J Korean Soc Endocrinol.
2006 Feb;21(1):1-10. 10.3803/jkes.2006.21.1.1.
Susceptible Genes of Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Experimental Therapeutics, Translational Research Center, Kyoto University Hospital, Kyoto University School of Medicine, Kyoto, Japan.
- KMID: 2200651
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.1.1
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
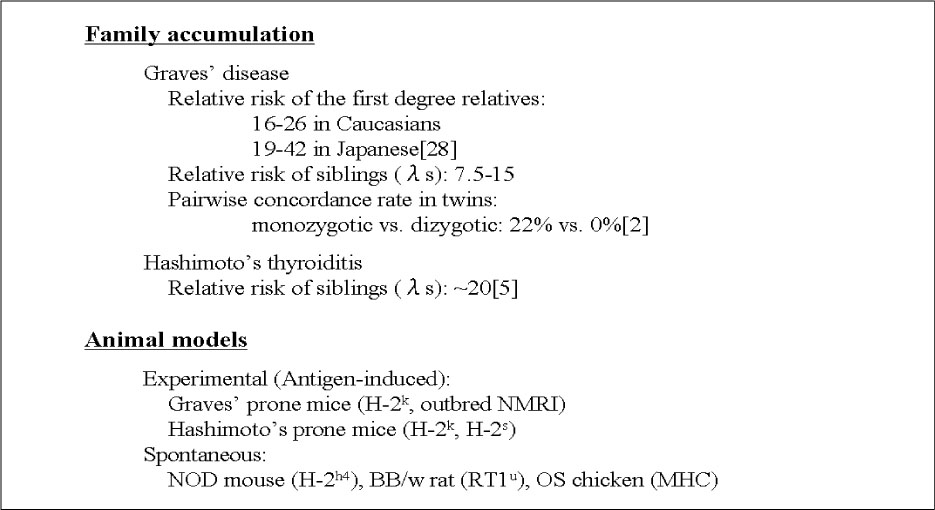
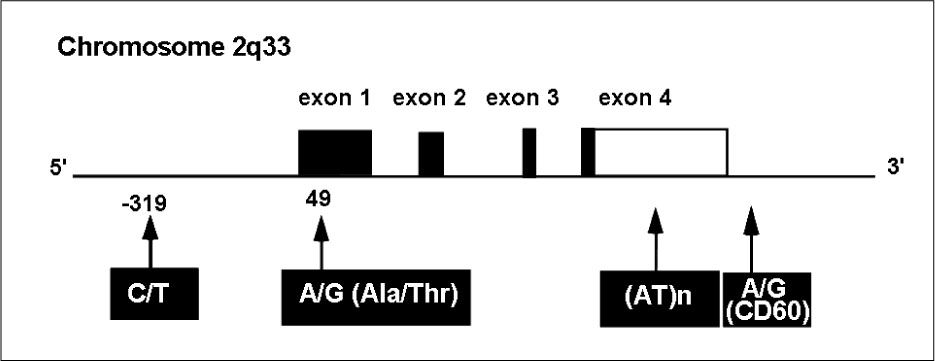
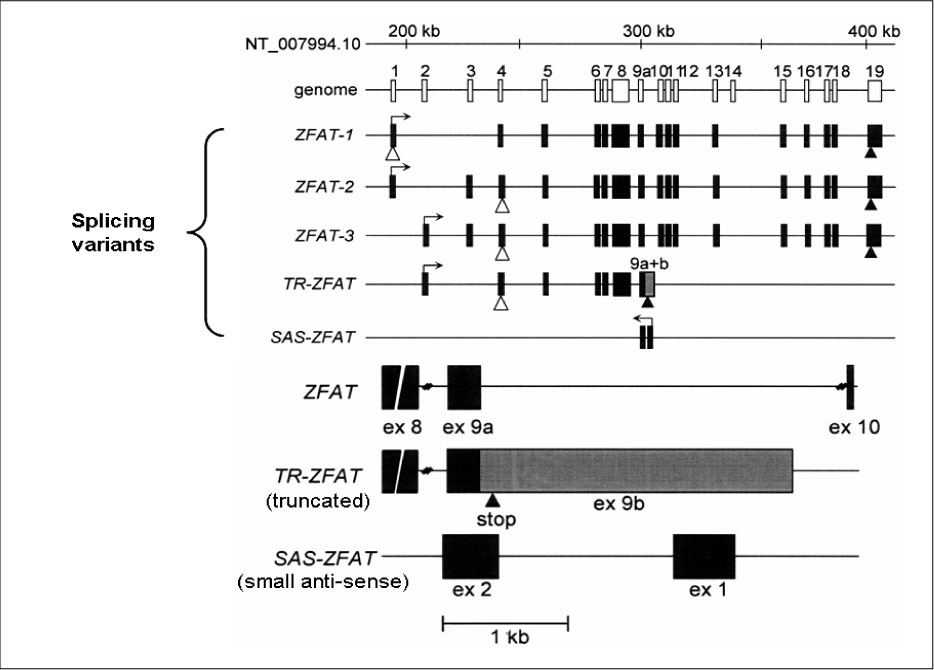
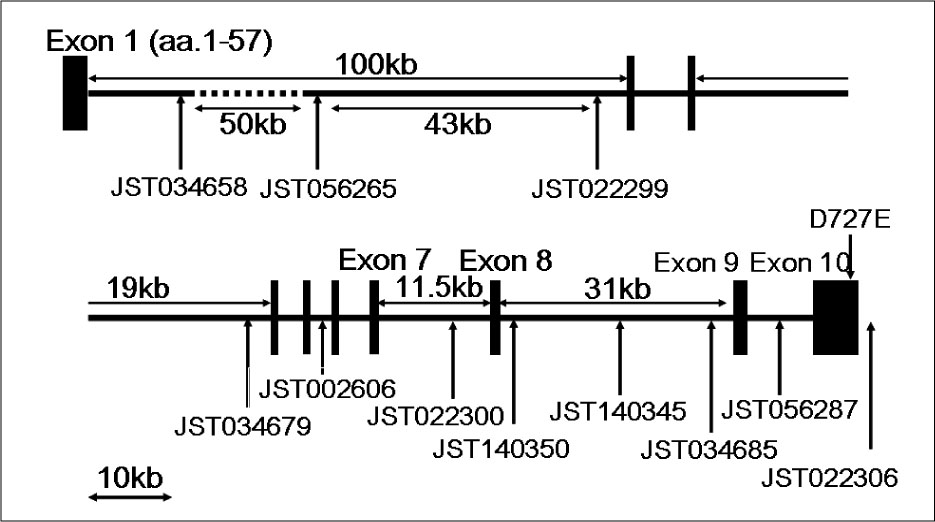
1. Akamizu T, Nakamura Y, Tamaoki A, Inaba Y, Amino N, Seino Y. Prevalence and clinico-epidemiology of familial Graves' disease in Japan based on nationwide epidemiologic survey in 2001. Endocr J. 2003. 50:429–436.2. Brix TH, Kyvik KO, Hegedus L. What is the evidence of genetic factors in the etiology of Graves' disease? A brief review. Thyroid. 1998. 8:727–734.3. Gough SC. The genetics of Graves' disease. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2000. 29:255–266.4. Akamizu T, Sale MM, Rich SS, Hiratani H, Noh JY, Kanamoto N, Saijo M, Miyamoto Y, Saito Y, Nakao K, Bowden DW. Association of autoimmune thyroid disease with microsatellite markers for the thyrotropin receptor gene and CTLA-4 in Japanese patients. Thyroid. 2000. 10:851–858.5. Barbesino G, Tomer Y, Concepcion ES, Davies TF, Greenberg DA. Linkage analysis of candidate genes in autoimmune thyroid disease. II. Selected gender-related genes and the X-chromosome. International Consortium for the Genetics of Autoimmune Thyroid Disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998. 83:3290–3295.6. Blakemore AI, Watson PF, Weetman AP, Duff GW. Association of Graves' disease with an allele of the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1995. 80:111–115.7. Donner H, Rau H, Walfish PG, Braun J, Siegmund T, Finke R, Herwig J, Usadel KH. CTLA4 Alanine-17 confers genetic susceptibility to Graves' disease and to type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997. 82:143–146.8. Farid NR, Sampson L, Noel EP, Barnard JM, Mandeville R, Larsen B, Marshall WH, Carter ND. A study of human leukocyte D locus related antigens in Graves' disease. J Clin Invest. 1979. 