Korean J Radiol.
2014 Aug;15(4):464-471. 10.3348/kjr.2014.15.4.464.
Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Infiltrative Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Clinical Safety and Efficacy and Factors Influencing Patient Survival
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul 138-736, Korea. m1fenew@daum.net
- KMID: 1731050
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.4.464
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the safety and efficacy of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) in patients with infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and to identify the prognostic factors associated with patient survival.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fifty two patients who underwent TACE for infiltrative HCC were evaluated between 2007 and 2010. The maximum diameter of the tumors ranged from 7 cm to 22 cm (median 15 cm). Of 46 infiltrative HCC patients with portal vein tumor thrombosis, 32 patients received adjuvant radiation therapy for portal vein tumor thrombosis after TACE.
RESULTS
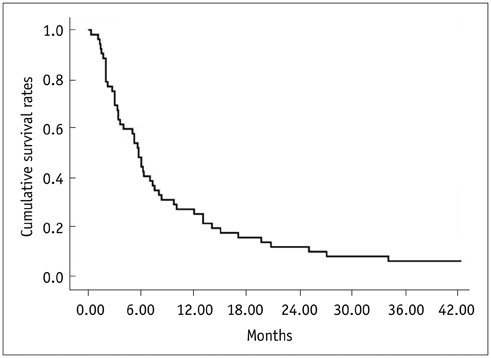
The tumor response by European Association for the Study of the Liver criteria was partial in 18%, stable in 47%, and progressive in 35% of the patients. The median survival time was 5.7 months (Kaplan-Meier analysis). The survival rates were 48% at six months, 25% at one year, and 12% at two years. In the multivariable Cox regression analysis, Child-Pugh class (p = 0.02), adjuvant radiotherapy (p = 0.003) and tumor response after TACE (p = 0.004) were significant factors associated with patient survival. Major complications occurred in nine patients. The major complication rate was significantly higher in patients with Child-Pugh B than in patients with Child-Pugh A (p = 0.049, chi2 test).
CONCLUSION
Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization can be a safe treatment option in infiltrative HCC patients with Child Pugh class A. Child Pugh class A, radiotherapy for portal vein tumor thrombosis after TACE and tumor response are good prognostic factors for an increased survival after TACE in patients with infiltrative HCCs.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Carcinoma, Hepatocellular/mortality/pathology/*therapy
Chemoembolization, Therapeutic/*adverse effects/methods/mortality
Female
Humans
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
Liver Neoplasms/mortality/pathology/*therapy
Male
Middle Aged
Prognosis
Retrospective Studies
Survival Rate
Tumor Burden
Venous Thrombosis/etiology
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Optimized Performance of FlightPlan during Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Importance of the Proportion of Segmented Tumor Area
Seung-Moon Joo, Yong Pyo Kim, Tae Jun Yum, Na Lae Eun, Dahye Lee, Kwang-Hun Lee
Korean J Radiol. 2016;17(5):771-778. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2016.17.5.771.
Reference
-
1. El-Serag HB, Mason AC. Rising incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1999; 340:745–750.2. Takayasu K. Transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma over three decades: current progress and perspective. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2012; 42:247–255.3. Demirjian A, Peng P, Geschwind JF, Cosgrove D, Schutz J, Kamel IR, et al. Infiltrating hepatocellular carcinoma: seeing the tree through the forest. J Gastrointest Surg. 2011; 15:2089–2097.4. Kanematsu M, Semelka RC, Leonardou P, Mastropasqua M, Lee JK. Hepatocellular carcinoma of diffuse type: MR imaging findings and clinical manifestations. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2003; 18:189–195.5. Kneuertz PJ, Demirjian A, Firoozmand A, Corona-Villalobos C, Bhagat N, Herman J, et al. Diffuse infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma: assessment of presentation, treatment, and outcomes. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012; 19:2897–2907.6. Hu HT, Kim JH, Lee LS, Kim KA, Ko GY, Yoon HK, et al. Chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: multivariate analysis of predicting factors for tumor response and survival in a 362-patient cohort. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2011; 22:917–923.7. Llovet JM, Real MI, Montaña X, Planas R, Coll S, Aponte J, et al. Arterial embolisation or chemoembolisation versus symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002; 359:1734–1739.8. Luo J, Guo RP, Lai EC, Zhang YJ, Lau WY, Chen MS, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: a prospective comparative study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011; 18:413–420.9. Xue TC, Xie XY, Zhang L, Yin X, Zhang BH, Ren ZG. Transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: a meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013; 13:60.10. Chung JW, Park JH, Han JK, Choi BI, Han MC. Hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein invasion: results of treatment with transcatheter oily chemoembolization. