J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Apr;24(2):269-274. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.2.269.
Clinical Features and Outcomes of Microscopic Polyangiitis in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Allergy and Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. byoo@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Soon Chun Hyang University, College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- KMID: 1779129
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.2.269
Abstract
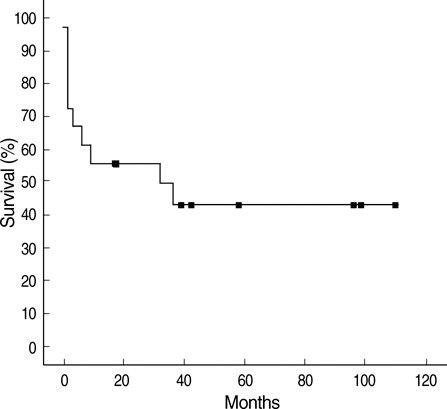
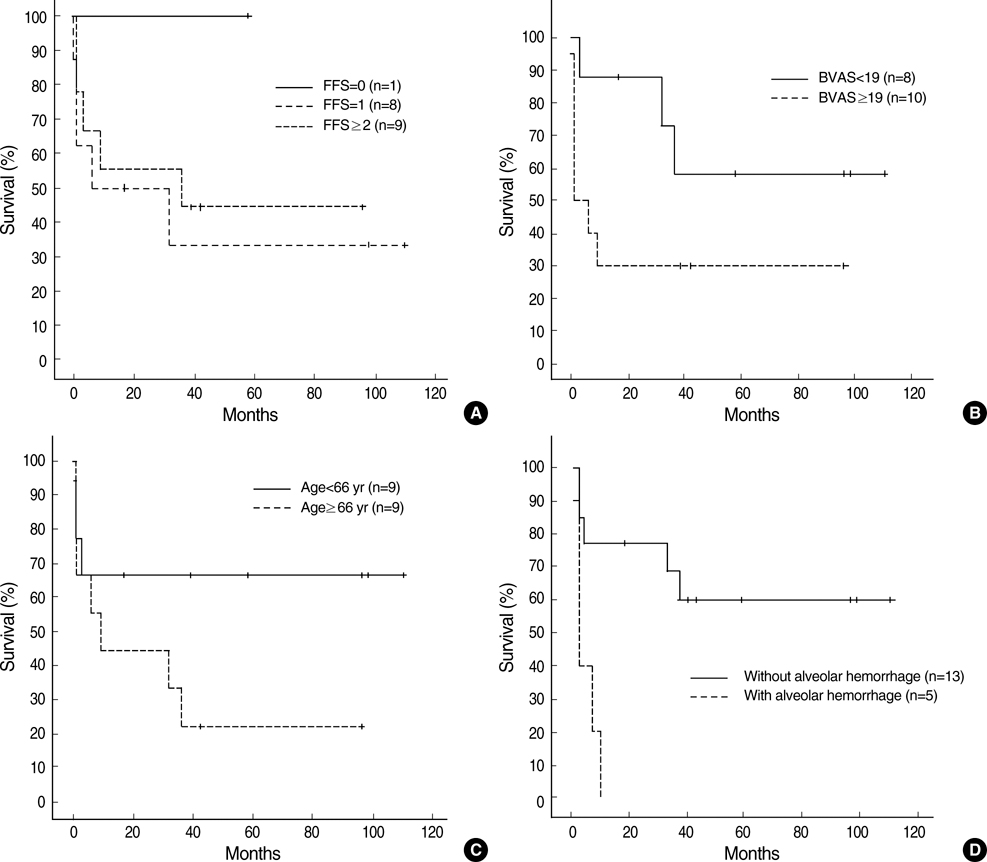
- Microscopic polyangiitis (MPA) is a systemic vasculitis affecting small vessels. To determine the clinical features and outcomes of MPA in Korean patients, we retrospectively reviewed the medical records of patients diagnosed with MPA at a single medical center in Korea between 1989 and 2006. The 18 patients who met the Chapel Hill criteria for MPA had a mean (+/-SD) age at the time of diagnosis of 62.4+/-12.7 yr. Renal manifestations and general symptoms were the most common features of MPA, with lung involvement also very common. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA) were present in 17 of the 18 patients (94%). Of 17 patients treated with steroids and cyclophosphamide, 11 (65%) had stable or improved course. One patient treated with steroids without cyclophosphamide showed disease progression. Ten of the 18 patients (56%) died at a median follow-up of 8 months. MPA in Korean patients was distinguished by a higher rate of lung involvement, especially alveolar hemorrhage, which was the leading cause of death in our patients. Korean patients were also older at MPA onset and were more likely positive for ANCA. Other overall clinical manifestations did not differ significantly.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Age Factors
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Antibodies, Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic/blood
Cyclophosphamide/therapeutic use
Drug Therapy, Combination
Female
Hemorrhage/etiology
Humans
Kidney Failure/etiology
Korea
Lung Diseases/etiology
Male
Middle Aged
Polyarteritis Nodosa/*diagnosis/drug therapy/mortality
Pulmonary Alveoli/blood supply/pathology
Retrospective Studies
Steroids/therapeutic use
Survival Analysis
Treatment Outcome
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis in Korea: A Narrative Review
Chan-Bum Choi, Yong-Beom Park, Sang-Won Lee
Yonsei Med J. 2019;60(1):10-21. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.1.10.ANCA Associated Vasculitis
Wan-sik Uhm
J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2010;17(2):108-132. doi: 10.4078/jkra.2010.17.2.108.
