J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2014 Feb;55(2):106-109. 10.3340/jkns.2014.55.2.106.
Spinal Arteriovenous Fistula with Progressive Paraplegia after Spinal Anaesthesia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neuroradiology, University Hospital of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland. Gerasimos.Baltsavias@usz.ch
- 2Neuroendovascular Unit, Interbalkan Medical Center, Thessaloniki, Greece.
- KMID: 2191056
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2014.55.2.106
Abstract
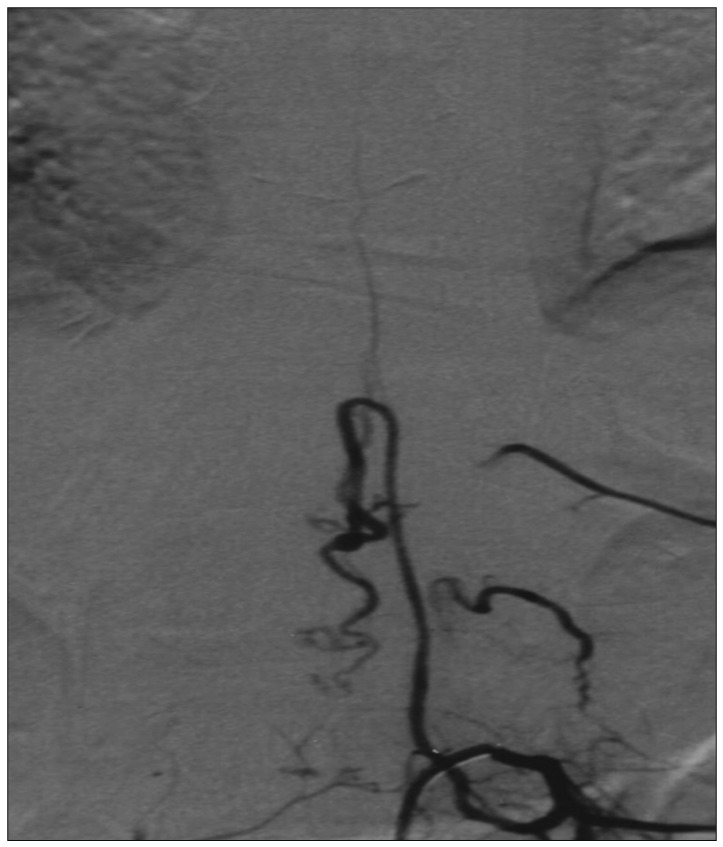
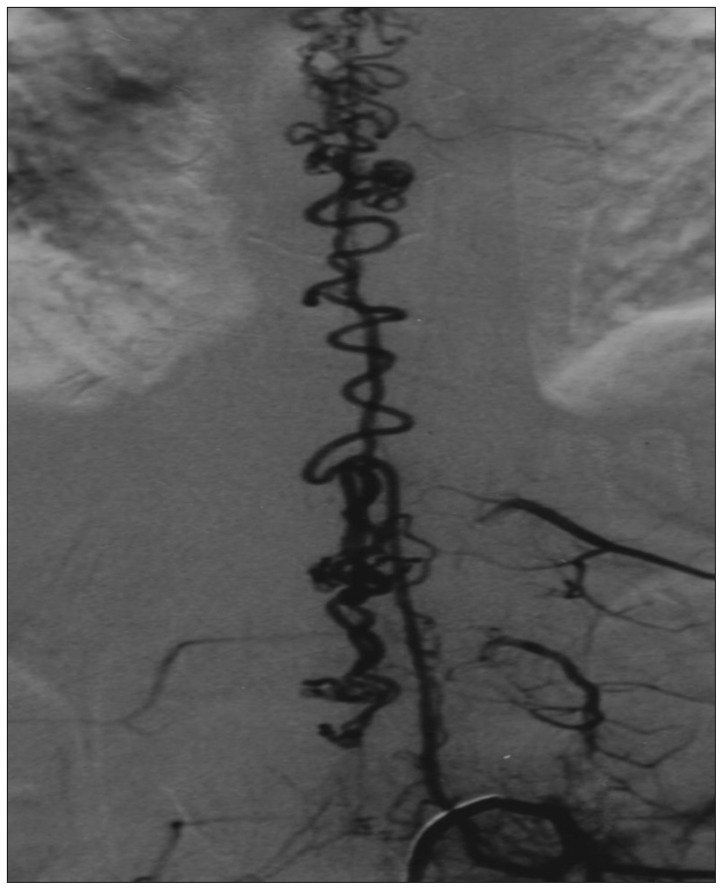
- A case of an iatrogenic spinal arteriovenous fistula with progressive paraplegia in a young woman is reported. The fistula was eventually created after repetitive lumbar punctures performed in the process of spinal anaesthesia. Her symptoms were progressed to paraplegia over a period of 2 years. The digital subtraction angiography demonstrated a single-hole fistula, involving the anterior spinal artery and vein. The lesion was occluded by embolization with immediate improvement. The potential mechanism is discussed.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ahmad FU, Pandey P, Sharma BS, Garg A. Foot drop after spinal anesthesia in a patient with a low-lying cord. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2006; 15:233–236. PMID: 16798451.
