Diabetes Metab J.
2014 Feb;38(1):44-50. 10.4093/dmj.2014.38.1.44.
Plasma Glucose Regulation and Mortality in Korea: A Pooled Analysis of Three Community-Based Cohort Studies
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Ansan, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Institute of Human Genomic Study, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Ansan, Korea.
- 7Department of Internal Medicine, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine and Bioengineering, Hanyang University Seoul Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. parkys@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2174184
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.1.44
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Although diabetes is a well-known risk factor for death, its impact on cancer death is not clearly understood. Furthermore, it remains controversial whether impaired fasting glucose (IFG) and/or impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) are associated with increased risk of mortality. We investigated the impact of diabetes or glucose tolerance categories on all cause and cause-specific mortality.
METHODS
Mortality analysis was conducted in three population-based cohort studies of 3,801 participants, divided according to fasting plasma glucose (FPG) (normal; stage 1 IFG [5.6< or =FPG<6.1 mmol/L]; stage 2 IFG [6.1< or =FPG<7.0 mmol/L]; diabetes mellitus [DM]-FPG); or 2-hour glucose after 75 g glucose loading (2hPG) (normal; IGT; DM-2hPG), or a combination of FPG and 2hPG criteria.
RESULTS
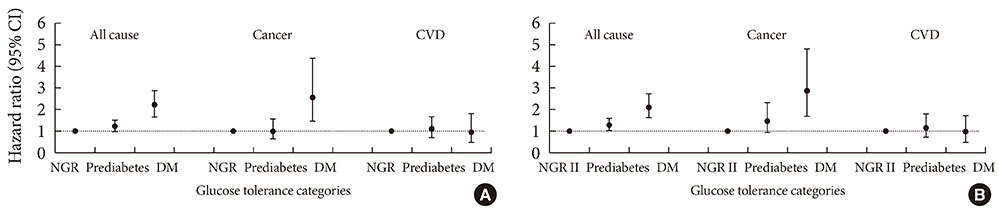
During a median follow-up of 11.0 years, 474 subjects died from all causes. Hazard ratios (HRs) for all cause death were higher in those with diabetes as defined by either FPG or 2hPG criteria than their normal counterparts (HR, 2.2, 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.6 to 2.9 for DM-FPG; HR, 2.0, 95% CI, 1.5 to 2.7 for DM-2hPG). Similarly, diabetes defined by either FPG or 2hPG was associated with cancer death (HR, 2.9, 95% CI, 1.7 to 5.0; and HR, 2.1, 95% CI, 1.2 to 3.9, respectively). Although neither IFG nor IGT conferred higher risk for death, when combining stage 2 IFG and/or IGT, the risk of all cause death was higher than in subjects with normal glucose regulation (HR, 1.3; 95% CI, 1.0 to 1.6).
CONCLUSION
Diabetes is associated with higher risk of death from all causes and cancer. In subjects without diabetes, stage 2 IFG and/or IGT confers increased risk for mortality.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effect of Socio-Economic Status on the Prevalence of Diabetes
Yu Jeong Kim, Ja Young Jeon, Seung Jin Han, Hae Jin Kim, Kwan Woo Lee, Dae Jung Kim
Yonsei Med J. 2015;56(3):641-647. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.3.641.
Reference
-
1. Kim DJ. The epidemiology of diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:303–308.2. Statistics Korea: Causes of death statistics in 2011. updated 2012 Sep 13. Available from: http://www.index.go.kr.3. Johnson JA, Carstensen B, Witte D, Bowker SL, Lipscombe L, Renehan AG. Diabetes and Cancer Research Consortium. Diabetes and cancer (1): evaluating the temporal relationship between type 2 diabetes and cancer incidence. Diabetologia. 2012; 55:1607–1618.4. Jee SH, Ohrr H, Sull JW, Yun JE, Ji M, Samet JM. Fasting serum glucose level and cancer risk in Korean men and women. JAMA. 2005; 293:194–202.5. Coughlin SS, Calle EE, Teras LR, Petrelli J, Thun MJ. Diabetes mellitus as a predictor of cancer mortality in a large cohort of US adults. Am J Epidemiol. 2004; 159:1160–1167.6. Batty GD, Shipley MJ, Marmot M, Smith GD. Diabetes status and post-load plasma glucose concentration in relation to site-specific cancer mortality: findings from the original Whitehall study. Cancer Causes Control. 2004; 15:873–881.7. Saydah SH, Loria CM, Eberhardt MS, Brancati FL. Abnormal glucose tolerance and the risk of cancer death in the United States. Am J Epidemiol. 2003; 157:1092–1100.8. Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1997; 20:1183–1197.9. Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med. 1998; 15:539–553.10. The DECODE study group, Diabetes Epidemiology: Collaborative analysis Of Diagnostic criteria in Europe. European Diabetes Epidemiology Group. Glucose tolerance and mortality: comparison of WHO and American Diabetes Association diagnostic criteria. Lancet. 1999; 354:617–621.11. Pankow JS, Kwan DK, Duncan BB, Schmidt MI, Couper DJ, Golden S, Ballantyne CM. Cardiometabolic risk in impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Diabetes Care. 2007; 30:325–331.12. Kim NH, Pavkov ME, Looker HC, Nelson RG, Bennett PH, Hanson RL, Curtis JM, Sievers ML, Knowler WC. Plasma glucose regulation and mortality in pima Indians. Diabetes Care. 2008; 31:488–492.13. Harding JL, Soderberg S, Shaw JE, Zimmet PZ, Pauvaday V, Kowlessur S, Tuomilehto J, Alberti KG, Magliano DJ. All-cause cancer mortality over 15 years in multi-ethnic Mauritius: the impact of diabetes and intermediate forms of glucose tolerance. Int J Cancer. 