Korean J Urol.
2006 Jan;47(1):75-79. 10.4111/kju.2006.47.1.75.
Prognostic Significance of E2F3 Expression in Bladder Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea. hychoi1@yahoo.co.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2294219
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2006.47.1.75
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: E2F3 is important for cell cycle regulation and DNA replication. Recent studies have reported that members of the E2F family can play specific and diverse roles in the tumorigenesis of human malignancies, and the E2F3 expression appears to provide a growth advantage to tumor cells by activating cell proliferation in bladder tumors. We studied the prognostic significance of E2F3 expression in bladder cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We examined the expression of E2F3 with using immunohistochemical staining in the tumor samples from 109 patients suffering with bladder cancer, and we analyzed the prognostic significance of E2F3 according to the grade, stage, recurrence and progression of bladder cancer.
RESULTS
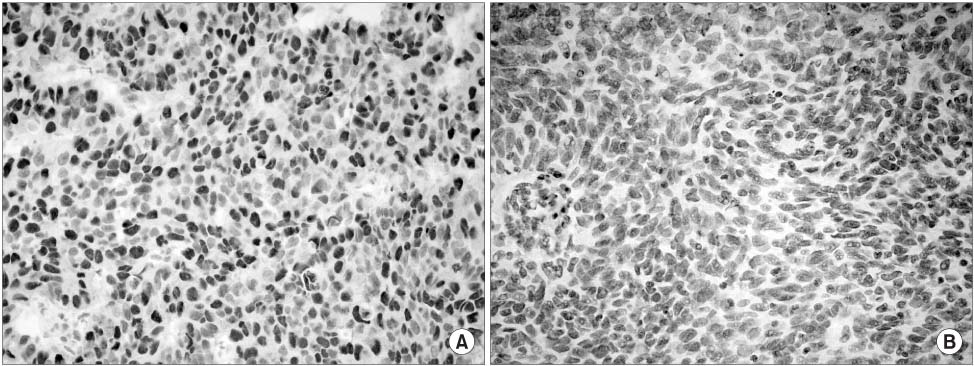
We found positive staining for E2F3 in 23 cases (21.1%). The E2F3 expression was correlated with the tumor stage (superficial vs. invasive, p<0.001) and the tumor grade (p=0.001). The E2F3 expression was not correlated with the recurrence and progression of superficial bladder cancer.
CONCLUSIONS
In this study, our results showed that the E2F3 expression was observed in a portion of the bladder cancer specimens. These results suggest that E2F3 may contribute to the development of bladder cancer, but it may not play a role as a prognostic factor of bladder cancer.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Simon R, Burger H, Semjonow A, Hertle L, Terpe H, Bocker W. Patterns of chromosomal imbalances in muscle invasive bladder cancer. Int J Oncol. 2000. 17:1025–1029.2. Koo SH, Kwon KC, Ihm CH, Jeon YM, Park JW, Sul CK. Detection of genetic alterations in bladder tumors by comparative genomic hybridization and cytogenetic analysis. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1999. 110:87–93.3. Hovey RM, Chu L, Balazs M, DeVries S, Moore D, Sauter G, et al. Genetic alterations in primary bladder cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res. 1998. 58:3555–3560.4. Kim WJ, Yoon SJ. Current trend in molecular aspects of bladder cancer. Korean J Urol. 2005. 46:211–220.5. Wu Q, Hoffmann MJ, Hartmann FH, Schulz WA. Amplification and overexpression of the ID4 gene at 6p22.3 in bladder cancer. Mol Cancer. 2005. 4:16.6. Bruch J, Schulz WA, Haussler J, Melzner I, Bruderlein S, Moller P, et al. Delineation of the 6p22 amplification unit in urinary bladder carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 2000. 60:4526–4530.7. Saavedra HI, Maiti B, Timmers C, Altura R, Tokuyama Y, Fukasawa K, et al. Inactivation of E2F3 results in centrosome amplification. Cancer Cell. 2003. 3:333–346.8. Wu L, Timmers C, Malti B, Saavedra HI, Sang L, Chong GT, et al. The E2F1-3 transcription factors are essential for cellular proliferation. Nature. 2001. 414:457–462.9. Saito M, Helin K, Valentine MB, Griffith BB, Wilman CL, Harlow E, et al. Amplification of the E2F1 transcription factor gene in the HEL erythroleukemia cell line. Genomics. 1995. 25:130–138.10. Rabbani F, Richon VM, Orlow I, Lu ML, Drobnjak M, Dudas M, et al. Prognostic significance of transcription factor E2F-1 in bladder cancer: genotypic and phenotypic characterization. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999. 91:874–881.11. Humbert PO, Verona R, Trimarchi JM, Rogers C, Dandapani S, Lees JA. E2F3 is critical for normal cellular proliferation. Genes Dev. 2000. 14:690–703.12. Feber A, Clark J, Goodwin G, Dodson AR, Smith PH, Fletcher A, et al. Amplification and overexpression of E2F3 in human bladder cancer. Oncogene. 2004. 23:1627–1630.13. Oeggerli M, Tomovska S, Schrami P, Calvano-Forte D, Schafroth S, Simon R, et al. E2F3 amplification and overexpression is associated with invasive tumor growth and rapid tumor cell proliferation in urinary bladder cancer. Oncogene. 2004. 23:5616–5623.14. Foster CS, Falconer A, Dodson AR, Norman AR, Dennis N, Fletcher A. Transcription factor E2F3 overexpressed in prostate cancer independently predicts clinical outcome. Oncogene. 2004. 23:5871–5879.15. Araki K, Nakajima Y, Eto K, Ikeda M. Distinct recruitment of E2F family members to specific E2F-binding sites mediates activation and repression of the E2F1 promoter. Oncogene. 2003. 22:7632–7641.16. Zhu W, Giangrande PH, Nevins JR. E2Fs link the control of G1/S and G2/M transcription. EMBO J. 2004. 23:4615–4626.17. Leone G, DeGregori J, Yan Z, Jakoi L, Ishida S, Williams RS, et al. E2F3 activity is regulated during the cell cycle and is required for the induction of S phase. Genes Dev. 1998. 12:2120–2130.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Significance of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Expression in Bladder Cancer
- Prognostic Significance of Bcl-2 Expression in Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Bladder
- Prognostic Significance of p53, pRb, and p21(waf1) in T1G3 Bladder Cancer
- The Study of Expression of Caspase-3 in Bladder Cancer and Renal Cell Carcinima
- Prognostic Value of Expression of c-erbB-2 in Urinary Bladder Cancer