Korean J Radiol.
2012 Aug;13(4):515-520. 10.3348/kjr.2012.13.4.515.
Covered Bronchial Stent Insertion to Manage Airway Obstruction with Hemoptysis Caused by Lung Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Dankook University College of Medicine, Dankook University Hospital, Cheonan 330-715, Korea. hae0820@naver.com
- 2Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Dankook University College of Medicine, Dankook University Hospital, Cheonan 330-715, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Bundang CHA General Hospital, CHA University, Seongnam 463-712, Korea.
- KMID: 1383867
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.4.515
Abstract
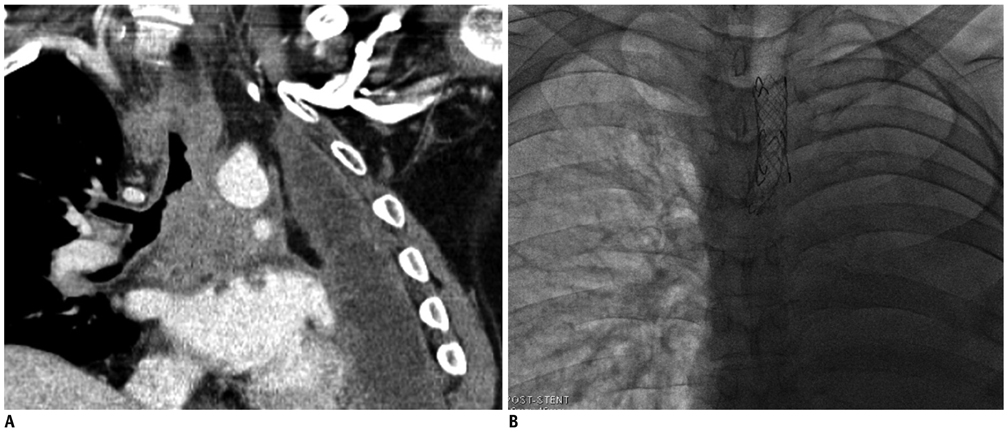
- Malignant airway obstruction and hemoptysis are common in lung cancer patients. Recently, airway stent is commonly used to preserve airway in malignant airway obstruction. Hemoptysis can be managed through various methods including conservative treatment, endobronchial tamponade, bronchoscopic intervention, embolization and surgery. In our case studies, we sought to investigate the effectiveness of airway stents for re-opening the airway as well as tamponade effects in four patients with malignant airway obstruction and bleeding caused by tumors or lymph node invasions.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chin CS, Litle V, Yun J, Weiser T, Swanson SJ. Airway stents. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008. 85:S792–S796.2. Saji H, Furukawa K, Tsutsui H, Tsuboi M, Ichinose S, Usuda J, et al. Outcomes of airway stenting for advanced lung cancer with central airway obstruction. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2010. 11:425–428.3. Chung IH, Park MH, Kim DH, Jeon GS. Endobronchial stent insertion to manage hemoptysis caused by lung cancer. J Korean Med Sci. 2010. 25:1253–1255.4. Dweik RA, Stoller JK. Role of bronchoscopy in massive hemoptysis. Clin Chest Med. 1999. 20:89–105.5. Hirshberg B, Biran I, Glazer M, Kramer MR. Hemoptysis: etiology, evaluation, and outcome in a tertiary referral hospital. Chest. 1997. 112:440–444.6. Lee SM, Kim HY, Ahn Y. Parallel technique of endobronchial balloon catheter tamponade for transient alleviation of massive hemoptysis. J Korean Med Sci. 2002. 17:823–825.7. Fernando HC, Stein M, Benfield JR, Link DP. Role of bronchial artery embolization in the management of hemoptysis. Arch Surg. 1998. 133:862–866.8. Wang GR, Ensor JE, Gupta S, Hicks ME, Tam AL. Bronchial artery embolization for the management of hemoptysis in oncology patients: utility and prognostic factors. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009. 20:722–729.9. Lund ME, Garland R, Ernst A. Airway stenting: Applications and practice management considerations. Chest. 2007. 131:579–587.10. Zakaluzny SA, Lane JD, Mair EA. Complications of tracheobronchial airway stents. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003. 128:478–488.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endobronchial Stent Insertion to Manage Hemoptysis caused by Lung Cancer
- Massive Hemoptysis Cases Intubated with the Univent(R) Bronchial Blocker for Lung Protection
- Two Double Stents Insertion for Commen Bile Duct and Duodenal Obstruction Caused by Pancreatic Cancer
- Silicone Covered vs. Non-covered Endotracheal Self-expandable Metallic Stent: An Experimental Study
- A Case of Biphasic Flow-volume Loop in Left Mainstem Bronchial Stenosis