Hanyang Med Rev.
2013 Feb;33(1):39-44. 10.7599/hmr.2013.33.1.39.
Mechanism of Allergic Asthma Pathogenesis by Protease Allergen
- Affiliations
-
- 1Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Korea. seung-hyo.lee@kaist.ac.kr
- KMID: 2168219
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7599/hmr.2013.33.1.39
Abstract
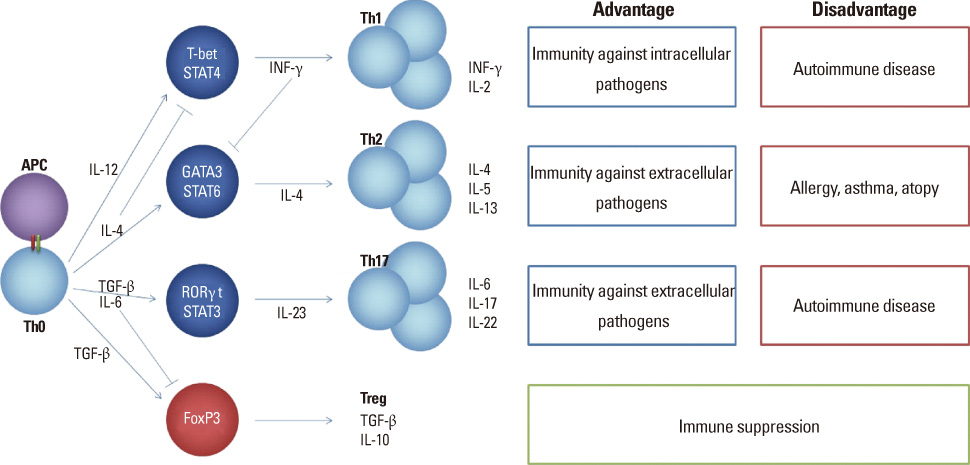
- Asthma is a complex immune mediated chronic inflammatory lung disease characterized by chronic inflammation of the airways, airway hyper-responsiveness and airway obstruction, and the prevalence of this disease has increased in recent years. It is well known that many features of allergic asthma are consequences of Th2 cell dominated immune responses against allergens, thus allergen specific Th2 cells play a critical role in the pathogenesis. In this review, we will discuss the properties of common indoor and outdoor allergens including house dust mite, fungus, pollen and cockroach, the activation and differentiation of naive CD4 T cells by protease allergens, how specific allergens modify host's immune system to mediate immune evasion, and regulation of homing receptor expression and trafficking of allergen specific Th2 cells. Lastly, we will also overview the general course of pathogenesis of allergic asthma and discuss prospects of development of novel immuno-therapies to asthma.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Busse WW, Lemanske RF. Asthma. N Engl J Med. 2001. 344:350–362.
Article2. Wills-Karp M, Nathan A, Page K, Karp CL. New insights into innate immune mechanisms underlying allergenicity. Mucosal Immunol. 2010. 3:104–110.
Article3. Roche N, Chinet TC, Belouchi NE, Julié C, Huchon GJ. Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus and bioelectric properties of airway epithelium: role of cysteine proteases. Eur Respir J. 2000. 16:309–315.
Article4. Kawamoto S, Mizuguchi Y, Morimoto K, Aki T, Shigeta S, Yasueda H, et al. Cloning and expression of Der f 6, a serine protease allergen from the house dust mite, Dermatophagoides farinae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999. 1454:201–207.
Article5. John RJ, Rusznak C, Ramjee M, Lamont AG, Abrahamson M, Hewitt EL. Functional effects of the inhibition of the cysteine protease activity of the major house dust mite allergen Der p 1 by a novel peptide-based inhibitor. Clin Exp Allergy. 2000. 30:784–793.
Article6. Takahashi K, Takai T, Yasuhara T, Yuuki T, Ohtake Y, Yokota T, et al. Production of enzymatically and immunologically active Der f 1 in Escherichia coli. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2000. 122:108–114.
Article7. Stewart GA. Dust mite allergens. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 1995. 13:135–150.
Article8. Horner WE, Helbling A, Salvaggio JE, Lehrer SB. Fungal allergens. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1995. 8:161–179.
Article9. Kheradmand F, Kiss A, Xu J, Lee SH, Kolattukudy PE, Corry DB. A protease-activated pathway underlying Th cell type 2 activation and allergic lung disease. J Immunol. 2002. 169:5904–5911.
Article10. Porter P, Polikepahad S, Qian Y, Knight JM, Lu W, Tai WM, et al. Respiratory tract allergic disease and atopy: experimental evidence for a fungal infectious etiology. Med Mycol. 2011. 49:Suppl 1. S158–S163.
