J Breast Cancer.
2011 Jun;14(2):147-152. 10.4048/jbc.2011.14.2.147.
Feasibility of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Breast Cancer Patients with Initial Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis after Primary Systemic Therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. brcakorea@gmail.com
- 2Department of Surgery, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2286515
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2011.14.2.147
Abstract
- PURPOSE
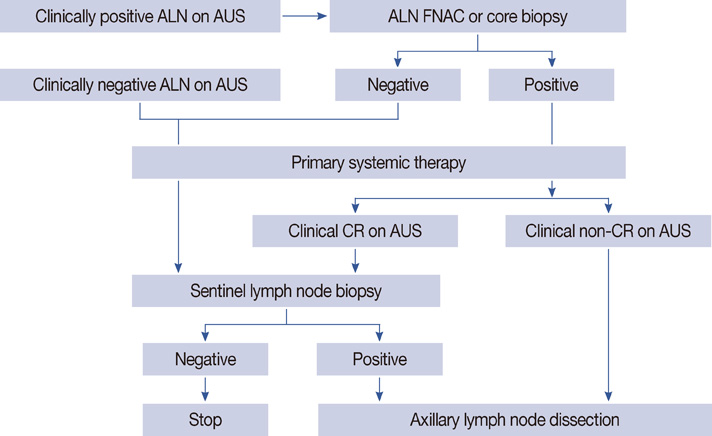
Primary systemic therapy (PST) downstages up to 40% of initial documented axillary lymph node (ALN) metastases in breast cancer. The current surgical treatment after PST consists of breast tumor resection and axillary lymph node dissection (ALND). This strategy, however, does not eliminate unnecessary ALND in patients with complete remission of axillary metastases. The aim of this study was to examine the accuracy of sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) after PST among patients with documented ALN metastasis at presentation and to identify the rate of pathologic complete-remission (CR) with ALN after PST.
METHODS
We analyzed 66 patients with ALN metastasis that was pathologically proven preoperatively who underwent SLNB and concomitant ALND after PST. Axillary ultrasound (AUS) was used to evaluate the clinical response of initially documented ALN metastasis after PST. Intraoperative lymphatic mapping was performed using blue dye with or without radioisotope.
RESULTS
After PST, 34.8% of patients had clinical CR of ALN on AUS and 28.8% patients had pathologic CR of ALN. The overall success rate of SLNB after PST was 87.9%, and the sentinel lymph node identification rate in patients with clinical CR was 95.7%. In patients with successful lymphatic mapping, 70.7% of patients had residual axillary metastases. The overall accuracy and false-negative rate were 87.9% and 17.1% in all patients: 95.5% and 10.0% in patients with clinical CR of ALN, and 83.3% and 19.4% in patients with residual axillary disease after PST.
CONCLUSION
Our findings suggest that SLNB may be feasible in patients with initial documented ALN metastasis who have clinical CR for metastatic ALN after PST. Further investigation in a prospective setting should be performed to confirm our results.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Reliability of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients
Ahram Han, Hyeong-Gon Moon, Jisun Kim, Soo Kyung Ahn, In Ae Park, Wonshik Han, Dong-Young Noh
J Breast Cancer. 2013;16(4):378-385. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2013.16.4.378.
Reference
-
1. Bonadonna G. Evolving concepts in the systemic adjuvant treatment of breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1992. 52:2127–2137.2. Fisher B, Bryant J, Wolmark N, Mamounas E, Brown A, Fisher ER, et al. Effect of preoperative chemotherapy on the outcome of women with operable breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1998. 16:2672–2685.
Article3. van der Hage JA, van de Velde CJ, Julien JP, Tubiana-Hulin M, Vandervelden C, Duchateau L. Preoperative chemotherapy in primary operable breast cancer: results from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer trial 10902. J Clin Oncol. 2001. 19:4224–4237.
Article4. Kim T, Giuliano AE, Lyman GH. Lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy in early-stage breast carcinoma: a metaanalysis. Cancer. 2006. 106:4–16.
Article5. Naik AM, Fey J, Gemignani M, Heerdt A, Montgomery L, Petrek J, et al. The risk of axillary relapse after sentinel lymph node biopsy for breast cancer is comparable with that of axillary lymph node dissection: a follow-up study of 4008 procedures. Ann Surg. 2004. 240:462–468.6. Schrenk P, Rieger R, Shamiyeh A, Wayand W. Morbidity following sentinel lymph node biopsy versus axillary lymph node dissection for patients with breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2000. 88:608–614.
Article7. Nason KS, Anderson BO, Byrd DR, Dunnwald LK, Eary JF, Mankoff DA, et al. Increased false negative sentinel node biopsy rates after preoperative chemotherapy for invasive breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2000. 89:2187–2194.
