Clin Endosc.
2024 Mar;57(2):181-190. 10.5946/ce.2023.065.
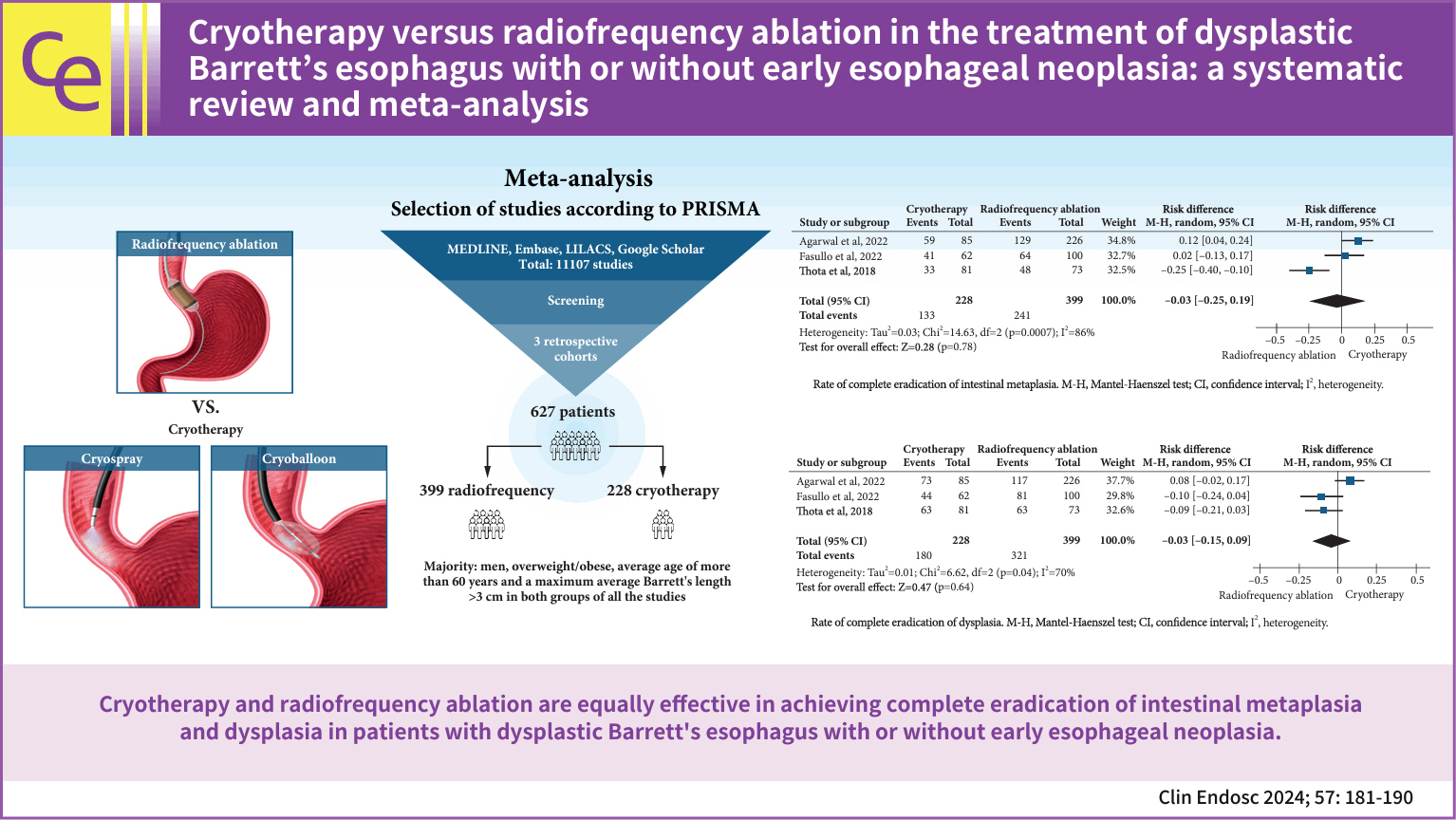
Cryotherapy versus radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of dysplastic Barrett’s esophagus with or without early esophageal neoplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Unit, Hospital das Clínicas, University of São Paulo School of Medicine, São Paulo, Brazil
- 2Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Endoscopy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
- KMID: 2553753
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2023.065
Abstract
- Background/Aims
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is the first-line therapy for dysplastic Barrett’s esophagus (BE). Therefore, cryotherapy has emerged as an alternative treatment option. This study aimed to compare the efficacies of these two techniques based on the rates of complete eradication of intestinal metaplasia (CE-IM) and dysplasia (CE-D). Adverse events and recurrence have also been reported.
