Korean J Radiol.
2006 Mar;7(1):73-76. 10.3348/kjr.2006.7.1.73.
Hyaline Vascular-Type Castleman Disease Presenting as an Esophageal Submucosal Tumor: Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Diagnostic Radiology, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Pusan, Korea. gnlee@daunet.donga.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Pusan, Korea.
- 3Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Pusan, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Pusan, Korea.
- KMID: 753919
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2006.7.1.73
Abstract
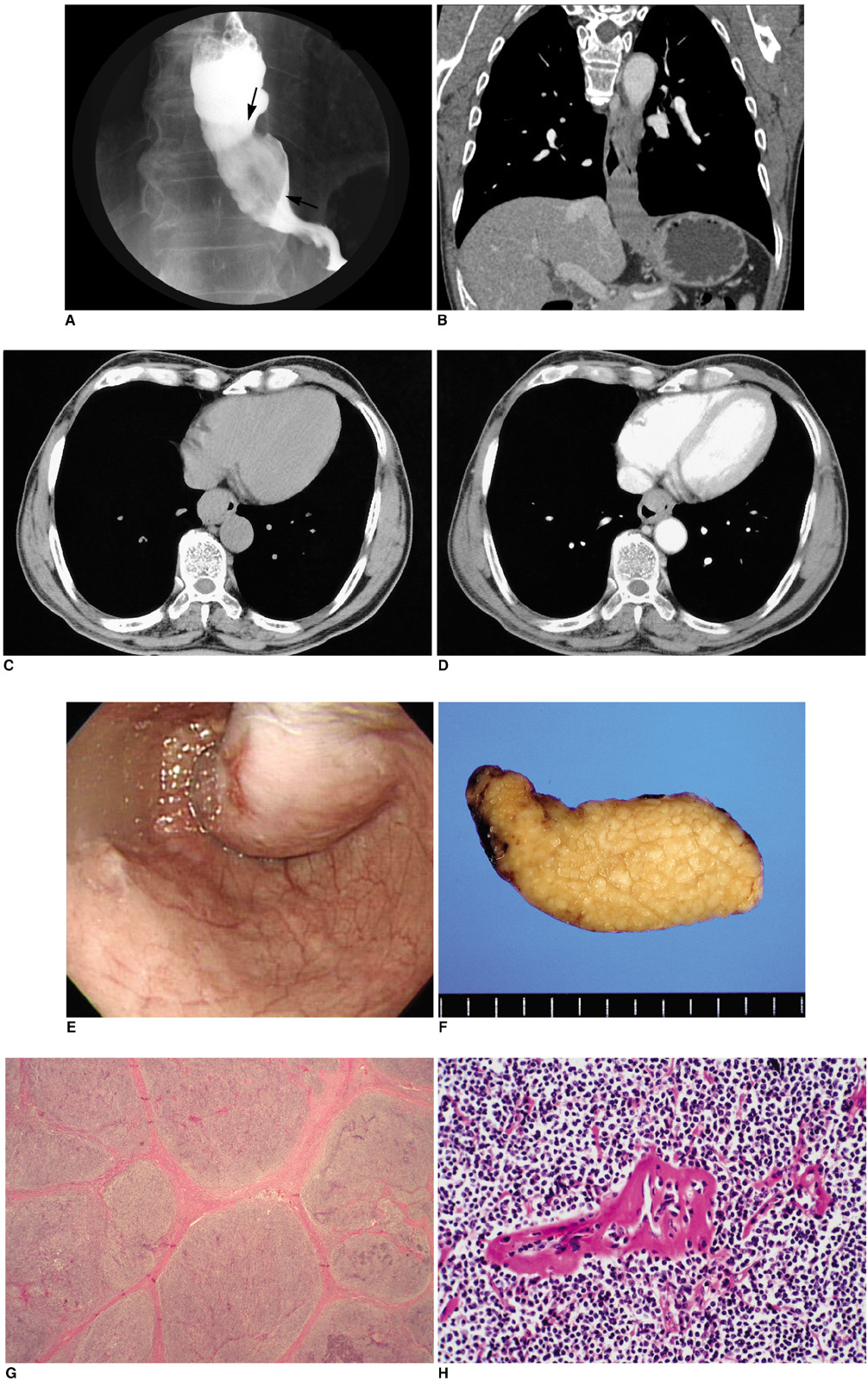
- Castleman disease is a relatively rare disorder of lymphoid tissue that involves the gastrointestinal tract in a variety of clinical and pathologic manifestations. A submucosal location has never been described in the medical literature. We report a case of esophageal Castleman disease involving thesubmucosal layer in a 62-year-old man, which was confirmed on pathology. Esophagography and CT demonstrated an intramural tumor, and a leiomyoma or leiomyosarcoma was suspected based on the known incidence of such tumors.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zamir A, Prasher G, Moukarzel AA, Zeien L, Feldman F. Castleman's disease: a rare cause of hematemesis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1999. 28:112–115.2. Wengrower D, Libson E, Okon E, Goldin E. Gastrointestinal manifestation in Castleman's disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1990. 85:1179–1182.3. Kaneko T, Takahashi S, Takeuchi T, Goto T, Kitamura T. Castleman's disease in the retroperitoneal space. J Urol. 2003. 169:265–266.4. Kojima M, Nakamura S, Iijima M, Murayama K, Sakata N, Masawa N. Lymphoid variant of hyaline vascular Castleman's disease containing numerous mantle zone lymphocytes with clear cytoplasm. APMIS. 2005. 113:75–80.5. Seo BK, Oh YW, Cho KR, Lee NJ, Kim JH, Kim IS, et al. Imaging findings of Castleman's disease localized in the axilla: a case report. Korean J Radiol. 2002. 3:136–139.6. Park KS, Choi YJ, Song KS. Hyaline-vascular type Castleman's disease involving both orbits. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2002. 80:537–539.7. Gaunt GA, Gostout BS, Remstein E, Cliby WA. Pelvic Castleman disease presenting as vaginal occlusion. Obstet Gynecol. 2002. 100:1082–1085.8. Sotrel A, Castellano-Sanchez AA, Prusmack C, Birchansky S, Brathwaite C, Ragheb J. Castleman's disease in a child presenting with a partly mineralized solitary meningeal mass. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2003. 38:232–237.9. Serin E, Ozer B, Gumurdulu Y, Yildirim T, Barutcu O, Boyacioglu S. A case of castleman's disease with "downhill" varices in the absence of superior vena cava obstruction. Endoscopy. 2002. 34:160–162.10. Shirakusa T, Iwsaki A, Okazaki M. Downhill esophageal varices caused by benign giant lymphoma. Scand J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1988. 22:135–138.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hyaline-vascular Variant of Castleman's Disease in Retroperitoneum
- A Case of Retroperitoneal Castleman`s Disease
- Roentgenogram of the Issue : A Case of Castleman`s Disease(Hyaline Vascular type)
- A Case of Castleman's Disease Presenting as an Isolated Hypervascular Tumor in Neck
- A Case of Localized Castleman's Disease in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis