J Korean Med Sci.
2011 Jun;26(6):785-790. 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.6.785.
Efficacy of Levofloxacin and Rifaximin based Quadruple Therapy in Helicobacter pylori Associated Gastroduodenal Disease: A Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, St. Vincent Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon, Korea. jwchulkr@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1785965
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2011.26.6.785
Abstract
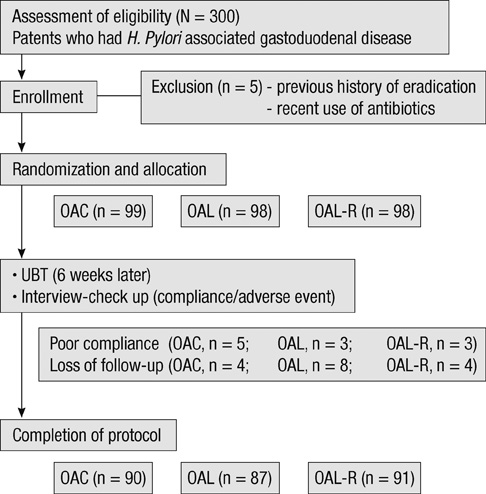
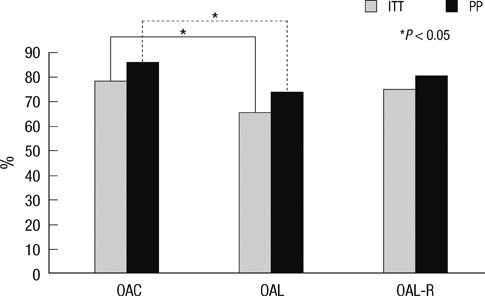
- The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of levofloxacin and rifaximin based quadruple regimen as first-line treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection. A prospectively randomized, double-blinded, parallel group, comparative study was performed. Three hundred consecutive H. pylori positive patients were randomized to receive: omeprazole, amoxicillin, clarithromycin (OAC); omeprazole, amoxicillin, levofloxacin (OAL); and omeprazole, amoxicillin, levofloxacin, rifaximin (OAL-R). The eradication rates in the intention to treat (ITT) and per protocol (PP) analyses were: OAC, 77.8% and 85.6%; OAL, 65.3% and 73.6%; and OAL-R, 74.5% and 80.2%. The eradication rate achieved with OAC was higher than with OAL on the ITT (P = 0.05) and PP analysis (P = 0.04). OAL-R regimen was not inferior to OAC. The frequency of moderate to severe adverse effects was significantly higher in OAC treatment group. Especially, diarrhea was most common complaint, and there was a significantly low rate of moderate to severe diarrhea with the rifaximin containing regimen. In conclusion, the levofloxacin and rifaximin based regimen comes up to the standard triple therapy, but has a limited efficacy in a Korean cohort. The rifaximin containing regimen has a very high safety profile for H. pylori eradication therapy.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Amoxicillin/administration & dosage
Anti-Bacterial Agents/*administration & dosage
Clarithromycin/administration & dosage
Diarrhea/chemically induced
Double-Blind Method
Drug Therapy, Combination
Female
Helicobacter Infections/complications/*drug therapy
*Helicobacter pylori
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Ofloxacin/*administration & dosage
Omeprazole/administration & dosage
Peptic Ulcer/complications/*drug therapy
Prospective Studies
Rifamycins/*administration & dosage
Figure
Reference
-
1. Graham DY, Lew GM, Klein PD, Evans DG, Evans DJ Jr, Saeed ZA, Malaty HM. Effect of treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection on the long-term recurrence of gastric or duodenal ulcer. A randomized, coltrolled study. Ann Intern Med. 1992. 116:705–708.2. Lind T, Mégraud F, Unge P, Bayerdörffer E, O'morain C, Spiller R, Veldhuyzen Van Zanten S, Bardhan KD, Hellblom M, Wrangstadh M, Zeijlon L, Cederberg C. The MACH2 study: role of omeprazole in eradication of Helicobacter pylori with 1-week triple therapies. Gastroenterology. 1999. 116:248–253.3. Bochenek WJ, Peters S, Fraga PD, Wang W, Mack ME, Osato MS, El-Zimaity HM, Davis KD, Graham DY. Helicobacter pylori Pantoprazole Eradication (HELPPE) Study Group. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori by 7-day triple-therapy regimens combining pantoprazole with clarithromycin, metronidazole, or amoxicillin in patients with peptic ulcer disease: results of two double-blind, randomized studies. Helicobacter. 2003. 8:626–642.4. Perri F, Villani MR, Festa V, Quitadamo M, Andriulli A. Predictors of failure of Helicobacter pylori eradication with the standard 'Maastricht triple therapy'. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2001. 15:1023–1029.5. Queiroz DM, Dani R, Silva LD, Santos A, Moreira LS, Rocha GA, Corrêa PR, Reis LF, Nogueira AM, Alvares Cabral MM, Esteves AM, Tanure J. Factors associated with treatment failure of Helicobacter pylori infection in a developing country. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2002. 35:315–320.6. Houben MH, van de Beek D, Hensen EF, de Craen AJ, Rauws EA, Tytgat GN. A systematic review of Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy-the impact of antimicrobial resistance on eradication rates. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1999. 13:1047–1055.7. van der Wouden EJ, Thijs JC, van Zwet AA, Sluiter WJ, Kleibeuker JH. The influence of in vitro nitroimidazole resistance on the efficacy of nitroimidazole-containing anti-Helicobacter pylori regimens: a meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999. 94:1751–1759.8. Huang DB, DuPont HL. Rifaximin - a novel antimicrobial for enteric infections. J Infect. 2005. 50:97–106.9. Quesada M, Sanfeliu I, Junquera F, Segura F, Calvet X. Evaluation of Helicobacter pylori susceptibility to rifaximin. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004. 27:393–396.10. Gasbarrini A, Lauritano EC, Nista EC, Candelli M, Gabrielli M, Santoro M, Zocco MA, Cazzato A, Finizio R, Ojetti V, Cammarota G, Gasbarrini G. Rifaximin-based regimens for eradication of Helicobacter pylori: a pilot study. Dig Dis. 2006. 24:195–200.11. Tanaka M, Isogai E, Isogai H, Hayashi S, Hirose K, Kimura K, Sugiyama T, Sato K. Synergic effect of quinolone antibacterial agents and proton pump inhibitors on Helicobacter pylori. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2002. 49:1039–1040.12. Assem M, El Azab G, Rasheed MA, Abdelfatah M, Shastery M. Efficacy and safety of levofloxacin, clarithromycin and esomeprazol as first line triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication in Middle East. Prospective, randomized, blind, comparative, multicenter study. Eur J Intern Med. 2010. 21:310–314.13. Lee JH, Hong SP, Kwon CI, Phyun LH, Lee BS, Song HU, Ko KH, Hwang SG, Park PW, Rim KS, Kim S. The efficacy of levofloxacin based triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2006. 48:19–24.14. Malfertheiner P, Mégraud F, O'Morain C, Bell D, Bianchi Porro G, Deltenre M, Forman D, Gasbarrini G, Jaup B, Misiewicz JJ, Pajares J, Quina M, Rauws E. The European Helicobacter Pylori Study Group (EHPSG). Current European concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection - the Maastricht Consensus Report. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1997. 9:1–2.15. Malfertheiner P, Mégraud F, O'Morain C, Hungin AP, Jones R, Axon A, Graham DY, Tytgat G. European Helicobacter Pylori Study Group (EHPSG). Current concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection-the Maastricht 2-2000 Consensus Report. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2002. 16:167–180.16. Houben MH, van de Beek D, Hensen EF, Craen AJ, Rauws EA, Tytgat GN. A systematic review of Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy-the impact of antimicrobial resistance on eradication rates. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1999. 13:1047–1055.17. Sasaki M, Ogasawara N, Utsumi K, Kawamura N, Kamiya T, Kataoka H, Tanida S, Mizoshita T, Kasugai K, Joh T. Changes in 12-year first-line eradication rate of Helicobacter pylori based on triple therapy with proton pump iInhibitor, amoxicillin and clarithromycin. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2010. 47:53–58.18. Graham DY, Fischbach L. Helicobacter pylori treatment in the era of increasing antibiotic resistance. Gut. 2010. 59:1143–1153.19. Malfertheiner P, Megraud F, O'Morain C, Bazzoli F, El-Omar E, Graham D, Hunt R, Rokkas T, Vakil N, Kuipers EJ. Current concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection: the Maastricht III Consensus Report. Gut. 2007. 56:772–781.20. Xia HX, Buckley M, Keane CT, O'Morain CA. Clarithromycin resistance in Helicobacter pylori: prevalence in untreated dyspeptic patients and stability in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1996. 37:473–481.21. Mégraud F. Strategies to treat patients with antibiotic resistant Helicobacter pylori. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2000. 16:507–509.22. Alarcón T, Vega AE, Domingo D, Martínez MJ, López-Brea M. Clarithromycin resistance among Helicobacter pylori strains isolated from children: Prevalence and study of mechanism of resistance by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. 41:486–499.23. Mégraud F. H. pylori antimicrobial resistance: prevalence, importance, and advances in testing. Gut. 2004. 53:1374–1384.24. Eun CS, Han DS, Park JY, Jeon YC, Hahm JS, Kim KS, Kang JO. Changing pattern of antimicrobial resistance of Helicobacter pylori in Korean patients with peptic ulcer diseases. J Gastroenterol. 2003. 38:436–441.25. Bang SY, Han DS, Eun CS, Kim JE, Ahn SB, Sohn JH, Jeon YC, Kang JO. Changing patterns of antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori in patients with peptic ulcer disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2007. 50:356–362.26. Sung H, Chung HJ, Kim MN, Lee GH. Clinical usefulness of antimicrobial susceptibility test for Helicobacter pylori. Korean J Lab Med. 2006. 26:179–184.27. Rokkas T, Sechopoulos P, Robotis I, Margantinis G, Pistiolas D. Cumulative H. pylori eradication rates in clinical practice by adopting first and second-line regimens proposed by the Maastricht III consensus and a third-line empirical regimen. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009. 104:21–25.28. Wong WM, Gu Q, Lam SK, Fung FM, Lai KC, Hu WH, Yee YK, Chan CK, Xia HH, Yuen MF, Wong BC. Randomized controlled study of rabeprazole, levofloxacin and rifabutin triple therapy versus quadruple therapy as second-line treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003. 17:553–560.29. Kim JM, Kim JS, Kim N, Kim SG, Jung HC, Song IS. Comparison of primary and secondary antimicrobial minimum inhibitory concentrations for Helicobacter pylori isolated from Korean patients. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2006. 28:6–13.30. Lee JH, Jung HY, Choi KD, Song HJ, Lee GH, Kim JH. The influence of CYP2C19 polymorphism on eradication of Helicobacter pylori: a prospective randomized study of lansoprazole and rabeprazole. Gut Liver. 2010. 4:201–206.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rifaximin Plus Levofloxacin-Based Rescue Regimen for the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori
- The Efficacy of Levofloxacin Based Triple Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Eradication
- Efficacy of and Resistance to Rifaximin-based Quadruple Therapy in Helicobacter pylori Eradication
- Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapy in Korea
- Efficacy of Levofloxacin-based Triple Therapy as Second-lineHelicobacter pylori Eradication