Article2. Auroy Y, Narchi P, Messiah A, Litt L, Rouvier B, Samii K. Serious complications related to regional anesthesia: results of a prospective survey in France. Anesthesiology. 1997; 87:479–486. PMID: 9316950.3. Birnbach DJ, Hernandez M, van Zundert AA. Neurologic complications of neuraxial analgesia for labor. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2005; 18:513–517. PMID: 16534285.
Article4. Boon JM, Abrahams PH, Meiring JH, Welch T. Lumbar puncture: anatomical review of a clinical skill. Clin Anat. 2004; 17:544–553. PMID: 15376294.
Article5. Charuluxananan S, Thienthong S, Rungreungvanich M, Chanchayanon T, Chinachoti T, Kyokong O, et al. The Thai Anesthesia Incidents Study (THAI study) of morbidity after spinal anesthesia: a multi-centered registry of 40,271 anesthetics. J Med Assoc Thai. 2007; 90:1150–1160. PMID: 17624210.6. Domenicucci M, Ramieri A, Ciappetta P, Delfini R. Nontraumatic acute spinal subdural hematoma: report of five cases and review of the literature. J Neurosurg. 1999; 91(1 suppl):65–73. PMID: 10419371.7. Faccenda KA, Finucane BT. Complications of regional anaesthesia Incidence and prevention. Drug Saf. 2001; 24:413–442. PMID: 11368250.8. Halbach VV, Higashida RT, Dowd CF, Fraser KW, Edwards MS, Barnwell SL. Treatment of giant intradural (perimedullary) arteriovenous fistulas. Neurosurgery. 1993; 33:972–979. discussion 979-980. PMID: 8134010.
Article9. LaFerlita BW. Postoperative paraplegia coincident with single shot spinal anaesthesia. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2007; 35:605–607. PMID: 18020083.
Article10. Lasjaunias P, Berenstein A, ter Brugge K. Surgical Neuroangiography. ed 2. Berlin: Springer-Verlag;2004. p. 767–813.11. Likar R, Mathiaschitz K, Spendel M, Krumpholz R, Martin E. [Acute spinal subdural hematoma after attempted spinal anesthesia]. Anaesthesist. 1996; 45:66–69. PMID: 8678281.12. Liu YC, Wu RS, Wong CS. Unexpected complication of attempted epidural anaesthesia: cauda equina syndrome. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2003; 31:461–464. PMID: 12973972.
Article13. Niimi Y, Berenstein A. Endovascular treatment of spinal vascular malformations. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1999; 10:47–71. PMID: 9855649.
Article14. Paech MJ, Godkin R, Webster S. Complications of obstetric epidural analgesia and anaesthesia: a prospective analysis of 10,995 cases. Int J Obstet Anesth. 1998; 7:5–11. PMID: 15321239.
Article15. Pogatzki-Zahn EM, Wenk M, Wassmann H, Heindel WL, Van Aken H. [Complications of regional anesthesia: diagnostic and management]. Anasthesiol Intensivmed Notfallmed Schmerzther. 2007; 42:42–52. PMID: 17253336.16. Pradhan S, Yadav R, Maurya PK, Mishra VN. Focal myelomalacia and syrinx formation after accidental intramedullary lidocaine injection during lumbar anesthesia: a report of 3 cases. J Neurol Sci. 2006; 251:70–72. PMID: 17097107.
Article17. Rajakulendran Y, Rahman S, Venkat N. Long-term neurological complication following traumatic damage to the spinal cord with a 25 gauge whitacre spinal needle. Int J Obstet Anesth. 1999; 8:62–66. PMID: 15321178.
Article18. Rodesch G, Hurth M, Alvarez H, David P, Tadie M, Lasjaunias P. Embolization of spinal cord arteriovenous shunts: morphological and clinical follow-up and results--review of 69 consecutive cases. Neurosurgery. 2003; 53:40–49. discussion 49-50. PMID: 12823872.
Article19. Rodesch G, Hurth M, Alvarez H, Lasjaunias P. Embolisation of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations with Glue through the Anterior Spinal Axis. Review of 20 Cases. Interv Neuroradiol. 1997; 3:131–143. PMID: 20678351.
Article20. Rodesch G, Hurth M, Alvarez H, Tadié M, Lasjaunias P. Classification of spinal cord arteriovenous shunts: proposal for a reappraisal--the Bicêtre experience with 155 consecutive patients treated between 1981 and 1999. Neurosurgery. 2002; 51:374–379. discussion 379-380. PMID: 12182775.
Article21. Rodesch G, Hurth M, Alvarez H, Tadie M, Lasjaunias P. Spinal cord intradural arteriovenous fistulae: anatomic, clinical, and therapeutic considerations in a series of 32 consecutive patients seen between 1981 and 2000 with emphasis on endovascular therapy. Neurosurgery. 2005; 57:973–983. discussion 973-983. PMID: 16284566.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Successful Treatment of a Spinal Intradural Arteriovenous Fistula
- Surgical Treatment of Arteriovenous Malformations of the Spinal Cord
- Myelopathy Caused by Spinal Dural Arterio-Venous Fistula after First Lumbar Vertebral Body Fracture: A Case Report
- Foix-Alajouanine Syndrome: Case Report
- Cervical spinal extradural arteriovenous fistula successfully treated using transarterial balloon-assisted coil embolization