Reference
-
1. Davson J, Ball J, Platt R. The kidney in periarteritis nodosa. Q J Med. 1948. 17:175–202.2. Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Andrassy K, Bacon PA, Churg J, Gross WL, Hagen EC, Hoffman GS, Hunder GG, Kallenberg CG, McCluskey RT, Sinico RA, Rees AJ, Van Es LA, Waldherr R, Wiik A. Nomenclature of systemic vasculitides. Proposal of an international consensus conference. Arthritis Rheum. 1994. 37:187–192.3. Guillevin L, Durand-Gasselin B, Cevallos R, Gayraud M, Lhote F, Callard P, Amouroux J, Casassus P, Jarrousse B. Microscopic polyangiitis: clinical and laboratory findings in eighty-five patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1999. 42:421–430.
Article4. Guillevin L, Lhote F, Gayraud M, Cohen P, Jarrousse B, Lortholary O, Thibult N, Casassus P. Prognostic factors in polyarteritis nodosa and Churg-Strauss syndrome. A prospective study in 342 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 1996. 75:17–28.
Article5. Luqmani RA, Bacon PA, Moots RJ, Janssen BA, Pall A, Emery P, Savage C, Adu D. Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score (BVAS) in systemic necrotizing vasculitis. QJM. 1994. 87:671–678.6. Savage CO, Winearls CG, Evans DJ, Rees AJ, Lockwood CM. Microscopic polyarteritis: presentation, pathology and prognosis. Q J Med. 1985. 56:467–483.7. Adu D, Howie AJ, Scott DG, Bacon PA, McGonigle RJ, Micheal J. Polyarteritis and the kidney. Q J Med. 1987. 62:221–237.8. Pusey CD, Gaskin G. Disease associations with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1993. 336:145–155.
Article9. Hauschild S, Schmitt WH, Csernok E, Flesch BK, Rautmann A, Gross WL. ANCA in systemic vasculitides, collagen vascular diseases, rheumatic disorders and inflammatory bowel diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1993. 336:245–251.
Article10. Guillevin L, Visser H, Noel LH, Pourrat J, Vernier I, Gayraud M, Oksman F, Lesavre P. Antineutrophil cytoplasm antibodies in systemic polyarteritis nodosa with and without hepatitis B virus infection and Churg-Strauss syndrome--62 patients. J Rheumatol. 1993. 20:1345–1349.11. Lightfoot RW Jr, Michel BA, Bloch DA, Hunder GG, Zvaifler NJ, McShane DJ, Arend WP, Calabrese LH, Leavitt RY, Lie JT, Masi AT, Mills JA, Stevens MB. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of polyarteritis nodosa. Arthritis Rheum. 1990. 33:1088–1093.
Article12. Bae YD, Choi HJ, Lee JC, Park JJ, Lee YJ, Lee EB, Song YW. Clinical features of polyarteritis nodosa in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2006. 21:591–595.
Article13. Song BC, Kim SH, Kim H, Ying YH, Kim HJ, Kim YJ, Yoon JH, Lee HS, Cha CY, Kook YH, Kim BJ. Prevalence of naturally occurring surface antigen variants of hepatitis B virus in Korean patients infected chronically. J Med Virol. 2005. 76:194–202.
Article14. Gayraud M, Guillevin L, le Toumelin P, Cohen P, Lhote F, Casassus P, Jarrousse B. French Vasculitis Study Group. Long-term followup of polyarteritis nodosa, microscopic polyangiitis, and Churg-Strauss syndrome: analysis of four prospective trials including 278 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2001. 44:666–675.
Article15. Hogan SL, Nachman PH, Wilkman AS, Jennette JC, Falk RJ. Prognostic markers in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated microscopic polyangiitis and glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1996. 7:23–32.
Article16. Serra A, Cameron JS, Turner DR, Hartley B, Ogg CS, Neild GH, Williams DG, Taube D, Brown CB, Hicks JA. Vasculitis affecting the kidney: presentation, histopathology and long-term outcome. Q J Med. 1984. 53:181–207.17. D'Agati V, Chander P, Nash M, Mancilla-Jimenez R. Idiopathic microscopic polyarteritis nodosa: ultrastructural observations on the renal vascular and glomerular lesions. Am J Kidney Dis. 1986. 7:95–110.