Yonsei Med J.
2015 Mar;56(2):410-417. 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.2.410.
Factors Associated with Ischemic Stroke on Therapeutic Anticoagulation in Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jhheo@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Neurology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Severance Institute for Vascular and Metabolic Research, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurology, National Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Neurology, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University College of Medicine and Biomedical Research Institute, Busan, Korea.
- 6Department of Neurology, National Health Insurance Corporation Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 7Department of Neurology, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- 8Department of Neurology, Samsung Changwon Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Changwon, Korea.
- 9Department of Neurology, Chosun University School of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea.
- 10Department of Neurology, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea.
- 11Department of Neurology, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 12Department of Neurology, Changwon Fatima Hospital, Changwon, Korea.
- 13Department of Neurology, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Korea.
- 14Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, Konkuk University, Chungju, Korea.
- 15Department of Biostatistics, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 16Department of Preventive Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 17Department of Cardiology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2070018
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.2.410
Abstract
- PURPOSE
In this study, we investigated the stroke mechanism and the factors associated with ischemic stroke in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF) who were on optimal oral anticoagulation with warfarin.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
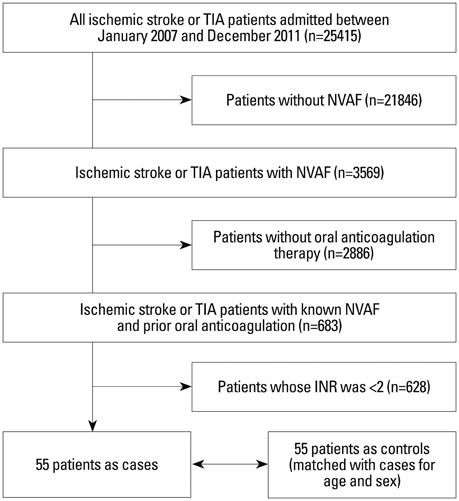
This was a multicenter case-control study. The cases were consecutive patients with NVAF who developed cerebral infarction or transient ischemic attack (TIA) while on warfarin therapy with an international normalized ratio (INR) > or =2 between January 2007 and December 2011. The controls were patients with NVAF without ischemic stroke who were on warfarin therapy for more than 1 year with a mean INR > or =2 during the same time period. We also determined etiologic mechanisms of stroke in cases.
RESULTS
Among 3569 consecutive patients with cerebral infarction or TIA who had NVAF, 55 (1.5%) patients had INR > or =2 at admission. The most common stroke mechanism was cardioembolism (76.0%). Multivariate analysis demonstrated that smoking and history of previous ischemic stroke were independently associated with cases. High CHADS2 score (> or =3) or CHA2DS2-VASc score (> or =5), in particular, with previous ischemic stroke along with > or =1 point of other components of CHADS2 score or > or =3 points of other components of CHA2DS2-VASc score was a significant predictor for development of ischemic stroke.
CONCLUSION
NVAF patients with high CHADS2/CHA2DS2-VASc scores and a previous ischemic stroke or smoking history are at high risk of stroke despite optimal warfarin treatment. Some other measures to reduce the risk of stroke would be necessary in those specific groups of patients.
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Anticoagulants/adverse effects/*therapeutic use
Atrial Fibrillation/*complications
Cardiovascular Diseases
Case-Control Studies
Cerebral Infarction/complications
Female
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Multivariate Analysis
Risk Factors
Stroke/etiology/*prevention & control
Warfarin/adverse effects/*therapeutic use
Anticoagulants
Warfarin
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Early Experience of Novel Oral Anticoagulants in Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation: Efficacy and Safety Comparison to Warfarin
Dong Geum Shin, Tae-Hoon Kim, Jae-Sun Uhm, Joung-Youn Kim, Boyoung Joung, Moon-Hyoung Lee, Hui-Nam Pak
Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(2):342-349. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.2.342.
Reference
-
1. Cardiogenic brain embolism. Cerebral Embolism Task Force. Arch Neurol. 1986; 43:71–84.2. Han SW, Nam HS, Kim SH, Lee JY, Lee KY, Heo JH. Frequency and significance of cardiac sources of embolism in the TOAST classification. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2007; 24:463–468.
Article3. Wann LS, Curtis AB, January CT, Ellenbogen KA, Lowe JE, Estes NA 3rd, et al. 2011 ACCF/AHA/HRS focused update on the management of patients with atrial fibrillation (Updating the 2006 Guideline): a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011; 57:223–242.4. Furie KL, Kasner SE, Adams RJ, Albers GW, Bush RL, Fagan SC, et al. Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke or transient ischemic attack: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/american stroke association. Stroke. 2011; 42:227–276.
Article5. European Stroke Organisation (ESO) Executive Committee. ESO Writing Committee. Guidelines for management of ischaemic stroke and transient ischaemic attack 2008. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2008; 25:457–507.6. Paciaroni M, Agnelli G, Ageno W, Caso V, Corea F, Lanari A, et al. Risk factors for cerebral ischemic events in patients with atrial fibrillation on warfarin for stroke prevention. Atherosclerosis. 2010; 212:564–566.
Article7. Gage BF, Waterman AD, Shannon W, Boechler M, Rich MW, Radford MJ. Validation of clinical classification schemes for predicting stroke: results from the National Registry of Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA. 2001; 285:2864–2870.
