Korean Circ J.
2016 Jan;46(1):15-22. 10.4070/kcj.2016.46.1.15.
Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Left Ventricular Remodeling in Patients with ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction after Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiology, School of Medicine, Kafkas University, Kars, Turkey.
- 2Department of Cardiology, Yenimahalle State Hospital, Ankara, Turkey.
- 3Department of Cardiology, Adana Numune Training and Research Hospital, Adana, Turkey. atanerseker@hotmail.com
- 4Department of Cardiology, School of Medicine, Dicle University, Diyarbakir, Turkey.
- KMID: 2223765
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2016.46.1.15
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
It has been demonstrated that the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR) might be a useful marker to predict cardiovascular risk and events. We aimed to investigate the role of the NLR to predict ventricular remodeling (VR) in patients with anterior ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) who were treated with primary percutaneous coronary intervention.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
We prospectively included 274 consecutive anterior STEMI patients. Echocardiography was performed during admission and at six months after myocardial infarction. VR was defined as at least 20% increase from baseline in left ventricular end-diastolic volume. Patients were divided into two groups according to their VR status: VR (n=67) and non-VR (n=207). Total and differential leukocyte count, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and other biochemical markers were measured at admission and 24 hours later.
RESULTS
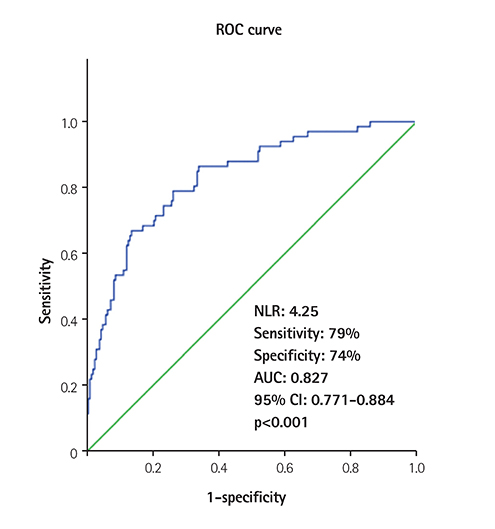
Compared with the non-VR group, peak creatine kinase MB (CK-MB), NT-proBNP (24 h), neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio, presence of diabetes, no-reflow frequency and wall motion score index were significantly higher in patients with VR (p<0.05 for all). On multivariate logistic regression analysis, NLR (beta=2.000, 95% confidence interval=1.577-2.537, p<0.001) as well as peak CK-MB, NT-proBNP (24 h), WMSI and diabetes incidence were associated with VR. The cutoff value of the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio obtained by receiver operator characteristic curve analysis was 4.25 for the prediction of VR (sensitivity: 79 %, specificity: 74%).
CONCLUSION
In patients with anterior STEMI, initial NLR and NT-proBNP measured 24 hours after admission may be useful for predicting adverse cardiovascular events including left VR.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Parikh NI, Gona P, Larson MG, et al. Long-term trends in myocardial infarction incidence and case fatality in the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute's Framingham Heart study. Circulation. 2009; 119:1203–1210.2. Yoon HJ, Jeong MH, Jeong Y, et al. Progressive dilation of the left atrium and ventricle after acute myocardial infarction is associated with high mortality. Korean Circ J. 2013; 43:731–738.3. Olivetti G, Abbi R, Quaini F, et al. Apoptosis in the failing human heart. N Engl J Med. 1997; 336:1131–1141.4. Heusch G, Libby P, Gersh B, et al. Cardiovascular remodelling in coronary artery disease and heart failure. Lancet. 2014; 383:1933–1943.5. Seropian IM, Toldo S, Van Tassell BW, Abbate A. Anti-inflammatory strategies for ventricular remodeling following ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014; 63:1593–1603.6. Nahrendorf M, Swirski FK. Monocyte and macrophage heterogeneity in the heart. Circ Res. 2013; 112:1624–1633.7. Frangogiannis NG. The immune system and the remodeling infarcted heart: cell biological insights and therapeutic opportunities. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2014; 63:185–195.8. Cohn JN, Ferrari R, Sharpe N. Cardiac remodeling--concepts and clinical implications: a consensus paper from an international forum on cardiac remodeling. Behalf of an International Forum on Cardiac Remodeling. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000; 35:569–582.9. Horne BD, Anderson JL, John JM, et al. Which white blood cell subtypes predict increased cardiovascular risk? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005; 45:1638–1643.10. Lax A, Sanchez-Mas J, Asensio-Lopez MC, et al. Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists modulate galectin-3 and interleukin-33/ST2 signaling in left ventricular systolic dysfunction after acute myocardial infarction. JACC Heart Fail. 2015; 3:50–58.11. Sianos G, Morel MA, Kappetein AP, et al. The SYNTAX Score: an angiographic tool grading the complexity of coronary artery disease. EuroIntervention. 