oncol Rep. 2004. 12:967–971.19. Mhawech-Fauceglia P, Cheney RT, Fischer G, Beck A, Herrmann FR. FGFR3 and p53 protein expressions in patients with pTa and pT1 urothelial bladder cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2006. 32:231–237.20. van Oers JM, Wild PJ, Burger M, Denzinger S, Stoehr R, Rosskopf E, et al. FGFR3 mutations and a normal CK20 staining pattern define low-grade noninvasive urothelial bladder tumours. Eur Urol. 2007. 52:760–768.21. Hernández S, López-Knowles E, Lloreta J, Kogevinas M, Amorós A, Tardón A, et al. Prospective study of FGFR3 mutations as a prognostic factor in nonmuscle invasive urothelial bladder carcinomas. J Clin Oncol. 2006. 24:3664–3671.22. Røtterud R, Fossa SD, Nesland JM. Protein networking in bladder cancer: immunoreactivity for FGFR3, EGFR, ERBB2, KAI1, PTEN, and RAS in normal and malignant urothelium. Histol Histopathol. 2007. 22:349–363.23. Fujimoto K, Yamada Y, Okajima E, Kakizoe T, Sasaki H, Sugimura T, et al. Frequent association of p53 gene mutation in invasive bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 1992. 52:1393–1398.24. Llopis J, Alcaraz A, Ribal MJ, Solé M, Ventura PJ, Barranco MA, et al. P53 expression predicts progression and poor survival in T1 bladder tumours. Eur Urol. 2000. 37:644–653.25. Ecke TH, Sachs MD, Lenk SV, Loening SA, Schlechte HH. TP53 gene mutations as an independent marker for urinary bladder cancer progression. Int J Mol Med. 2008. 21:655–661.26. Brunner A, Verdorfer I, Prelog M, Mayeri C, Mikuz G, Tzankov A. Large-scale analysis of cell cycle regulators in urothelial bladder cancer identifies p16 and p27 as potentially useful prognostic markers. Pathobiology. 2008. 75:25–33.27. Malats N, Bustos A, Nascimento CM, Fernandez F, Rivas M, Puente D, et al. P53 as a prognostic marker for bladder cancer: a meta-analysis and review. Lancet Oncol. 2005. 6:678–686.28. Quintero A, Alvarez-Kindelan J, Luque RJ, Gonzalez-Campora R, Requena MJ, Montironi R, et al. Ki-67 MIB1 labelling index and the prognosis of primary TaT1 urothelial cell carcinoma of the bladder. J Clin Pathol. 2006. 59:83–88.29. Yurakh AO, Ramos D, Calabuig-Fariñas S, López-Guerrero JA, Rubio J, Solsona E, et al. Molecular and immunohistochemical analysis of the prognostic value of cell-cycle regulators in urothelial neoplasms of the bladder. Eur Urol. 2006. 50:506–515.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Significance of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Expression in Bladder Cancer
- Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1 Overexpression Is Associated with Poor Survival in Patients with Resected Muscle Invasive Urothelial Carcinoma
- Autophagy and urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: A review
- Prognostic Value of Expression of c-erbB-2 in Urinary Bladder Cancer
- Pronostic Value of The Expression of Mutant p53 and EGFR mRNA in Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Bladder