J Korean Med Sci.
2005 Jun;20(3):509-511. 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.3.509.
Giant Cystic Chondroid Hamartoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Gachon Medical School Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Pathology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. jhhan@smc.samsung.co.kr
- 3Department of Thoracic Surgery, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology and Center for Imaging Science, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1778517
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2005.20.3.509
Abstract
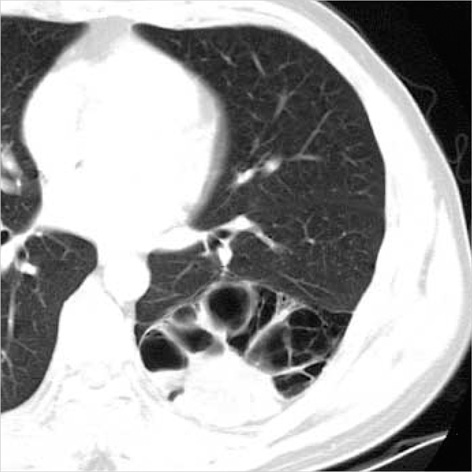
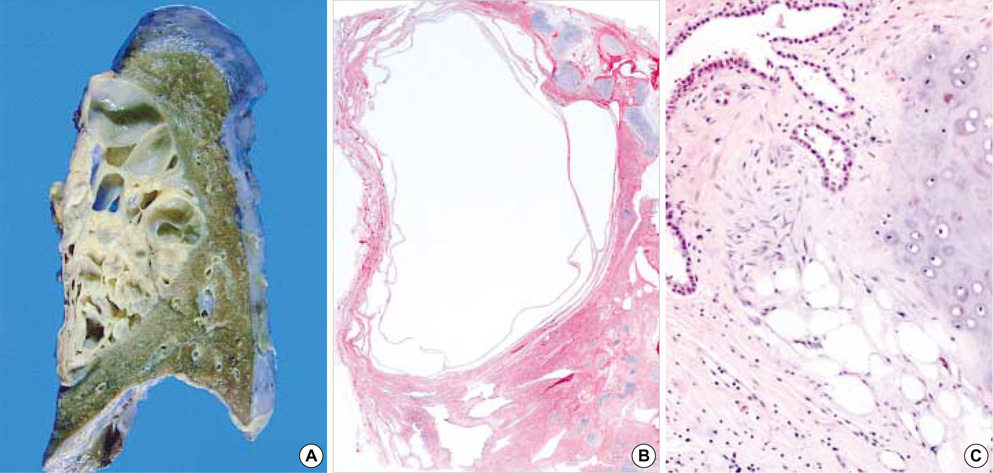
- We report a case of huge pulmonary chondroid hamartoma with multilocular cysts in a 38-yr-old male patient. The lobectomy specimen of the left lower lobe showed a large multilocular cystic mass, 11.5 x 10 cm in size. The mass had thin-walled, variable-sized cysts and areas of solid cartilaginous small nodules in the interstitium, which occupied the superior segment and the upper portion of the basal segment. There was no connection with bronchus or vessel. Microscopically, the cysts and cleft-like spaces were lined by ciliated columnar epithelium and the solid components were composed of cartilage, myxohyalinized connective tissue, and adipose tissue. Also seen were foci of calcification within the sclerotic stroma.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jackson RC, McDonald JR, Clagett OT. Massive cystic pulmonary hamartoma; report of two cases. J Thorac Surg. 1956. 31:504–510.2. Bateson EM, Abbott EK. Mixed tumors of the lung, or hamarto-chondromas. A review of the radiological appearances of cases published in the literature and a report of fifteen new cases. Clin Radiol. 1960. 11:232–247.3. Doppman J, Wilson G. Cystic pulmonary hamartoma. Br J Radiol. 1965. 38:629–631.
Article4. Demos TC, Armin A, Chandrasekhar AJ, Barron J. Cystic hamartoma of the lung. J Can Assoc Radiol. 1983. 34:149–150.5. Miura K, Hori T, Yoshizawa K, Hamaguchi N, Morita J. Cystic pulmonary hamartoma. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990. 49:828–829.
Article6. Austin JR, deTar M, Rice DH. Pulmonary chondroid hamartoma presenting as an inflatable neck mass. Case report and clinicopathologic analysis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1994. 120:440–443.
Article7. Lee SY, Park HJ, Lee CS, Lee KR. Giant pulmonary hamartoma. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2002. 22:1006.
Article8. King TE Jr, Christopher KL, Schwarz MI. Multiple pulmonary chondromatous hamartomas. Hum Pathol. 1982. 13:496–497.
Article9. Kazmierczak B, Rosigkeit J, Wanschura S, Meyer-Bolte K, Van de Ven WJ, Kayser K, Krieghoff B, Kastendiek H, Bartnitzke S, Bullerdiek J. HMGI-C rearrangements as the molecular basis for the majority of pulmonary chondroid hamartomas: a survey of 30 tumors. Oncogene. 1996. 12:515–521.10. Rogalla P, Lemke I, Kazmierczak B, Bullerdiek J. An identical HMGIC-LPP fusion transcript is consistently expressed in pulmonary chondroid hamartomas with t(3;12)(q27-28;q14-15). Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2000. 29:363–366.