2005; 1:219–227.12. Bolognese L, Neskovic AN, Parodi G, et al. Left ventricular remodeling after primary coronary angioplasty: patterns of left ventricular dilation and long-term prognostic implications. Circulation. 2002; 106:2351–2357.13. Frangogiannis NG, Smith CW, Entman ML. The inflammatory response in myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. 2002; 53:31–47.14. Frangogiannis NG, Youker KA, Rossen RD, et al. Cytokines and the microcirculation in ischemia and reperfusion. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1998; 30:2567–2576.15. Gajarsa JJ, Kloner RA. Left ventricular remodeling in the post-infarction heart: a review of cellular, molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic modalities. Heart Fail Rev. 2011; 16:13–21.16. Tamhane UU, Aneja S, Montgomery D, Rogers EK, Eagle KA, Gurm HS. Association between admission neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 2008; 102:653–657.17. Sahin DY, Elbasan Z, Gür M, et al. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is associated with the severity of coronary artery disease in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Angiology. 2013; 64:423–429.18. Han YC, Yang TH, Kim DI, et al. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio predicts long-term clinical outcomes in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Korean Circ J. 2013; 43:93–99.19. Tanindi A, Erkan AF, Ekici B, Alhan A, Töre HF. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is associated with more extensive, severe and complex coronary artery disease and impaired myocardial perfusion. Turk Kardiyol Dern Ars. 2014; 42:125–130.20. Mezzaroma E, Toldo S, Farkas D, et al. The inflammasome promotes adverse cardiac remodeling following acute myocardial infarction in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011; 108:19725–19730.21. Maxwell SR, Lip GY. Reperfusion injury: a review of the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations and therapeutic options. Int J Cardiol. 1997; 58:95–117.22. Ott I, Neumann FJ, Gawaz M, Schmitt M, Schömig A. Increased neutrophil-platelet adhesion in patients with unstable angina. Circulation. 1996; 94:1239–1246.23. Jaeschke H, Smith CW. Mechanisms of neutrophil-induced parenchymal cell injury. J Leukoc Biol. 1997; 61:647–653.24. Hermann HP, Zeitz O, Lehnart SE, et al. Potentiation of beta-adrenergic inotropic response by pyruvate in failing human myocardium. Cardiovasc Res. 2002; 53:116–123.25. Ducloux D, Challier B, Saas P, Tiberghien P, Chalopin JM. CD4 cell lymphopenia and atherosclerosis in renal transplant recipients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003; 14:767–772.26. de Lemos JA, McGuire DK, Drazner MH. B-type natriuretic peptide in cardiovascular disease. Lancet. 2003; 362:316–322.27. Staub D, Nusbaumer C, Zellweger MJ, et al. Use of B-type natriuretic peptide in the detection of myocardial ischemia. Am Heart J. 2006; 151:1223–1230.28. Cochet A, Zeller M, Cottin Y, et al. The extent of myocardial damage assessed by contrast-enhanced MRI is a major determinant of N-BNP concentration after myocardial infarction. Eur J Heart Fail. 2004; 6:555–560.29. Haeck JD, Verouden NJ, Kuijt WJ, et al. Comparison of usefulness of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide as an independent predictor of cardiac function among admission cardiac serum biomarkers in patients with anterior wall versus nonanterior wall ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Am J Cardiol. 2010; 105:1065–1069.30. Kleczyński P, Legutko J, Rakowski T, et al. Predictive utility of NT-pro BNP for infarct size and left ventricle function after acute myocardial infarction in long-term follow-up. Dis Markers. 2013; 34:199–204.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Left main artery stenting under percutaneous cardiopulmonary support after right coronary artery ST elevation infarction
- Consecutive Multivessel Myocardial Infarction during Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
- The Effects of Abciximab on Left Ventricular Remodeling in Patient with Acute Myocardial Infarction Treated with Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
- Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio at Emergency Room Predicts Mechanical Complications of ST-segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
- Current Status of Coronary Intervention in Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction and Multivessel Coronary Artery Disease