J Korean Soc Radiol.
2016 Jan;74(1):22-25. 10.3348/jksr.2016.74.1.22.
Cholesterol Granuloma of the Breast Incidentally Detected on Dynamic Abdominal CT: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea. grace@schmc.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2150459
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.74.1.22
Abstract
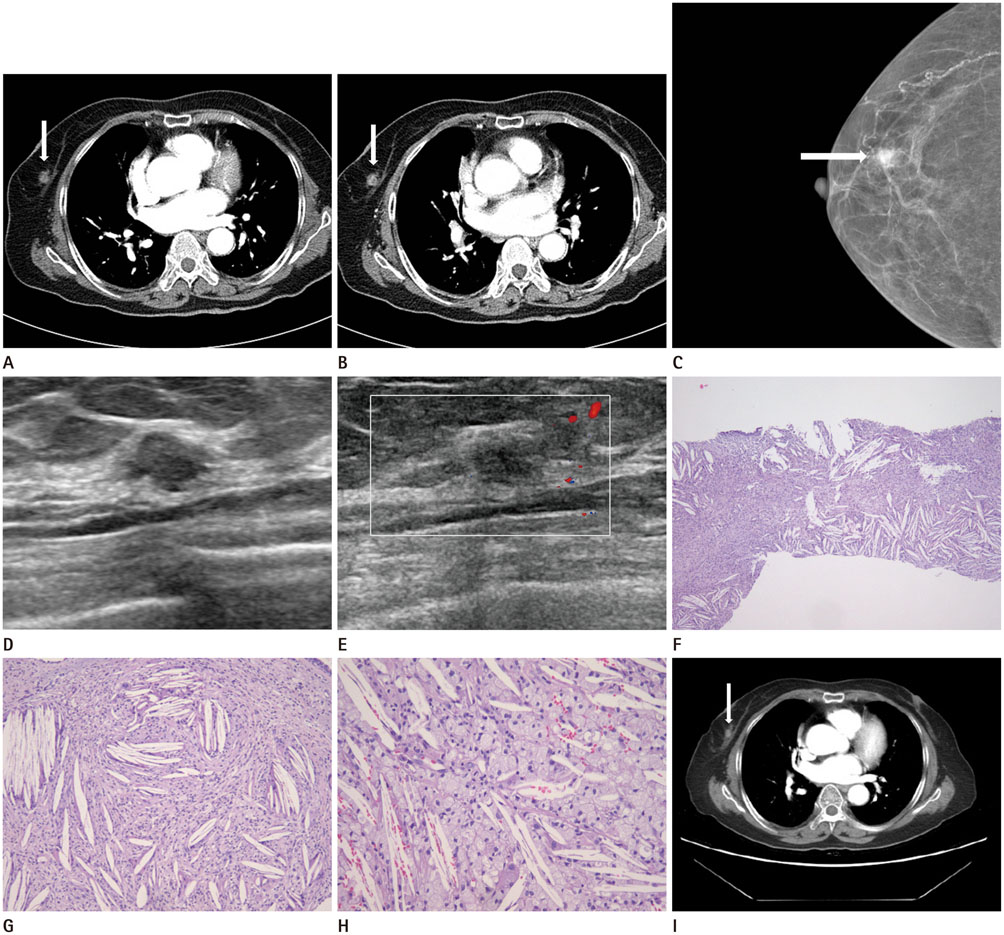
- A breast cholesterol granuloma is an uncommon nodular breast lesion. We incidentally detected a persistently enhancing breast mass on the dynamic abdominal computed tomography (CT) of a 78-year-old woman. The mass decreased in diameter over 50 days following a core needle biopsy. This report is the first to describe the dynamic-enhanced CT features of a breast cholesterol granuloma.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wilhelmus JL, Schrodt GR, Mahaffey LM. Cholesterol granulomas of the breast. A lesion which clinically mimics carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982; 77:592–597.2. Reynolds HE, Cramer HM. Cholesterol granuloma of the breast: a mimic of carcinoma. Radiology. 1994; 191:249–250.3. Osada T, Kitayama J, Nagawa H. Cholesterol granuloma of the breast mimicking carcinoma: report of a case. Surg Today. 2002; 32:981–984.4. Ahn HS, Kim SM, Yun BL, Kim MS, Jang M, Park SY, et al. The unusual ultrasound features of a breast cholesterol granuloma manifesting as an intracystic mass: case report and literature review. Korean J Radiol. 2013; 14:179–182.5. Bezić J, Piljić-Burazer M. Breast cholesterol granuloma: a report of two cases with discussion on potential pathogenesis. Pathologica. 2013; 105:349–352.6. Ishizaki M, Ohsumi S, Takashima S, Mandai K. Two cases of cholesterol granuloma of the breast. Breast Cancer. 2001; 8:158–161.7. Fujii T, Yajima R, Morita H, Yamaguchi S, Tsutsumi S, Asao T, et al. Cholesterol granuloma of the breast suspected as breast carcinoma. Int J Case Rep Images. 2013; 4:723–726.8. Döring L, Wedemeier G. [Cholesterol granuloma of the female breast]. Chirurg. 1974; 45:520–521.9. Fujita T, Doihara H, Takabatake D, Takahashi H, Yoshitomi S, Ishibe Y, et al. Multidetector row computed tomography for diagnosing intraductal extension of breast carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2005; 91:10–16.10. Sardanelli F, Calabrese M, Zandrino F, Melani E, Parodi R, Imperiale A, et al. Dynamic helical CT of breast tumors. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1998; 22:398–407.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cholesterol Granuloma of the Breast: A Case Report
- Incidentally detected laryngeal granuloma during orotracheal intubation under direct laryngoscope: A case report
- Cholesterol Granuloma Presenting as Retroperitoneal Mass: A case report
- A Case of Cholesterol Granuloma in Pancreas
- The Unusual Ultrasound Features of a Breast Cholesterol Granuloma Manifesting as an Intracystic Mass: Case Report and Literature Review