J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Jan;25(1):128-134. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.1.128.
The Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Ulinastatin in Trauma Patients with Hemorrhagic Shock
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Emergency Medicine, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju, Korea.
- 2Department of Emergency Medicine, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea. ed119@yonsei.ac.kr
- KMID: 1713843
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.1.128
Abstract
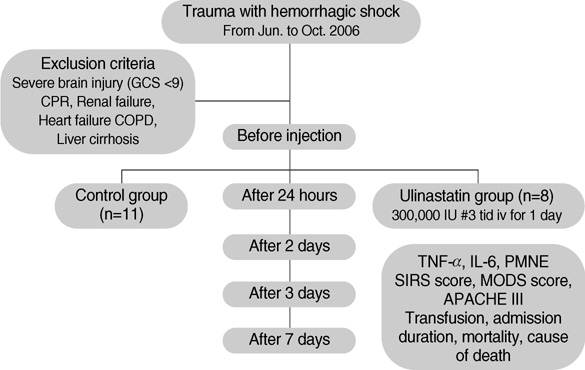
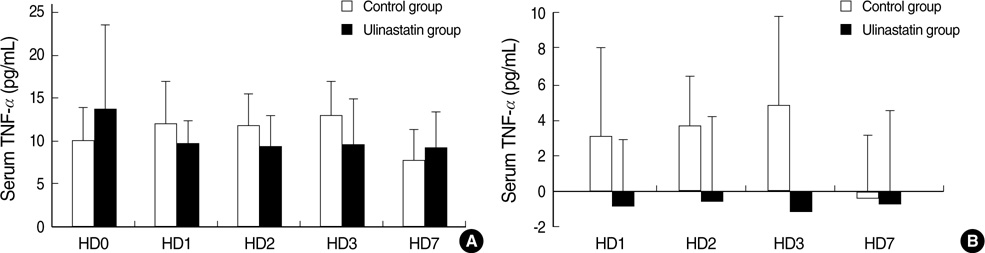
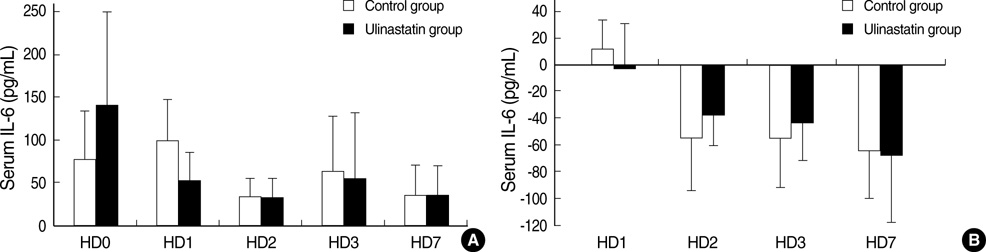
- We investigated the use of ulinastatin in association with the suppression of polymorphonuclear leukocyte elastase (PMNE), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin 6 (IL-6), and its effects on the prognosis of patients with traumatic hemorrhagic shock. Nineteen patients who visited the emergency department for traumatic hemorrhagic shock were enrolled. Eleven patients were randomly selected to receive a total of 300,000 IU of ulinastatin. Measurements of serum PMNE, TNF-alpha and IL-6 were taken before ulinastatin treatment at 24 hr, two days, three days, and seven days after admission. We compared the Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome scores, Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome scores and Acute Physiology, age, Chronic Health Evaluation III scores of the control and ulinastatin groups. There were no significant differences in baseline values, laboratory data, treatment or mortality between the two groups. The serum PMNE levels in the ulinastatin group were lower than in the control group on the second hospitalized day. Serum TNF-alpha and IL-6 levels in the ulinastatin group decreased 24 hr after admission but had no significance. It is suggested that ulinastatin treatment could decrease the serum PMNE levels in trauma patients with hemorrhagic shock at 48 hr after treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal/*therapeutic use
Female
Glycoproteins/*therapeutic use
Humans
Interleukin-6/blood
Leukocyte Elastase/blood
Male
Middle Aged
Severity of Illness Index
Shock, Hemorrhagic/*drug therapy
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha/blood
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Glycoproteins
Interleukin-6
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Leukocyte Elastase
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Urinary trypsin inhibitor attenuates liver enzyme elevation after liver resection
Cheol-Won Jeong, Cha-Sup Lee, Seong-Heon Lee, Hye Jin Jeung, Sang-Hyun Kwak
Korean J Anesthesiol. 2012;63(2):120-123. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2012.63.2.120.Effects of ulinastatin on coagulation in high-risk patients undergoing off-pump coronary artery bypass graft surgery
Na-Young Kim, Jae-Kwang Shim, Seo-Ouk Bang, Jee-Suk Sim, Jong-Wook Song, Young-Lan Kwak
Korean J Anesthesiol. 2013;64(2):105-111. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2013.64.2.105.The Effect of Urinary Trypsin Inhibitor Against Neuropathic Pain in Rat Models
Ki Tae Jung, Hyun Young Lee, Myung Ha Yoon, Kyung Joon Lim
Korean J Pain. 2013;26(4):356-360. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2013.26.4.356.
Reference
-
1. Brun-Buisson C. The epidemiology of the systemic inflammatory response. Intensive Care Med. 2000. 26:Suppl 1. S64–S74.
Article2. Maitra SR, Gestring M, el-Maghrabi MR. Alternations in hepatic 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase and glucose-6-phosphatase gene expression after hemorrhagic hypotension and resuscitation. Shock. 1997. 8:385–388.3. Lee CC, Marill KA, Carter WA, Crupi RS. A current concept of trauma-induced multiorgan failure. Ann Emerg Med. 2001. 38:170–176.
