Ann Rehabil Med.
2013 Jun;37(3):389-395. 10.5535/arm.2013.37.3.389.
The Relationship Between Muscle Fatigue and Balance in the Elderly
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Hallym University Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea. kangsoa1@daum.net
- 2Department of Physical Therapy, Hallym College, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2219536
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2013.37.3.389
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the effect of gastrocnemius muscle fatigue on postural control ability in elderly people.
METHODS
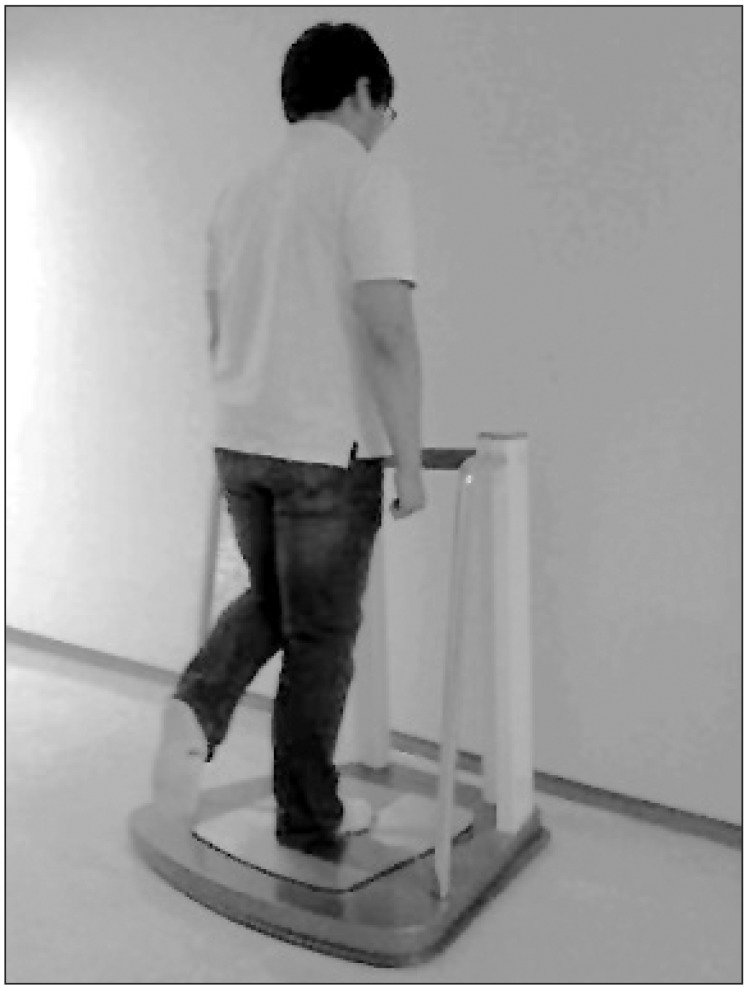
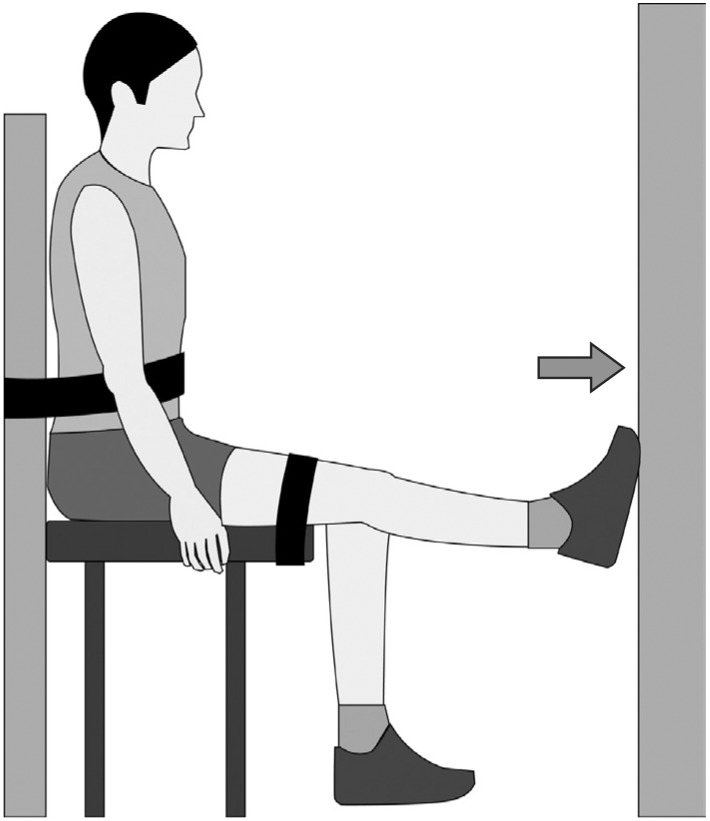
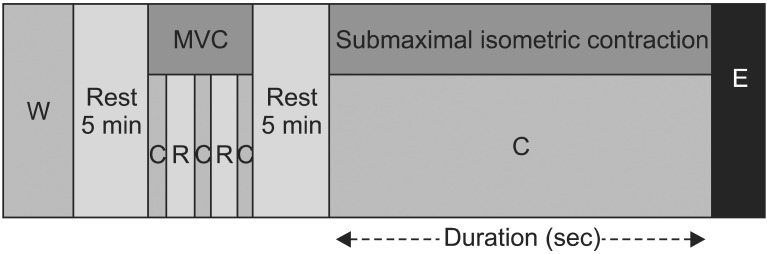
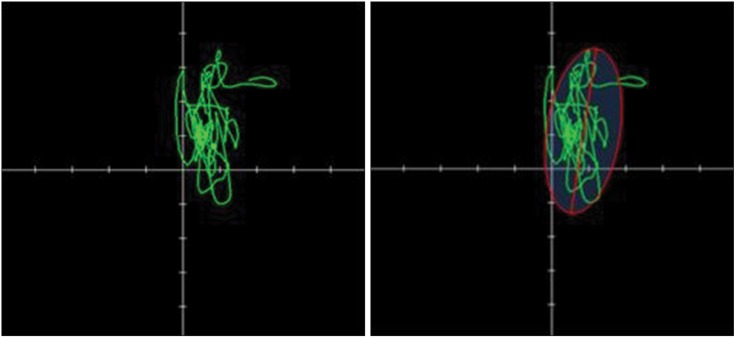
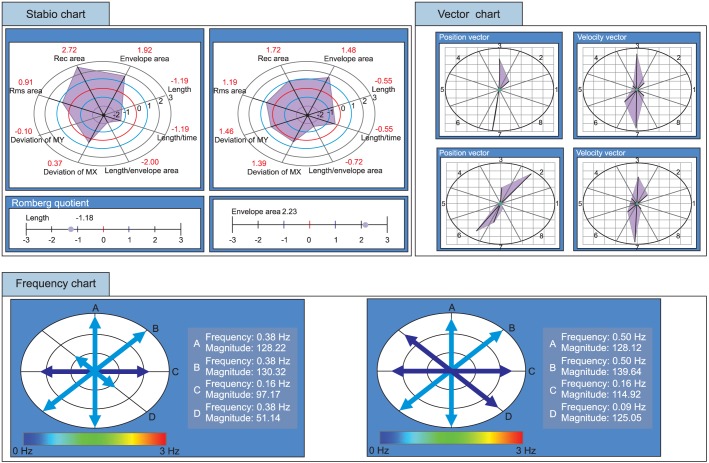
Twenty-four healthy elderly people participated in this study. The postural control ability of single leg standing was evaluated with Health Improvement & Management System (HIMS) posturography before and after fatiguing exercises. After evaluating initial postural control ability, the maximal voluntary contraction (MVC) of ankle plantarflexion was assessed using a surface electromyogram from the medial belly of the gastrocnemius muscle. After a 5-minute resting period, subjects began submaximal isometric ankle plantarflexion (40% MVC) until 40% of MVC was dropped below 95% for 5 seconds, or subject couldn't continue working out due to muscle fatigue. And postural control ability was assessed after fatiguing exercise. The mean deviation of center of pressure (COP), length of COP movement, occupied area of COP were measured, and analyzed by paired t-test.
RESULTS
Mediolateral deviation, length of COP movement, and area of COP occupied were increased after fatiguing exercise of the gastrocnemius muscle. Anteroposterior deviation and length of COP movement were also increased, but had low statistical significance.
CONCLUSION
These findings suggest that the gastrocnemius muscle fatigue affects mediolateral stability and accuracy during single leg standing in elderly people. Therefore muscle endurance training is necessary to prevent falls in elderly people.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Statistics Korea. Population projections for Korea: 2010-2060. Seoul: Statistics Korea;2012.2. Campbell AJ, Reinken J, Allan BC, Martinez GS. Falls in old age: a study of frequency and related clinical factors. Age Ageing. 1981; 10:264–270. PMID: 7337066.