2012; 131:2385–2393.14. Stengard JH, Tuomilehto J, Pekkanen J, Kivinen P, Kaarsalo E, Nissinen A, Karvonen MJ. Diabetes mellitus, impaired glucose tolerance and mortality among elderly men: the Finnish cohorts of the Seven Countries Study. Diabetologia. 1992; 35:760–765.15. Zhou XH, Qiao Q, Zethelius B, Pyorala K, Soderberg S, Pajak A, Stehouwer CD, Heine RJ, Jousilahti P, Ruotolo G, Nilsson PM, Calori G, Tuomilehto J. DECODE Study Group. Diabetes, prediabetes and cancer mortality. Diabetologia. 2010; 53:1867–1876.16. Genuth S, Alberti KG, Bennett P, Buse J, Defronzo R, Kahn R, Kitzmiller J, Knowler WC, Lebovitz H, Lernmark A, Nathan D, Palmer J, Rizza R, Saudek C, Shaw J, Steffes M, Stern M, Tuomilehto J, Zimmet P. Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Follow-up report on the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:3160–3167.17. Kanaya AM, Herrington D, Vittinghoff E, Lin F, Bittner V, Cauley JA, Hulley S, Barrett-Connor E. Impaired fasting glucose and cardiovascular outcomes in postmenopausal women with coronary artery disease. Ann Intern Med. 2005; 142:813–820.18. Kim HK, Kim CH, Kim EH, Bae SJ, Choe J, Park JY, Park SW, Yun YD, Baek SJ, Mok Y, Jee SH. Impaired fasting glucose and risk of cardiovascular disease in Korean men and women: the Korean Heart Study. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36:328–335.19. Oh JY, Lim S, Kim DJ, Kim NH, Kim DJ, Moon SD, Jang HC, Cho YM, Song KH, Ahn CW, Sung YA, Park JY, Shin C, Lee HK, Park KS. Committee of the Korean Diabetes Association on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. A report on the diagnosis of intermediate hyperglycemia in Korea: a pooled analysis of four community-based cohort studies. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008; 80:463–468.20. Park Y, Lee H, Koh CS, Min H, Yoo K, Kim Y, Shin Y. Prevalence of diabetes and IGT in Yonchon County, South Korea. Diabetes Care. 1995; 18:545–548.21. Park JY, Kim YI, Choi CS, Chung YE, Kim SW, Lee MS, Lee SI, Hong SK, Lee KU. Prevalence of diabetes, impaired glucose tolerance, and impaired fasting glucose in a rural population of Korea, according to 1997 American Diabetes Association and 1985 World Health Organization criteria. Diabetes Care. 2000; 23:707–708.22. Jo I, Ahn Y, Lee J, Shin KR, Lee HK, Shin C. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, control and risk factors of hypertension in Korea: the Ansan study. J Hypertens. 2001; 19:1523–1532.23. Ko SH, Kim SR, Kim DJ, Oh SJ, Lee HJ, Shim KH, Woo MH, Kim JY, Kim NH, Kim JT, Kim CH, Kim HJ, Jeong IK, Hong EK, Cho JH, Mok JO, Yoon KH. Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association. 2011 Clinical practice guidelines for type 2 diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:431–436.24. Yoon KH, Lee JH, Kim JW, Cho JH, Choi YH, Ko SH, Zimmet P, Son HY. Epidemic obesity and type 2 diabetes in Asia. Lancet. 2006; 368:1681–1688.25. Pollak M. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor signalling in neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008; 8:915–928.26. Ma J, Pollak MN, Giovannucci E, Chan JM, Tao Y, Hennekens CH, Stampfer MJ. Prospective study of colorectal cancer risk in men and plasma levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-binding protein-3. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999; 91:620–625.27. Bohlke K, Cramer DW, Trichopoulos D, Mantzoros CS. Insulin-like growth factor-I in relation to premenopausal ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Epidemiology. 1998; 9:570–573.28. Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun MJ. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348:1625–1638.29. van de Poll-Franse LV, Houterman S, Janssen-Heijnen ML, Dercksen MW, Coebergh JW, Haak HR. Less aggressive treatment and worse overall survival in cancer patients with diabetes: a large population based analysis. Int J Cancer. 2007; 120:1986–1992.30. Giovannucci E, Harlan DM, Archer MC, Bergenstal RM, Gapstur SM, Habel LA, Pollak M, Regensteiner JG, Yee D. Diabetes and cancer: a consensus report. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33:1674–1685.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- HbA1c for Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes in Korea
- HbA1c Variability and Micro- and Macrovascular Complications of Diabetes
- Effects of Metformin on Breast Cancer Risk and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Role of HbA1c in the Screening of Diabetes Mellitus in a Korean Rural Community
- Circulating Vitamin D Level and Risk of Sudden Cardiac Death and Cardiovascular Mortality: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies