Korean J Urol.
2010 Oct;51(10):724-728.
Sarcomatoid Carcinoma of the Urinary Bladder: A Clinicopathological Study of 4 Cases and a Review of the Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Tzaneio General Hospital of Pireas, Pireas, Greece. stamatiouk@gmail.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Tzaneio General Hospital of Pireas, Pireas, Greece.
Abstract
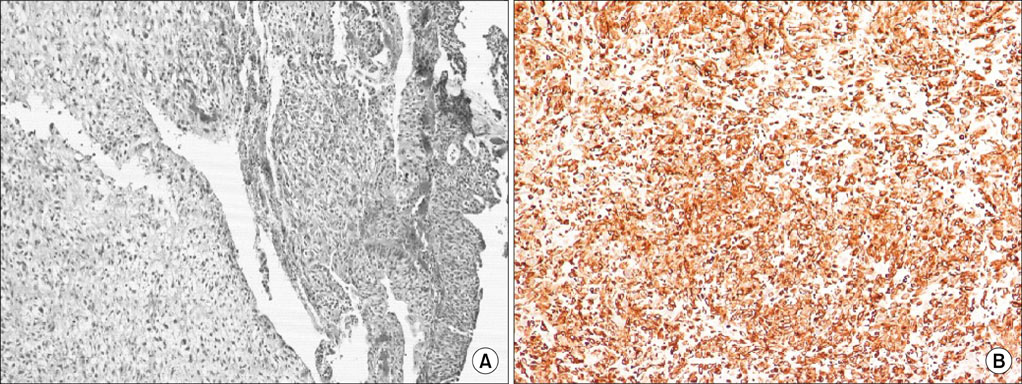
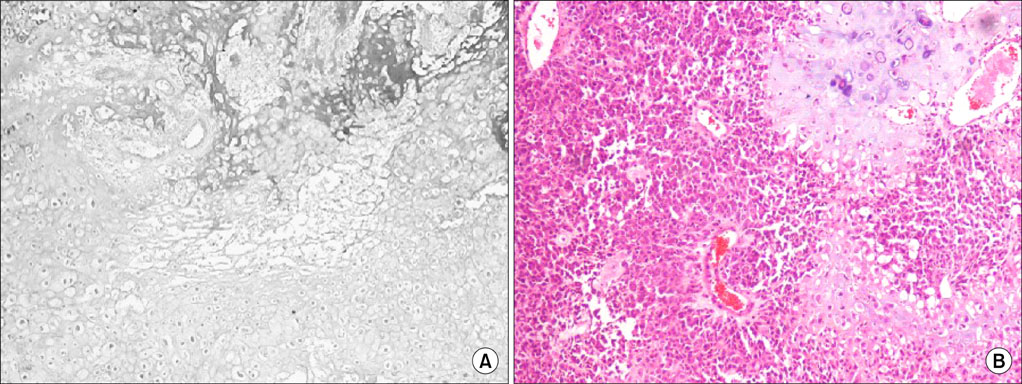
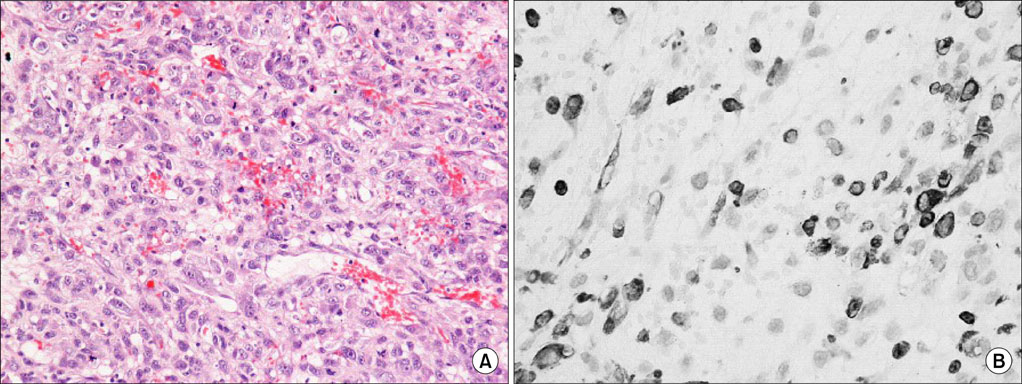
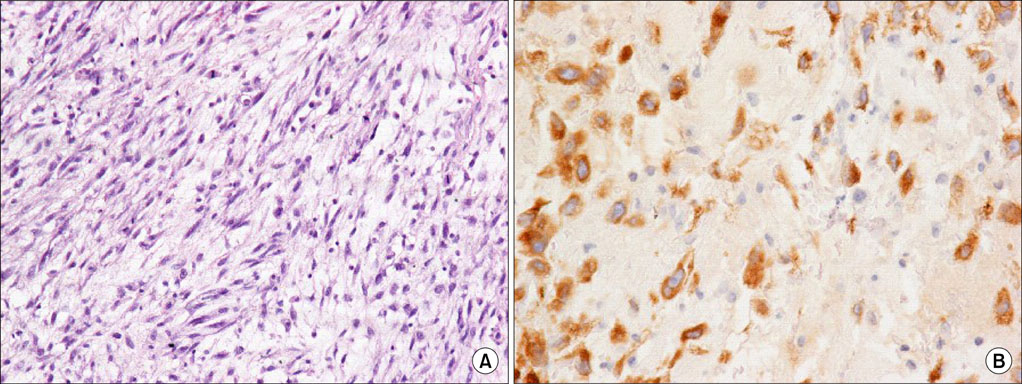
- Sarcomatoid carcinoma (SC) of urinary bladder is a rare tumor exhibiting aggressive behavior. Here we are reviewing the pathologic and clinical characteristics of 4 consecutive cases of this rare tumor. Three out of 4 patients were males and one female. The median age was 72.8 years (range, 60-79 years). Patients underwent transurethral resection of bladder tumor and the diagnosis of bladder SC was established on the pathologic examination of the resected bladder tissue. Despite treatment all patients died within 22 months of the diagnosis of SC. SC of the bladder are true biphasic malignant neoplasm exhibiting morphologic and immunohistochemical evidence of epithelial and mesenchymal differentiation with the presence or absence of heterologous elements. The aggressive of the tumor precludes radical therapy whenever possible, since adjuvant therapy seems to have little effect.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI. World Health Organization Classification of tumors: pathology and genetics of tumors of the urinary system and male genital organs. 