Article3. Alamgir H, Muazzam S, Nasrullah M. Unintentional falls mortality among elderly in the United States: time for action. Injury. 2012; 43:2065–2071. PMID: 22265137.
Article4. Alexander BH, Rivara FP, Wolf ME. The cost and frequency of hospitalization for fall-related injuries in older adults. Am J Public Health. 1992; 82:1020–1023. PMID: 1609903.
Article5. Horak FB, Shupert CL, Mirka A. Components of postural dyscontrol in the elderly: a review. Neurobiol Aging. 1989; 10:727–738. PMID: 2697808.
Article6. Horak FB. Postural orientation and equilibrium: what do we need to know about neural control of balance to prevent falls? Age Ageing. 2006; 35(Suppl 2):ii7–ii11. PMID: 16926210.
Article7. Finley JM, Dhaher YY, Perreault EJ. Regulation of feed-forward and feedback strategies at the human ankle during balance control. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2009; 2009:7265–7268. PMID: 19965100.
Article8. King GW, Stylianou AP, Kluding PM, Jernigan SD, Luchies CW. Effects of age and localized muscle fatigue on ankle plantar flexor torque development. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2012; 35:8–14. PMID: 22189949.
Article9. Yaggie JA, McGregor SJ. Effects of isokinetic ankle fatigue on the maintenance of balance and postural limits. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2002; 83:224–228. PMID: 11833026.
Article10. Ochsendorf DT, Mattacola CG, Arnold BL. Effect of orthotics on postural sway after fatigue of the plantar flexors and dorsiflexors. J Athl Train. 2000; 35:26–30. PMID: 16558604.11. Smidt M, Battig P, Verhaegh SJ, Niebisch A, Hanner M, Selak S, et al. Comprehensive antigen screening identifies Moraxella catarrhalis Proteins that induce protection in a mouse pulmonary clearance model. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e64422. PMID: 23671716.
Article12. Jun AY, Choi EH, Yoo YS, Park DS, Nam HS. The activities of trapezius and deltoid in rotator cuff tear patients injected local anesthetics in subacromial space. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2010; 34:316–324.13. Nordez A, Guevel A, Casari P, Catheline S, Cornu C. Assessment of muscle hardness changes induced by a submaximal fatiguing isometric contraction. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2009; 19:484–491. PMID: 18158253.
Article14. Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Landi F, Topinkova E, Michel JP. Understanding sarcopenia as a geriatric syndrome. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2010; 13:1–7. PMID: 19915458.
Article15. Vandervoort AA. Aging of the human neuromuscular system. Muscle Nerve. 2002; 25:17–25. PMID: 11754180.
Article16. Jenkins DB. Hollinshead's functional anatomy of the limbs and back. 9th ed. Edinburgh: Saunders;2008.17. Gribble PA, Hertel J, Denegar CR, Buckley WE. The Effects of fatigue and chronic ankle instability on dynamic postural control. J Athl Train. 2004; 39:321–329. PMID: 15592604.18. Warren GL, Hayes DA, Lowe DA, Prior BM, Armstrong RB. Materials fatigue initiates eccentric contraction-induced injury in rat soleus muscle. J Physiol. 1993; 464:477–489. PMID: 8229814.
Article19. Milner-Brown HS, Miller RG. Muscle membrane excitation and impulse propagation velocity are reduced during muscle fatigue. Muscle Nerve. 1986; 9:367–374. PMID: 3012329.
Article20. Gutierrez GM, Jackson ND, Dorr KA, Margiotta SE, Kaminski TW. Effect of fatigue on neuromuscular function at the ankle. J Sport Rehabil. 2007; 16:295–306. PMID: 18246896.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Influence of Unilateral Muscle Fatigue in Knee and Ankle Joint on Balance and Gait in Healthy Adults
- The Effect of an Abdominal Drawing-In Maneuver Combined with Low·High Frequency Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation on Trunk Muscle Activity, Muscle Fatigue, and Balance in Stroke Patients
- The Effect of Thera Band Exercise on Muscle Flexibility, Balance Ability, Muscle Strength in Elderly Women
- Muscle fatigue: general understanding and treatment
- Common Disorders Causing Balance Problems