Article4. Riedemann NC, Neff TA, Guo RF, Bernacki KD, Laudes IJ, Sarma JV, Lambris JD, Ward PA. Protective effects of IL-6 blockade in sepsis are linked to reduced c5a receptor expression. J Immunol. 2003. 170:503–507.
Article5. Nishiyama T, Hanaoka K. Do the effects of a protease inhibitor, ulinastatin, on elastase release by blood transfusion depend on interleukin 6? Crit Care Med. 2001. 29:2106–2110.
Article6. Aosasa S, Ono S, Mochizuki H, Tsujimoto H, Ueno C, Matsumoto A. Mechanism of the inhibitory effect of protease inhibitor on tumor necrosis factor a production of monocytes. Shock. 2001. 15:101–105.7. Sato Y, Ishikawa S, Otaki A, Takahashi T, Hasegawa Y, Suzuki M, Yamagishi T, Morishita Y. Induction of acute-phase reactive substances during open-heart surgery and efficacy of ulinastatin. Inhibiting cytokines and postoperative organ injury. Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2000. 48:428–434.8. Chen CC, Liu ZM, Wang HH, He W, Wang Y, Wu WD. Effect of ulinastatin on renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2004. 25:1334–1340.9. Ohnishi H, Suzuki K, Niho T, Ito C, Yamaguchi K. Protective effects of urinary trypsin inhibitor in experimental shock. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1985. 39:137–144.
Article10. Fries E, Blom AM. Bikunin-not just a plasma proteinase inhibitor. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2000. 32:125–137.11. Pugia MJ, Lott JA. Pathophysiology and diagnostic value of urinary trypsin inhibitors. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2005. 43:1–16.
Article12. Yano T, Anraku S, Nakayama R, Ushijima K. Neuroprotective effect of urinary trypsin inhibitor against focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Anesthesiology. 2003. 98:465–473.
Article13. Nakatani K, Takeshita S, Tsujimoto H, Kawamura Y, Sekine I. Inhibitory effect of serine protease inhibitors on neutrophil-mediated endothelial cell injury. J Leukoc Biol. 2001. 69:241–247.14. Tani T, Aoki H, Yoshioka T, Lin KJ, Kodama M. Treatment of septic shock with a protease inhibitor in a canine model: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Crit Care Med. 1993. 21:925–930.15. Tani T, Abe H, Endo Y, Hanasawa K, Kodama M. Effects of a urinary trypsin inhibitor on acute circulatory insufficiency after surgical operation. Am J Surg. 1998. 175:142–145.
Article16. Nishiyama T, Yokoyama T, Yamashita K. Effects of a protease inhibitor, ulinastatin, on coagulation and fibrinolysis in abdominal surgery. J Anesth. 2006. 20:179–182.
Article17. Cohen J. The immunopathogenesis of sepsis. Nature. 2002. 420:885–891.
Article18. Toth B, Yokoyama Y, Schwacha MG, George RL, Rue LW 3rd, Bland KI, Chaudry IH. Insights into the role of interleukin-6 in the induction of hepatic injury after trauma-hemorrhagic shock. J Appl Physiol. 2004. 97:2184–2189.
Article19. Witthaut R, Busch C, Fraunberger P, Walli A, Seidel D, Pilz G, Stuttmann R, Speichermann N, Verner L, Werdan K. Plasma atrial natriuretic peptide and brain natriuretic peptide are increased in septic shock: impact of interleukin-6 and sepsis associated left ventricular dysfunction. Intensive Care Med. 2003. 29:1696–1702.20. Duswald KH, Jochum M, Schramm W, Fritz H. Released granulocytic elastase: an indicator of pathobiochemical alterations in septicemia after abdominal surgery. Surgery. 1985. 98:892–899.21. Pacholok SG, Davies P, Dorn C, Finke P, Hanlon WA, Mumford RA, Humes JL. Formation of polymorphonuclear leukocyte elastase: alpha 1 proteinase inhibitor complex and A alpha (1-21) fibrinopeptide in human blood stimulated with the calcium ionophore A23187. A model to characterize inhibitors of polymorphonuclear leukocyte elastase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1995. 49:1513–1520.22. Mania-Pramanik J, Potdar SS, Vadigoppula A, Sawant S. Elastase: a predictive marker of inflammation and/or infection. J Clin Lab Anal. 2004. 18:153–158.
Article23. Ogawa M, Nishibe S, Mori T, Neumann S. Effect of human urinary trypsin inhibitor on granulocyte elastase activity. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1987. 55:271–274.24. Vallejo JG, Nemoto S, Ishiyama M, Yu B, Knuefermann P, Diwan A, Baker JS, Defreitas JS, Tweardy DJ, Mann DL. Functional significance of inflammatory mediators in a murine model of resuscitated hemorrhagic shock. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005. 288:H1272–H1277.
Article25. Neumann S, Gunzer G, Hennrich N, Lang H. "PMN-elastase assay": enzyme immunoassay for human polymorphonuclear elastase complexed with alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1984. 22:693–697.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects of Urinary Trypsin Inhibitor on the Outcomes of Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock Patients
- MULTIPLE FACIAL TRAUMA PATIENT ACCOMPANIED WITH SEVERE BLEEDING: REPORT OF A CASE
- Myocardial protective effect by ulinastatin via an anti-inflammatory response after regional ischemia/reperfusion injury in an in vivo rat heart model
- Pathophysiology of Hemorrhagic Shock
- The effect of ulinastatin on hemostasis in major orthopedic surgery