63:108–113.9. Hunt PJ, Marshall SE, Weetman AP, Bell JI, Wass JA, Welsh KI. Cytokine gene polymorphisms in autoimmune thyroid disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000. 85:1984–1988.10. Sale MM, Akamizu T, Howard TD, Yokota T, Nakao K, Mori T, Iwasaki H, Rich SS, Jennings-Gee JE, Yamada M, Bowden DW. Association of autoimmune thyroid disease with a microsatellite marker for the thyrotropin receptor gene and CTLA-4 in a Japanese population. Proc Assoc Amer Physician. 1997. 109:453–461.11. Tomer Y, Barbesino G, Greenberg DA, Concepcion E, Davies TF. Mapping the major susceptibility loci for familial Graves' and Hashimoto's diseases: evidence for genetic heterogeneity and gene interactions. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999. 84:4656–4664.12. Uno H, Sasazuki T, Tamai H, Matsumoto H. Two major genes, linked to HLA and Gm, control susceptibility to Graves' disease. Nature. 1981. 292:768–770.13. Vaidya B, Imrie H, Perros P, Young ET, Kelly WF, Carr D, Large DM, Toft AD, Kendall-Taylor P, Pearce SH. Evidence for a new Graves' disease susceptibility locus at chromosome 18q21. Am J Hum Genet. 2000. 66:1710–1714.14. Vaidya B, Imrie H, Perros P, Young ET, Kelly WF, Carr D, Large DM, Toft AD, McCarthy MI, Kendall-Taylor P, Pearce SH. The cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 is a major Graves' disease locus. Hum Mol Genet. 1999. 8:1195–1199.15. Yanagawa T, Hidaka Y, Guimaraes V, Soliman M, DeGroot LJ. Evidence for a new Graves' disease susceptibility locus at chromosome 18q21. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1995. 80:41–45.16. Sakai K, Shirasawa S, Ishikawa N, Ito K, Tamai H, Kuma K, Akamizu T, Tanimura M, Furugaki K, Yamamoto K, Sasazuki T. Identification of susceptibility loci for autoimmune thyroid disease to 5q31-q33 and Hashimoto's thyroiditis to 8q23-q24 by multipoint affected sib-pair linkage analysis in Japanese. Hum Mol Genet. 2001. 10:1379–1386.17. Park YJ, Chung HK, Park DJ, Kim WB, Kim SW, Koh JJ, Cho BY. Polymorphism in the promoter and exon 1 of the cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 gene associated with autoimmune thyroid disease in Koreans. Thyroid. 2000. 