Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2012 Aug;16(4):231-236. 10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.4.231.
Effects of Single Treatment of Anti-Dementia Drugs on Sleep-Wake Patterns in Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 700-422, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 700-422, Korea.
- 3Brain Science and Engineering Institute, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 700-422, Korea.
- 4Department of Pharmacology, School of Medicine, Keimyung University, Daegu 700-712, Korea.
- 5Department of Pharmacology, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 700-412, Korea.
- KMID: 2011156
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.4.231
Abstract
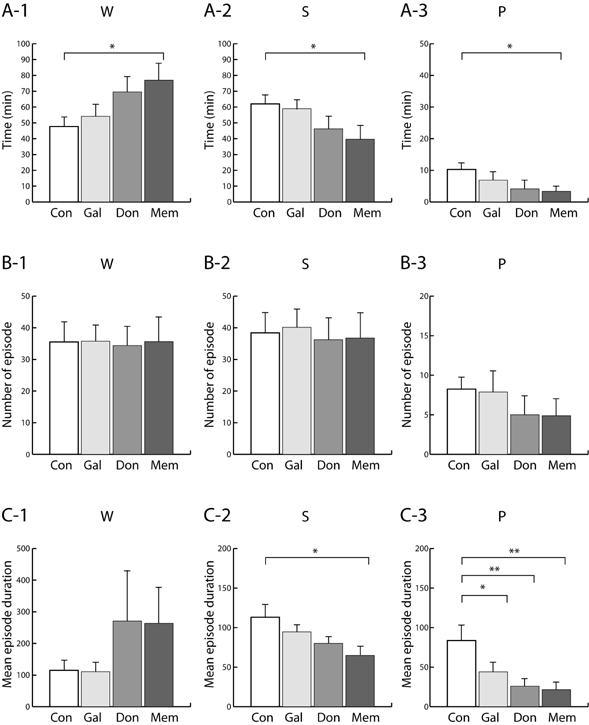
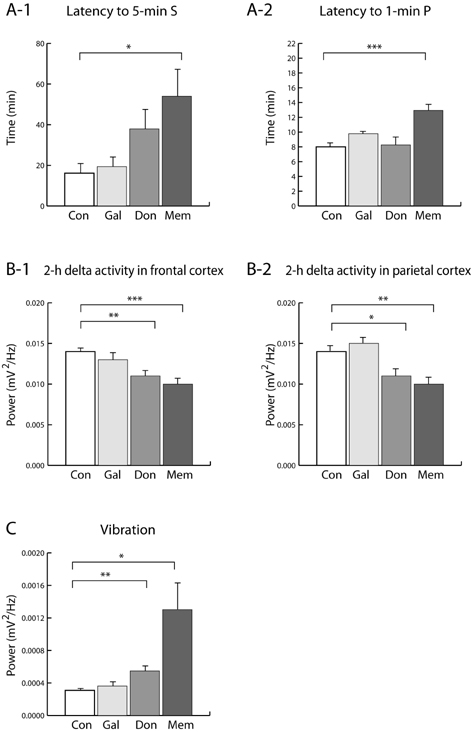
- We studied the effects of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, donepezil and galantamine, and an N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor blocker, memantine, on sleep-wake architecture in rats. Screw electrodes were chronically implanted into the frontal and parietal cortex for the electroencephalography (EEG). EEG was recorded with a bio-potential amplifier for 8 h from 09:30 to 17:30. Vibration was recorded to monitor animal activity with a vibration measuring device. Sleep-wake states such as wake (W), slow-wave sleep (S) and paradoxical or rapid eye movement sleep (P), were scored every 10 sec by an experimenter. We measured mean episode duration and number of episode to determine which factor sleep disturbance was attributed to. Donepezil and memantine showed a significant increase in total W duration and decreases in total S and P duration and delta activity. Memantine showed increases in sleep latency and motor activity. Changes of S and P duration in memantine were attributed from changes of mean episode duration. Galantamine had little effect on sleep architecture. From these results, it is showed that galantamine may be an anti-dementia drug that does not cause sleep disturbances and memantine may be a drug that causes severe sleep disturbance.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dauvilliers Y. Insomnia in patients with neurodegenerative conditions. Sleep Med. 2007. 8:Suppl 4. S27–S34.2. Yesavage JA, Friedman L, Ancoli-israel S, Bliwise D, Singer C, Vitiello MV, Monjan AA, Lebowitz B. Development of diagnostic criteria for defining sleep disturbance in Alzheimer's disease. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 2003. 16:131–139.3. Hope T, Keene J, Gedling K, Fairburn CG, Jacoby R. Predictors of institutionalization for people with dementia living at home with a carer. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 1998. 13:682–690.4. Thompson S, Lanctôt KL, Herrmann N. The benefits and risks associated with cholinesterase inhibitor therapy in Alzheimer's disease. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2004. 3:425–440.5. Wilkinson DG, Francis PT, Schwam E, Payne-Parrish J. Cholinesterase inhibitors used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: the relationship between pharmacological effects and clinical efficacy. Drugs Aging. 2004. 21:453–478.6. Rogers SL, Doody RS, Mohs RC, Friedhoff LT. Donepezil Study Group. Donepezil improves cognition and global function in Alzheimer disease: a 15-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Arch Intern Med. 1998. 158:1021–1031.7. Stahl SM, Markowitz JS, Papadopoulos G, Sadik K. Examination of nighttime sleep-related problems during double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of galantamine in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Curr Med Res Opin. 2004. 20:517–524.8. Ancoli-Israel S, Amatniek J, Ascher S, Sadik K, Ramaswamy K. Effects of galantamine versus donepezil on sleep in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer disease and their caregivers: a double-blind, head-to-head, randomized pilot study. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2005. 19:240–245.9. Schredl M, Weber B, Leins ML, Heuser I. Donepezil-induced REM sleep augmentation enhances memory performance in elderly, healthy persons. Exp Gerontol. 2001. 36:353–361.10. Guay DR. Drug forecast: memantine, prototype of a new approach to treatment of dementia. Consult Pharm. 2003. 18:625–634.11. Ishida T, Kamei C. Characteristic effects of anti-dementia drugs on rat sleep patterns. J Pharmacol Sci. 2009. 109:449–455.12. Ishida T, Obara Y, Kamei C. Studies on wakefulness-promoting effect of memantine in rats. Behav Brain Res. 2010. 206:274–278.13. Jung JY. Characterization of vibration signal patterns for rat behaviors using specially designed vibration sensors. 2010. Kyungpook National University Graduate School;MS Thesis.14. Kwon DH, Won SH, Kim KM, Chang SM, Kim SH, Lee MG. Effect of caffeine on sleep and EEG spectra in rats. J Korean Soc Biol Ther Psychiatry. 2006. 12:252–267.15. Lee MG, Kim M, Roh M, Jang IS, Won SH. Differences between physostigmine- and yohimbine-induced states are visualized in canonical space constructed from EEG during natural sleep-wake cycle in rats. Exp Neurobiol. 2011. 20:54–65.16. Farlow MR, Cummings JL. Effective pharmacologic management of Alzheimer's disease. Am J Med. 2007. 120:388–397.17. Blesa R. Galantamine: therapeutic effects beyond cognition. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2000. 11:Suppl 1. 28–34.18. Geerts H. Indicators of neuroprotection with galantamine. Brain Res Bull. 2005. 64:519–524.19. Hanania T, Zahniser NR. Locomotor activity induced by noncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonists versus dopamine transporter inhibitors: opposite strain differences in inbred long-sleep and short-sleep mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2002. 26:431–440.