A Case of Wheat-Dependent Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Seoul, Korea. dermlee@yahoo.co.kr
- KMID: 2156519
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2009.21.4.447
Abstract
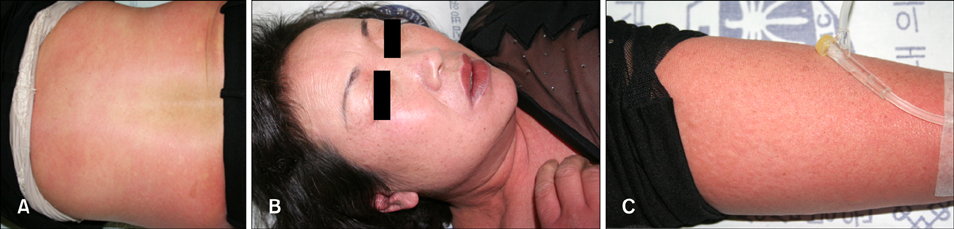
- Foods are recognized as a common cause of urticaria; however, the role of food is considered to be more important in acute not chronic urticaria. Wheat is a basic ingredient found in many common foods. Food allergy to wheat is primarily described in children in the form of atopic dermatitis. It is rare in adults; where it is mainly reported in exercise-induced anaphylaxis. We report a case of wheat dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis that occurred in a 54-year-old Korean woman.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Overview of anaphylaxis in Korea: diagnosis and management
Gwang Cheon Jang, Yoon-Seok Chang, Sun Hee Choi, Woo-Jung Song, Soo-Young Lee, Hae-Sim Park, Hye-Ryun Kang, Yeong-Min Ye, Hyun-Jung Jin, Mi Yong Shin, Soo-Jin Lee, Hye One Kim, Jihyun Kim, Jae-Woo Jung, Hee-Bom Moon, Youngmin Ahn
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013;1(3):181-196. doi: 10.4168/aard.2013.1.3.181.Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in Korean children: a single-center retrospective case study
Eun Lee, Min-Ju Kim, Song-I Yang, Jinho Yu, Soo-Jong Hong
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015;3(3):194-199. doi: 10.4168/aard.2015.3.3.194.Wheat-Induced Anaphylaxis in Korean Adults: A Report of 6 Cases
Seung-Eun Lee, Suh-Young Lee, Eun-Jung Jo, Mi-Young Kim, Sae-Hoon Kim, Yoon-Seok Chang
Clin Nutr Res. 2013;2(1):76-79. doi: 10.7762/cnr.2013.2.1.76.Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in Korea: a multicenter retrospective case study
Jae Hyoung Im, Hea Yoon Kwon, Young-Min Ye, Hae-Sim Park, Tae-Bum Kim, Gil-Soon Choi, Joo-Hee Kim, Gwang Cheon Jang, Mi Kyung Kim, Gyu-Young Hur, Young-Il Koh, Seong-Wook Sohn, Cheol-Woo Kim
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013;1(3):203-210. doi: 10.4168/aard.2013.1.3.203.
Reference
-
1. Moneret-Vautrin DA, Kanny G, Guerin L, Flabbee J, Lemerdy P. The multifood allergy syndrome. Allerg Immunol (Paris). 2000. 32:12–15.2. Palosuo K. Update on wheat hypersensitivity. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003. 3:205–209.
Article3. Jarvinen KM, Turpeinen M, Suomalainen H. Concurrent cereal allergy in children with cow's milk allergy manifested with atopic dermatitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2003. 33:1060–1066.
Article4. Sehgal VN, Rege VL. An interrogative study of 158 urticaria patients. Ann Allergy. 1973. 31:279–283.5. Harris A, Twarog FJ, Geha RS. Chronic urticaria in childhood: natural course and etiology. Ann Allergy. 1983. 51:161–165.6. Kanny G, Chenuel B, Moneret-Vautrin DA. Chronic urticaria to wheat. Allergy. 2001. 56:356–357.
Article7. Bock SA, Sampson HA, Atkins FM, Zeiger RS, Lehrer S, Sachs M, et al. Double-blind, placebo-controlled food challenge (DBPCFC) as an office procedure: a manual. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1988. 82:986–997.
Article8. Metcalfe DD. Food allergens. Clin Rev Allergy. 1985. 3:331–349.
Article9. Anderson JA. The establishment of common language concerning adverse reactions to foods and food additives. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986. 78:140–144.
Article10. Metcalfe DD, Sampson HA, Simon RA. Food allergy: adverse reactions to foods and food additives. 1997. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Blackwell Science;211–219.11. Du Toit G. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in childhood. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2007. 18:455–463.
Article12. Gall H, Steinert M, Peter RU. Exercise-induced anaphylaxis to wheat flour. Allergy. 2000. 55:1096–1097.
Article13. Romano A, Di Fonso M, Giuffreda F, Papa G, Artesani MC, Viola M, et al. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis: clinical and laboratory findings in 54 subjects. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2001. 125:264–272.
Article14. Battais F, Mothes T, Moneret-Vautrin DA, Pineau F, Kanny G, Popineau Y, et al. Identification of IgE-binding epitopes on gliadins for patients with food allergy to wheat. Allergy. 2005. 60:815–821.
Article15. Chong SU, Worm M, Zuberbier T. Role of adverse reactions to food in urticaria and exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2002. 129:19–26.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Wheat-dependent, Exercise-induced Anaphylaxis: A Successful Case of Prevention with Ketotifen
- Wheat - Dependent Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis Occurred With a Delayed Onset of 10 to 24 hours After Wheat Ingestion: A Case Report
- A case of food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis developed only in winter
- Three Cases of Food-dependent Exercise-induced Anaphylaxis
- A case of wheat-induced anaphylaxis in an adult