2004. Lyon: IARC Press;99–133.2. Lopez-Beltran A, Pacelli A, Rothenberg HJ, Wollan PC, Zincke H, Blute ML, et al. Carcinosarcoma and sarcomatoid carcinoma of the bladder: clinicopathological study of 41 cases. J Urol. 1998. 159:1497–1503.3. Wick MR, Swanson PE. Carcinosarcomas: current perspectives and an historical review of nosological concepts. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1993. 10:118–127.4. Young RH. Spindle cell lesions of the urinary bladder. Histol Histopathol. 1990. 5:505–512.5. Holtz F, Fox JE, Abell MR. Carcinosarcoma of the urinary bladder. Cancer. 1972. 29:294–304.6. Sung MT, Wang M, McLennan GT, Eble JN, Tan PH, Lopez-Beltran A, et al. Histogenesis of sarcomatoid urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder: evidence for a common clonal origin with divergent differentiation. J Pathol. 2007. 211:420–430.7. Hosokawa Y, Kuwada M, Kumamoto H, Hayashi Y, Fujimoto K, Hirao Y. Case of sarcomatoid carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Hinyokika Kiyo. 2008. 54:561–563.8. Kang SG, Yoon CY, Cho JH, Yoon DK, Kim IS. Sarcomatoid carcinoma of the renal pelvis. Korean J Urol. 2005. 46:651–654.9. Jeong YB, Park SC, Park JK, Kim HJ, Moon WS. A case of sarcomatoid carcinoma of the bladder. Korean J Urol. 1999. 40:252–255.10. Onal C, Pehlivan B, Bal N, Topkan E, Kilinc F, Topuk S. Sarcomatoid carcinoma of the urinary bladder treated with adjuvant radiotherapy: a case report. Clin Med. 2009. 12:39–42.