10:453–459.18. Kouki T, Sawai Y, Gardine CA, Fisfalen ME, Alegre ML, DeGroot LJ. CTLA-4 gene polymorphism at position 49 in exon 1 reduces the inhibitory function of CTLA-4 and contributes to the pathogenesis of Graves' disease. J Immunol. 2000. 165:6606–6611.19. Ueda H, Howson JM, Esposito L, Heward J, Snook H, Chamberlain G, Rainbow DB, Hunter KM, Smith AN, Di Genova G, Herr MH, Dahlman I, Payne F, Smyth D, Lowe C, Twells RC, Howlett S, Healy B, Nutland S, Rance HE, Everett V, Smink LJ, Lam AC, Cordell HJ, Walker NM, Bordin C, Hulme J, Motzo C, Cucca F, Hess JF, Metzker ML, Rogers J, Gregory S, Allahabadia A, Nithiyananthan R, Tuomilehto-Wolf E, Tuomilehto J, Bingley P, Gillespie KM, Undlien DE, Ronningen KS, Guja C, Ionescu-Tirgoviste C, Savage DA, Maxwell AP, Carson DJ, Patterson CC, Franklyn JA, Clayton DG, Peterson LB, Wicker LS, Todd JA, Gough SC. Association of the T-cell regulatory gene CTLA4 with susceptibility to autoimmune disease. Nature. 2003. 423:506–511.20. Dong RP, Kimura A, Okubo R, Shinagawa H, Tamai H, Nishimura Y, Sasazuki T. HLA-A and DPB1 loci confer susceptibility to Graves' disease. Hum Immunol. 1992. 35:165–172.21. Lonjou C, Barnes K, Chen H, Cookson WO, Deichmann KA, Hall IP, Holloway JW, Laitinen T, Palmer LJ, Wjst M, Morton NE. A first trial of retrospective collaboration for positional cloning in complex inheritance: assay of the cytokine region on chromosome 5 by the consortium on asthma genetics (COAG). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. 97:10942–10947.22. Meyers DA, Postma DS, Panhuysen CI, Xu J, Amelung PJ, Levitt RC, Bleecker ER. Evidence for a locus regulating total serum IgE levels mapping to chromosome 5. Genomics. 1994. 23:464–470.23. Postma DS, Bleecker ER, Amelung PJ, Holroyd KJ, Xu J, Panhuysen CI, Meyers DA, Levitt RC. Genetic susceptibility to asthma--bronchial hyperresponsiveness coinherited with a major gene for atopy. N Engl J Med. 1995. 333:894–900.24. Wills-Karp M. The gene encoding interleukin-13: a susceptibility locus for asthma and related traits. Respir Res. 2000. 1:19–23.25. Le Beau MM, Espinosa R 3rd, Neuman WL, Stock W, Roulston D, Larson RA, Keinanen M, Westbrook CA. Cytogenetic and molecular delineation of the smallest commonly deleted region of chromosome 5 in malignant myeloid diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993. 