Article11. Singh M, Lee SH, Porter P, Xu C, Ohno A, Atmar RL, et al. Human rhinovirus proteinase 2A induces TH1 and TH2 immunity in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. 125:1369–1378.e2.
Article12. Schnare M, Barton GM, Holt AC, Takeda K, Akira S, Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptors control activation of adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol. 2001. 2:947–950.
Article13. Josefowicz SZ, Lu LF, Rudensky AY. Regulatory T cells: mechanisms of differentiation and function. Annu Rev Immunol. 2012. 30:531–564.
Article14. Dong C. TH17 cells in development: an updated view of their molecular identity and genetic programming. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008. 8:337–348.
Article15. Szabo SJ, Kim ST, Costa GL, Zhang X, Fathman CG, Glimcher LH. A novel transcription factor, T-bet, directs Th1 lineage commitment. Cell. 2000. 100:655–669.
Article16. Ouyang W, Löhning M, Gao Z, Assenmacher M, Ranganath S, Radbruch A, et al. Stat6-independent GATA-3 autoactivation directs IL-4-independent Th2 development and commitment. Immunity. 2000. 12:27–37.
Article17. Ivanov II, McKenzie BS, Zhou L, Tadokoro CE, Lepelley A, Lafaille JJ, et al. The orphan nuclear receptor RORgammat directs the differentiation program of proinflammatory IL-17+ T helper cells. Cell. 2006. 126:1121–1133.
Article18. Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S. Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science. 2003. 299:1057–1061.
Article19. Bluestone JA, Mackay CR, O'Shea JJ, Stockinger B. The functional plasticity of T cell subsets. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009. 9:811–816.
Article20. Lamhamedi-Cherradi SE, Martin RE, Ito T, Kheradmand F, Corry DB, Liu YJ, et al. Fungal proteases induce Th2 polarization through limited dendritic cell maturation and reduced production of IL-12. J Immunol. 2008. 180:6000–6009.
Article21. Kobayashi T, Iijima K, Radhakrishnan S, Mehta V, Vassallo R, Lawrence CB, et al. Asthma-related environmental fungus, Alternaria, activates dendritic cells and produces potent Th2 adjuvant activity. J Immunol. 2009. 182:2502–2510.
Article22. Kamijo S, Takai T, Kuhara T, Tokura T, Ushio H, Ota M, et al. Cupressaceae pollen grains modulate dendritic cell response and exhibit IgE-inducing adjuvant activity in vivo. J Immunol. 2009. 183:6087–6094.
Article23. Porter PC, Yang T, Luong A, Delclos GL, Abramson SL, Kheradmand F, et al. Proteinases as molecular adjuvants in allergic airway disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. 1810:1059–1065.
Article24. Syrbe U, Siveke J, Hamann A. Th1/Th2 subsets: distinct differences in homing and chemokine receptor expression? Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1999. 21:263–285.
Article25. Acosta-Rodriguez EV, Rivino L, Geginat J, Jarrossay D, Gattorno M, Lanzavecchia A, et al. Surface phenotype and antigenic specificity of human interleukin 17-producing T helper memory cells. Nat Immunol. 2007. 8:639–646.
Article26. Austrup F, Vestweber D, Borges E, Löhning M, Bräuer R, Herz U, et al. P- and E-selectin mediate recruitment of T-helper-1 but not T-helper-2 cells into inflammed tissues. Nature. 1997. 385:81–83.
Article27. Pribila JT, Quale AC, Mueller KL, Shimizu Y. Integrins and T cell-mediated immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004. 22:157–180.
Article28. Lee SH, Prince JE, Rais M, Kheradmand F, Shardonofsky F, Lu H, et al. Differential requirement for CD18 in T-helper effector homing. Nat Med. 2003. 9:1281–1286.
Article29. Lee SH, Prince JE, Rais M, Kheradmand F, Ballantyne CM, Weitz-Schmidt G, et al. Developmental control of integrin expression regulates Th2 effector homing. J Immunol. 2008. 180:4656–4667.
Article30. Sasaki K, Tsuji T, Jinushi T, Matsuzaki J, Sato T, Chamoto K, et al. Differential regulation of VLA-2 expression on Th1 and Th2 cells: a novel marker for the classification of Th subsets. Int Immunol. 2003. 15:701–710.
Article31. Yoshizaki A, Yanaba K, Iwata Y, Komura K, Ogawa A, Akiyama Y, et al. Cell adhesion molecules regulate fibrotic process via Th1/Th2/Th17 cell balance in a bleomycin-induced scleroderma model. J Immunol. 2010. 185:2502–2515.
Article