Diabetes Metab J.
2013 Apr;37(2):125-131. 10.4093/dmj.2013.37.2.125.
The Relationship between Metformin and Cancer in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. kcwon@med.yu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2280714
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.2.125
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Recently, several studies reported that the cancer incidence in type 2 diabetes patients is higher than in the general population. Although a number of risks are shared between cancer and diabetes patients, there have been few studies of its correlation. We evaluated the influences of several factors including low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), albuminuria and use of metformin on the risk of cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes.
METHODS
We enrolled 1,320 patients with at least 5 years of follow-up and 73 patients were diagnosed with cancer during this period. The associations of the risk factors with cancer incidence were evaluated by multiple regression analysis. The subjects were placed into two subgroups based on metformin dosage (<1,000 mg/day, > or =1,000 mg/day) and we compared cancer incidence using analysis of covariance.
RESULTS
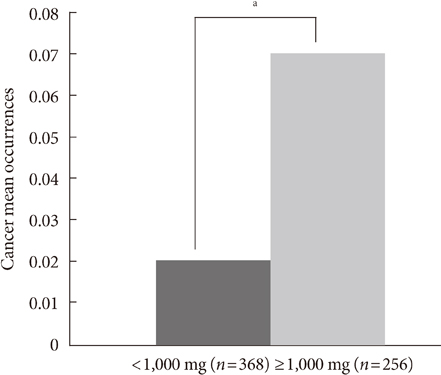
LDL-C and albuminuria were not significantly correlated with cancer risk. In contrast, metformin showed a reverse correlation with cancer risk (P=0.006; relative risk, 0.574). In the metformin nonadministration group, smoking, male gender, and high triglyceride levels tended to be contributing factors without statistical significance. Cancer occurence was lower in the low dose metformin group (less than 1,000 mg/day) (P=0.00).
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that the administration of low dose metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes may be associated with a reduced risk of cancer.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. International Agency for Research on Cancer: World cancer report 2008. cited 2010 Apr 1. Available from: http://www.iarc.fr/en/publications/pdfs-online/wcr/2008/index.php.2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: General information and national estimates on diabetes in the United States, 2007. cited 2010 Apr 1. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pubs/pdf/ndfs_2007.pdf.3. Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, Jamison DT, Murray CJ. Global and regional burden of disease and risk factors, 2001: systematic analysis of population health data. Lancet. 2006. 367:1747–1757.4. Statistics Korea: Statistics of cause of death. updated 2010 Sep 9. Available from: http://www.kostat.go.kr.5. Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun MJ. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med. 2003. 348:1625–1638.6. Chari ST, Leibson CL, Rabe KG, Timmons LJ, Ransom J, de Andrade M, Petersen GM. Pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes mellitus: prevalence and temporal association with diagnosis of cancer. Gastroenterology. 2008. 134:95–101.7. Joslin EP, Lombard HL, Burrows RE, Manning MD. Diabetes and cancer. N Engl J Med. 1959. 260:486–488.8. Zendehdel K, Nyren O, Ostenson CG, Adami HO, Ekbom A, Ye W. Cancer incidence in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a population-based cohort study in Sweden. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003. 95:1797–1800.9. Park SK, Park MK, Suk JH, Kim MK, Kim YK, Kim IJ, Kang YH, Lee KJ, Lee HS, Lee CW, Kim BH, Lee KI, Kim MK, Kim DK. Cause-of-death trends for diabetes mellitus over 10 years. Korean Diabetes J. 2009. 33:65–72.10. Vigneri P, Frasca F, Sciacca L, Pandini G, Vigneri R. Diabetes and cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2009. 16:1103–1123.11. Alimova IN, Liu B, Fan Z, Edgerton SM, Dillon T, Lind SE, Thor AD. Metformin inhibits breast cancer cell growth, colony formation and induces cell cycle arrest in vitro. Cell Cycle. 2009. 8:909–915.12. Currie CJ, Poole CD, Gale EA. The influence of glucose-lowering therapies on cancer risk in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2009. 52:1766–1777.13. Evans JM, Donnelly LA, Emslie-Smith AM, Alessi DR, Morris AD. Metformin and reduced risk of cancer in diabetic patients. BMJ. 2005. 330:1304–1305.14. Jiralerspong S, Palla SL, Giordano SH, Meric-Bernstam F, Liedtke C, Barnett CM, Hsu L, Hung MC, Hortobagyi GN, Gonzalez-Angulo AM. Metformin and pathologic complete responses to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in diabetic patients with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009. 27:3297–3302.15. Yang X, So W, Ko GT, Ma RC, Kong AP, Chow CC, Tong PC, Chan JC. Independent associations between low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and cancer among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. CMAJ. 2008. 179:427–437.16. Kasper JS, Giovannucci E. A meta-analysis of diabetes mellitus and the risk of prostate cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2006. 15:2056–2062.17. World Cancer Research Fund, American Institute for Cancer Research: Food, nutrition, physical activity, and the prevention of cancer: a global perspective. updated 2007 Nov 1. Available from: http://www.dietandcancerreport.org.18. Schuit AJ, Van Dijk CE, Dekker JM, Schouten EG, Kok FJ. Inverse association between serum total cholesterol and cancer mortality in Dutch civil servants. Am J Epidemiol. 1993. 137:966–976.19. Liao JK. Clinical implications for statin pleiotropy. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2005. 16:624–629.20. Yang X, So WY, Ma RC, Yu LW, Ko GT, Kong AP, Ng VW, Luk AO, Ozaki R, Tong PC, Chow CC, Chan JC. Use of sulphonylurea and cancer in type 2 diabetes: the Hong Kong Diabetes Registry. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010. 90:343–351.21. Blin P, Lassalle R, Dureau-Pournin C, Ambrosino B, Bernard MA, Abouelfath A, Gin H, Le Jeunne C, Pariente A, Droz C, Moore N. Insulin glargine and risk of cancer: a cohort study in the French National Healthcare Insurance Database. Diabetologia. 2012. 55:644–653.22. Shaw RJ, Lamia KA, Vasquez D, Koo SH, Bardeesy N, Depinho RA, Montminy M, Cantley LC. The kinase LKB1 mediates glucose homeostasis in liver and therapeutic effects of metformin. Science. 2005. 310:1642–1646.23. Dowling RJ, Zakikhani M, Fantus IG, Pollak M, Sonenberg N. Metformin inhibits mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent translation initiation in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2007. 67:10804–10812.24. Algire C, Zakikhani M, Blouin MJ, Shuai JH, Pollak M. Metformin attenuates the stimulatory effect of a high-energy diet on in vivo LLC1 carcinoma growth. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2008. 15:833–839.25. Libby G, Donnelly LA, Donnan PT, Alessi DR, Morris AD, Evans JM. New users of metformin are at low risk of incident cancer: a cohort study among people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009. 32:1620–1625.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Metformin and Cancer in Type 2 Diabetes
- Recent Perspective of Metformin
- Chemoprevention of Gastric Cancer: Metformin
- The Effect of Rosiglitazone and Metformin Therapy, as an Initial Therapy, in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Letter: Efficacy and Safety of Voglibose Plus Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43;276-86)