Article8. Lip GY, Nieuwlaat R, Pisters R, Lane DA, Crijns HJ. Refining clinical risk stratification for predicting stroke and thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation using a novel risk factor-based approach: the euro heart survey on atrial fibrillation. Chest. 2010; 137:263–272.
Article9. Kim YD, Cha MJ, Kim J, Lee DH, Lee HS, Nam CM, et al. Increases in cerebral atherosclerosis according to CHADS2 scores in patients with stroke with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Stroke. 2011; 42:930–934.
Article10. Melkas S, Putaala J, Oksala NK, Pohjasvaara T, Oksala A, Kaste M, et al. Small-vessel disease relates to poor poststroke survival in a 12-year follow-up. Neurology. 2011; 76:734–739.
Article11. Rosendaal FR, Cannegieter SC, van der Meer FJ, Briët E. A method to determine the optimal intensity of oral anticoagulant therapy. Thromb Haemost. 1993; 69:236–239.
Article12. Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, et al. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke. 1993; 24:35–41.
Article13. Agarwal S, Hachamovitch R, Menon V. Current trial-associated outcomes with warfarin in prevention of stroke in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med. 2012; 172:623–631.
Article14. Nakamura A, Ago T, Kamouchi M, Hata J, Matsuo R, Kuroda J, et al. Intensity of anticoagulation and clinical outcomes in acute cardioembolic stroke: the Fukuoka Stroke Registry. Stroke. 2013; 44:3239–3242.
Article15. Kanter MC, Tegeler CH, Pearce LA, Weinberger J, Feinberg WM, Anderson DC, et al. Carotid stenosis in patients with atrial fibrillation. Prevalence, risk factors, and relationship to stroke in the Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Study. Arch Intern Med. 1994; 154:1372–1377.
Article16. Evans A, Perez I, Yu G, Kalra L. Should stroke subtype influence anticoagulation decisions to prevent recurrence in stroke patients with atrial fibrillation? Stroke. 2001; 32:2828–2832.
Article17. Fuster V, Rydén LE, Cannom DS, Crijns HJ, Curtis AB, Ellenbogen KA, et al. 2011 ACCF/AHA/HRS focused updates incorporated into the ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 guidelines for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2011; 123:e269–e367.18. Ntaios G, Papavasileiou V, Diener HC, Makaritsis K, Michel P. Nonvitamin-K-antagonist oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation and previous stroke or transient ischemic attack: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Stroke. 2012; 43:3298–3304.
Article19. Albertsen IE, Rasmussen LH, Overvad TF, Graungaard T, Larsen TB, Lip GY. Risk of stroke or systemic embolism in atrial fibrillation patients treated with warfarin: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2013; 44:1329–1336.
Article20. Chiang CE, Wang KL, Lip GY. Stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation: an Asian perspective. Thromb Haemost. 2014; 111:789–797.
Article21. Reddy VY, Doshi SK, Sievert H, Buchbinder M, Neuzil P, Huber K, et al. Percutaneous left atrial appendage closure for stroke prophylaxis in patients with atrial fibrillation: 2.3-Year Follow-up of the PROTECT AF (Watchman Left Atrial Appendage System for Embolic Protection in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation) Trial. Circulation. 2013; 127:720–729.
Article22. Lip GY, Frison L, Halperin JL, Lane DA. Identifying patients at high risk for stroke despite anticoagulation: a comparison of contemporary stroke risk stratification schemes in an anticoagulated atrial fibrillation cohort. Stroke. 2010; 41:2731–2738.
Article23. Novello P, Ajmar G, Bianchini D, Bo GP, Cammarata S, Firpo MP, et al. Ischemic stroke and atrial fibrillation. A clinical study. Ital J Neurol Sci. 1993; 14:571–576.
Article24. Risk factors for stroke and efficacy of antithrombotic therapy in atrial fibrillation. Analysis of pooled data from five randomized controlled trials. Arch Intern Med. 1994; 154:1449–1457.25. Watson T, Shantsila E, Lip GY. Mechanisms of thrombogenesis in atrial fibrillation: Virchow's triad revisited. Lancet. 2009; 373:155–166.
Article26. Johnson CM, Mureebe L, Silver D. Hypercoagulable states: a review. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2005; 39:123–133.
Article27. Tracy RP, Psaty BM, Macy E, Bovill EG, Cushman M, Cornell ES, et al. Lifetime smoking exposure affects the association of C-reactive protein with cardiovascular disease risk factors and subclinical disease in healthy elderly subjects. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1997; 17:2167–2176.
Article28. Oh SM, Stefani KM, Kim HC. Development and application of chronic disease risk prediction models. Yonsei Med J. 2014; 55:853–860.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of sufficient anticoagulation on ischemic stroke outcomes in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation
- The Mechanism of and Preventive Therapy for Stroke in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation
- Application of New Oral Anticoagulants: Prevention of Stroke in Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
- Hemoptysis in Quadriplegia with Atrial Fibrillation Who Was Taking Edoxaban: a Case Report
- How and When to Screen for Atrial Fibrillation after Stroke: Insights from Insertable Cardiac Monitoring Devices