Article8. Fernández A, Cortés M, Benito E, Azpeitia D, Prieto L, Moreno A, et al. Gamma probe sentinel node localization and biopsy in breast cancer patients treated with a neoadjuvant chemotherapy scheme. Nucl Med Commun. 2001. 22:361–366.
Article9. Xing Y, Foy M, Cox DD, Kuerer HM, Hunt KK, Cormier JN. Meta-analysis of sentinel lymph node biopsy after preoperative chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2006. 93:539–546.
Article10. Classe JM, Bordes V, Campion L, Mignotte H, Dravet F, Leveque J, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for advanced breast cancer: results of Ganglion Sentinelle et Chimiotherapie Neoadjuvante, a French prospective multicentric study. J Clin Oncol. 2009. 27:726–732.
Article11. Mamounas EP, Brown A, Anderson S, Smith R, Julian T, Miller B, et al. Sentinel node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: results from National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project Protocol B-27. J Clin Oncol. 2005. 23:2694–2702.
Article12. Kuerer HM, Sahin AA, Hunt KK, Newman LA, Breslin TM, Ames FC, et al. Incidence and impact of documented eradication of breast cancer axillary lymph node metastases before surgery in patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Surg. 1999. 230:72–78.
Article13. Newman LA, Pernick NL, Adsay V, Carolin KA, Philip PA, Sipierski S, et al. Histopathologic evidence of tumor regression in the axillary lymph nodes of patients treated with preoperative chemotherapy correlates with breast cancer outcome. Ann Surg Oncol. 2003. 10:734–739.
Article14. Newman EA, Sabel MS, Nees AV, Schott A, Diehl KM, Cimmino VM, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy performed after neoadjuvant chemotherapy is accurate in patients with documented node-positive breast cancer at presentation. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007. 14:2946–2952.
Article15. Sharkey FE, Addington SL, Fowler LJ, Page CP, Cruz AB. Effects of preoperative chemotherapy on the morphology of resectable breast carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 1996. 9:893–900.16. Kuerer HM, Hunt KK. The rationale for integration of lymphatic mapping and sentinel node biopsy in the management of breast cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Semin Breast Dis. 2002. 5:80–87.17. Schwartz GF, Meltzer AJ. Accuracy of axillary sentinel lymph node biopsy following neoadjuvant (induction) chemotherapy for carcinoma of the breast. Breast J. 2003. 9:374–379.
Article18. Patel NA, Piper G, Patel JA, Malay MB, Julian TB. Accurate axillary nodal staging can be achieved after neoadjuvant therapy for locally advanced breast cancer. Am Surg. 2004. 70:696–699.19. Kang SH, Kim SK, Kwon Y, Kang HS, Kang JH, Ro J, et al. Decreased identification rate of sentinel lymph node after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. World J Surg. 2004. 28:1019–1024.
Article20. Dixon JM, Cody HS 3rd. Role of sentinel node biopsy in patients having neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2010. 36:511–513.
Article21. Fisher B, Jeong JH, Anderson S, Bryant J, Fisher ER, Wolmark N. Twenty-five-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing radical mastectomy, total mastectomy, and total mastectomy followed by irradiation. N Engl J Med. 2002. 347:567–575.
Article22. Nori J, Vanzi E, Bazzocchi M, Bufalini FN, Distante V, Branconi F, et al. Role of axillary ultrasound examination in the selection of breast cancer patients for sentinel node biopsy. Am J Surg. 2007. 193:16–20.
Article23. Sato K, Tamaki K, Tsuda H, Kosuda S, Kusano S, Hiraide H, et al. Utility of axillary ultrasound examination to select breast cancer patients suited for optimal sentinel node biopsy. Am J Surg. 2004. 187:679–683.
Article24. Swinson C, Ravichandran D, Nayagam M, Allen S. Ultrasound and fine needle aspiration cytology of the axilla in the pre-operative identification of axillary nodal involvement in breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2009. 35:1152–1157.
Article25. Straver ME, Aukema TS, Olmos RA, Rutgers EJ, Gilhuijs KG, Schot ME, et al. Feasibility of FDG PET/CT to monitor the response of axillary lymph node metastases to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010. 37:1069–1076.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Number of Removed Lymph Nodes for an Acceptable False Negative Rate in Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Breast Cancer
- Use of Mammary Lymphoscintigraphy and Intraoperative Radioguided Gamma Probe in Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy of Breast Cancer
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Breast Cancer: A Clinical Review and Update
- Validation and Controversy of Sentinel Node Biopsy for Breast Cancer
- Short Term Follow-up Data in Breast Cancer Patients with Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Alone