90:5484–5488.26. Rioux JD, Stone VA, Daly MJ, Cargill M, Green T, Nguyen H, Nutman T, Zimmerman PA, Tucker MA, Hudson T, Goldstein AM, Lander E, Lin AY. Familial eosinophilia maps to the cytokine gene cluster on human chromosomal region 5q31-q33. Am J Hum Genet. 1998. 63:1086–1094.27. van Leeuwen BH, Martinson ME, Webb GC, Young IG. Molecular organization of the cytokine gene cluster, involving the human IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, and GM-CSF genes, on human chromosome 5. Blood. 1989. 73:1142–1148.28. Akamizu T, Hiratani H, Ikegami S, Rich SS, Bowden DW. Association study of autoimmune thyroid disease at 5q23-q33 in Japanese patients. J Hum Genet. 2003. 48:236–242.29. Shirasawa S, Harada H, Furugaki K, Akamizu T, Ishikawa N, Ito K, Ito K, Tamai H, Kuma K, Kubota S, Hiratani H, Tsuchiya T, Baba I, Ishikawa M, Tanaka M, Sakai K, Aoki M, Yamamoto K, Sasazuki T. SNPs in the promoter of a B cell-specific antisense transcript, SAS-ZFAT, determine susceptibility to autoimmune thyroid disease. Hum Mol Genet. 2004. 13:2221–2231.30. Cuddihy RM, Dutton CM, Bahn RS. A polymorphism in the extracellular domain of the thyrotropin receptor is highly associated with autoimmune thyroid disease in females. Thyroid. 1995. 5:89–95.31. Ho SC, Goh SS, Khoo DH. Association of Graves' disease with intragenic polymorphism of the thyrotropin receptor gene in a cohort of Singapore patients of multi-ethnic origins. Thyroid. 2003. 13:523–528.32. Kotsa KD, Watson PF, Weetman AP. No association between a thyrotropin receptor gene polymorphism and Graves' disease in the female population. Thyroid. 1997. 7:31–33.33. Hiratani H, Bowden DW, Ikegami S, Shirasawa S, Shimizu A, Iwatani Y, Akamizu T. Multiple SNPs in intron 7 of thyrotropin receptor are associated with Graves' disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005. 90:2898–2903.34. Dechairo BM, Zabaneh D, Collins J, Brand O, Dawson GJ, Green AP, Mackay I, Franklyn JA, Connell JM, Wass JA, Wiersinga WM, Hegedus L, Brix T, Robinson BG, Hunt PJ, Weetman AP, Carey AH, Gough SC. Association of the TSHR gene with Graves' disease: the first disease specific locus. Eur J Hum Genet. 2005. 13:1223–1230.