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995; 165:315–321.11. Kim KM, Kim JH, Park IS, Ko GY, Yoon HK, Sung KB, et al. Reappraisal of repeated transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein invasion. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 24:806–814.12. Chung GE, Lee JH, Kim HY, Hwang SY, Kim JS, Chung JW, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization can be safely performed in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma invading the main portal vein and may improve the overall survival. Radiology. 2011; 258:627–634.13. Lo CM, Ngan H, Tso WK, Liu CL, Lam CM, Poon RT, et al. Randomized controlled trial of transarterial lipiodol chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2002; 35:1164–1171.14. Bruix J, Sherman M. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology. 2011; 53:1020–1022.15. Greene FL. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: updating the strategies in cancer staging. Bull Am Coll Surg. 2002; 87:13–15.16. Yoon HM, Kim JH, Kim EJ, Gwon DI, Ko GY, Ko HK. Modified cisplatin-based transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for large hepatocellular carcinoma: multivariate analysis of predictive factors for tumor response and survival in a 163-patient cohort. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2013; 24:1639–1646.17. Yoon SM, Lim YS, Won HJ, Kim JH, Kim KM, Lee HC, et al. Radiotherapy plus transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma invading the portal vein: long-term patient outcomes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012; 82:2004–2011.18. Bruix J, Sherman M. Practice Guidelines Committee, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2005; 42:1208–1236.19. Kamel IR, Liapi E, Reyes DK, Zahurak M, Bluemke DA, Geschwind JF. Unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: serial early vascular and cellular changes after transarterial chemoembolization as detected with MR imaging. Radiology. 2009; 250:466–473.20. Brown DB, Gould JE, Gervais DA, Goldberg SN, Murthy R, Millward SF, et al. Transcatheter therapy for hepatic malignancy: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009; 20:7 Suppl. S425–S434.21. Trevisani F, Caraceni P, Bernardi M, D'Intino PE, Arienti V, Amorati P, et al. Gross pathologic types of hepatocellular carcinoma in Italian patients. Relationship with demographic, environmental, and clinical factors. Cancer. 1993; 72:1557–1563.22. Lopez RR Jr, Pan SH, Hoffman AL, Ramirez C, Rojter SE, Ramos H, et al. Comparison of transarterial chemoembolization in patients with unresectable, diffuse vs focal hepatocellular carcinoma. Arch Surg. 2002; 137:653–657. discussion 657-658.23. Jang ES, Yoon JH, Chung JW, Cho EJ, Yu SJ, Lee JH, et al. Survival of infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma patients with preserved hepatic function after treatment with transarterial chemoembolization. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013; 139:635–643.24. Yamada K, Izaki K, Sugimoto K, Mayahara H, Morita Y, Yoden E, et al. Prospective trial of combined transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for portal vein tumor thrombus in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003; 57:113–119.25. Zeng ZC, Fan J, Tang ZY, Zhou J, Qin LX, Wang JH, et al. A comparison of treatment combinations with and without radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein and/or inferior vena cava tumor thrombus. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005; 61:432–443.26. Ishikura S, Ogino T, Furuse J, Satake M, Baba S, Kawashima M, et al. Radiotherapy after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein tumor thrombus. Am J Clin Oncol. 2002; 25:189–193.27. Takayasu K, Arii S, Ikai I, Omata M, Okita K, Ichida T, et al. Prospective cohort study of transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in 8510 patients. Gastroenterology. 2006; 131:461–469.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rupture of hepatocellular carcinoma after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization: A case report
- Pirarubicin, UFT, Leucovorin Chemotherapy in Non-embolizable and Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization-Failed Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients; A Phase II Clinical Study
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma Extending to the Inferior Vena Cava and Right Atrium-A Case Report of 4 Years Survival after Repeated Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization Therapy -
- Palliative Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Relieving Metastatic Bone Pain due to Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Case Report
- A Fatal Case of Pulmonary Embolism after Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma