J Korean Acad Conserv Dent.
2006 May;31(3):153-160. 10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.3.153.
The effect of neuropeptides on secretion of Interleukin-8 (IL-8)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, Division of Dentistry, Graduate School, Kyunghee University, Korea.
- 2Oral Biology Research Institute, College of Dentistry, Kyunghee University, Korea. psangjin@khu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2175814
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.3.153
Abstract
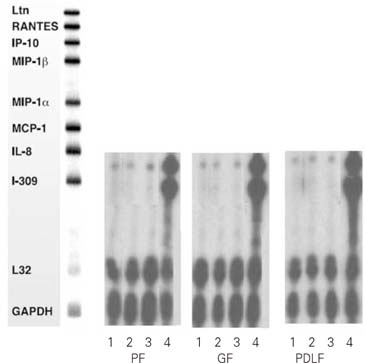
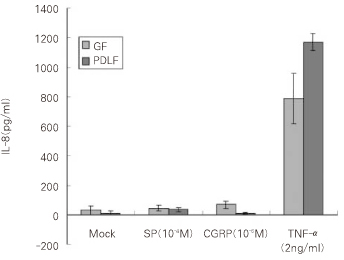
- We investigated the secretion of Interleukin-8 (IL-8) from ginviva and periodontal ligament stimulated with Substance P (SP) and Calcitonin Gene-related Peptide (CGRP). Gingiva (GF), periodontal ligament (PDLF) and pulp (PF) tissues were collected from extracted intact 3rd molars. Cultured cells were stimulated with different concentrations of SP for 4 hrs, and stimulated with SP, CGRP and Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) for 8 hrs. Then RNase Protection Assay was carried out. ELISA was performed using supernatants of stimulated cells for quantitative analysis of IL-8. Results were assessed using student t-test with significance of P < 0.05. According to this study, the results were as follows: 1. IL-8 mRNA was detected in all type of cells studied (PF, GF and PDLF). 2. IL-8 mRNA expression was not increased after stimulating 4 hrs with SP (10(-5)M) and SP (10(-8)M) compared with Mock stimulation in all type of cells studied. 3. IL-8 mRNA expression was not increased after stimulating 8 hrs with SP (10(-4)M) and CGRP (10(-6)M) compared with Mock stimulation in all type of cells studied. 4. TNF-alpha(2 ng/ml) increased the expression of IL-8 mRNA in all kind of cells studied. 5. The secretion of IL-8 from GF was increased 8 hrs after the stimulation with CGRP (10(-6)M) (p < 0.05). 6. The secretion of IL-8 from PDLF was increased 8 hrs after the stimulation with SP (10(-4)M) (p < 0.05). Calcitonin Gene-related Peptide (CGRP) increased Interleukin-8 (IL-8) which plays an important role in chemotaxis of neutrophil in Calcitonin Gene-related Peptide (CGRP) gingival tissue, whereas Substance P increased the secretion of IL-8 from periodontal ligament.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide
Cells, Cultured
Chemotaxis
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Gingiva
Humans
Interleukin-8*
Molar
Neuropeptides*
Neutrophils
Periodontal Ligament
Ribonucleases
RNA, Messenger
Substance P
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide
Interleukin-8
Neuropeptides
RNA, Messenger
Ribonucleases
Substance P
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kiss M, Kemeny L, Gyulai R, Michel G, Husz S, Kovacs R, Dobozy A, Ruzicka T. Effects of the neuropeptides substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide and α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone on the IL-8/IL-8 receptor system in a cultured human keratinocyte cell line and dermal fibroblasts. Inflammation. 1999. 23:557–567.2. Bartold PM, Kylstra A, Lawson R. Substance P. An Immunohistochemical and Biochemical Study in Human Gingival Tissues. A Role for Neurogenic Inflammation? J Periodontol. 1994. 65:1113–1121.
Article3. Rameshwar P, Gascon P. Induction of negative hematopoietic regulators by neurokinin-A in bone marrow stroma. Blood. 1996. 88:98–106.
Article4. Baggiolini M, Walz A, Kunkel SL. Neutrophil-activating peptide-1/Interleukin 8, a novel cytokine that activates neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1989. 84:1045–1049.
Article5. Kent LW, Dyken RA, Rahemtulla F, Allison AC, Michalek SM. Effects of in vitro passage of healthy human gingival fibroblasts on cellular morphology and cytokine expression. Arch Oral Biol. 1996. 41:263–270.
Article6. Guo CJ, Lai JP, Luo HM, Douglas SD, Ho WZ. Substance P up-regulates macrophage inflammatory protein-1β expression in human T lymphocytes. J Neuroimmunol. 2002. 131:160–167.
Article7. Huang GTJ, Potente AP, Kim JW, Chugal N, Zhang X. Increased interleukin-8 espression in inflamed human dental pulps. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1999. 88:214–220.8. Fitzgerald JE, Kreutzer DL. Localization of Interleukin-8 in human gingival tissues. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1996. 10:297–303.
Article9. Larsen CG, Anderson AO, Appella E, Oppenheim JJ, Matsushima K. The neutrophil-activating protein (NAP-1) is also chemotactic for T lymphocytes. Science. 1989. 243:1464–1466.
Article10. Peveri P, Walz A, Dewald B, Baggiolini M. A novel neutrophil activating factor produced by human mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1988. 167:1547–1559.
Article11. Cuesta MC, Quintero L, Pons H, Suarez-Roca H. Substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide increase IL-1β, IL-6 and TNFα secretion from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Neurochem Int. 2002. 40:301–306.
Article12. Park SH, Hsiao GYW, Huang GTJ. Role of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide in the regulation of interleukin-8 and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 expression in human dental pulp. Int Endod J. 2004. 37:185–192.
Article13. Bordin S, Narayanan S, Reddy J, Cleveland D, Page RC. Fibroblast subtypes in the periodontium. J Periodont Res. 1984. 19:642–644.
Article14. McCulloch CAG, Bordin S. Role of fibroblast subpopulations in periodontal physiology and pathology. J Periodont Res. 1991. 26:144–154.
Article15. Heyeraas KJ, Berggreen E. Interstitial fluid pressure in normal and inflamed pulp. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1999. 10(3):328–336.
Article16. Berggreen E, Heyeraas KJ. Effect of the sensory neuropeptide antagonists h-CGRP((8-37)) and SR 140.33 on pulpal and gingival blood flow in ferrets. Arch Oral Biol. 2000. 45(7):537–542.
Article17. Fristad I, Kvinnsland IH, Jonsson R, Heyeraas KJ. Effect of intermittent long-lasting electrical tooth stimulation on pulpal blood flow and immunocompetent cells: a hemodynamic and immunohistochemical study in young rat molars. Exp Neurol. 1997. 146(1):230–239.
Article18. Fristad I, Heyeraas KJ, Kwinnsland IH, Jonsson R. Recruitment of immunocompetent cells after dentinal injuries in innervated and denervated young rat molars: an innunohistochemcal study. J Histochem Cytochem. 1995. 43(9):871–879.
Article19. Bongenhielm U, Haegerstrand A, Theodorsson E, Fried K. Effect of neuropeptides on growth of cultivated rat molar pulp fibroblasts. Regul Pept. 1995. 60(2-3):91–98.
Article20. Patel T, Park SH, Lin LM, Chiappelli F, Huang GTJ. Substance P induces interleukin-8 secretion from human dental pulp cells. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2003. 96:478–485.
Article21. Ansel JC, Armstrong CA, Song I, Quinlan KL, Olerud JE, Caughman SW, Bunnett NW. Interaction of the skin and nervous system. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 1997. 2(1):23–26.22. Raap T, Justen HP, Miller LE, Cutolo M, Scholmerich J, Straub RH. Neurotransmitter modulation of interleukin 6(IL-6) and IL-8 secretion of synovial fibroblasts in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared to osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 2000. 27:2558–2565.23. Detmers PA, Lo SK, Olsen-Egbert E, Walz A, Baggiolini M, Cohn ZA. Neutrophil-activating protein 1/interleukin 8 stimulates the binding activity of the leukocyte adhesion receptor CD11b /CD18 on human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1990. 171:1155–1162.
Article24. Rot A. Neutrophil attractant/activation protein-1(interleukin-8) induces in vitro neutrophil migration by haptotactic mechanism. Eur J Immunol. 1993. 23:303–306.
Article25. Takashiba S, Takigawa M, Takahashi K, Myokai F, Nishimura F, Chihara T, Kurihara H, Nomura Y, Murayama Y. Interleukin-8 is a major neutrophil chemotactic factor derived from cultured human gingival fibroblasts stimulated with interleukin-1β or tumor necrosis factor alpha. Infection and Immunity. 1992. 60:5253–5258.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of 17beta-Estradiol and 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 on Interleukin-6 Production of Periodontal Ligament Cells
- Effects of B-16 Melanoma Cells and Mycoplasma pneumoniae on the Induction of IL-1 beta, IL-2, IL-6, IL-10, IL-12, and TNF - alpha from Mouse Astrocytes
- Secretion of Interleukin-8 from Human Keratocyte Stimulated by Aspergillus fumigatus and Effect of Amphotericin B and Dexamethasone on The Secretion
- Effects of Dexamethasone on expressions of IFN-gamma and IL-4 by PBMCs in response to IL-12
- Effects of Interleukin 4 on the Production of Interleukin 6 in Human Keratinocytes