Methods
An electronic search was conducted using the Medline (PubMed), Embase, LILACS, and Google Scholar databases until December 2022. Studies were included comparing cryotherapy and RFA for treating dysplastic BE with or without early esophageal neoplasia. This study was performed in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines.
Results
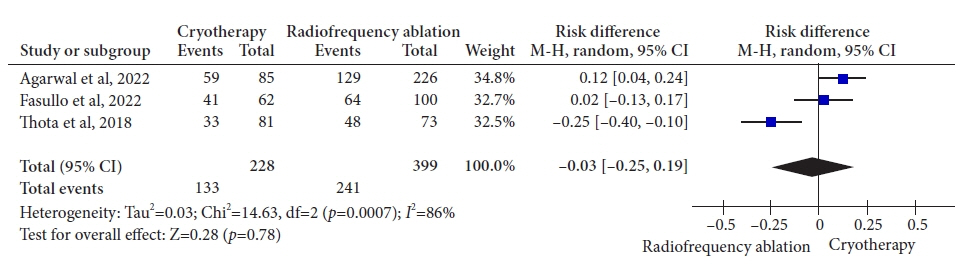
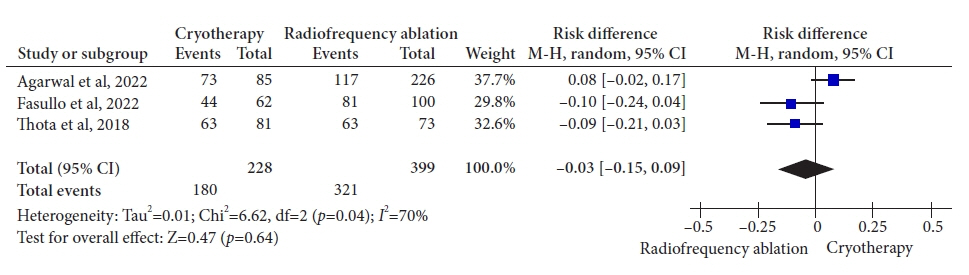
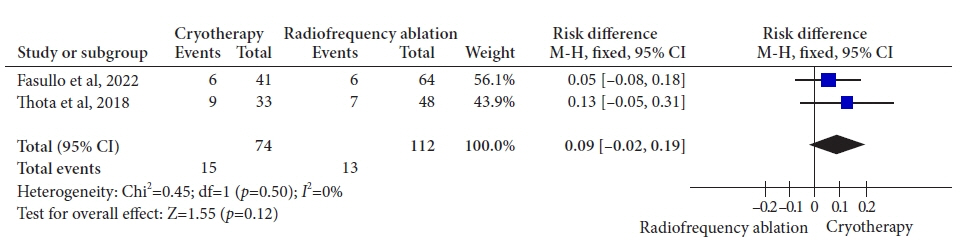
Three retrospective cohort studies involving 627 patients were included. Of these, 399 patients underwent RFA, and 228 were treated with cryotherapy. There was no difference in CE-IM (risk difference [RD], –0.03; 95% confidence interval [CI], –0.25 to 0.19; p=0.78; I2=86%) as well as in CE-D (RD, –0.03; 95% CI, –0.15 to 0.09; p=0.64; I2=70%) between the groups. The absolute number of adverse events was low, and there was no difference in the recurrence rate.
Conclusions
Cryotherapy and RFA were equally effective in treating dysplastic BE, with or without early esophageal neoplasia.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shaheen NJ, Sharma P, Overholt BF, et al. Radiofrequency ablation in Barrett’s esophagus with dysplasia. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360:2277–2288.2. Garg S, Xie J, Inamdar S, et al. Spatial distribution of dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus segments before and after endoscopic ablation therapy: a meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 2021; 53:6–14.3. de Matos MV, da Ponte-Neto AM, de Moura DTH, et al. Treatment of high-grade dysplasia and intramucosal carcinoma using radiofrequency ablation or endoscopic mucosal resection + radiofrequency ablation: meta-analysis and systematic review. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2019; 11:239–248.4. Pouw RE, Klaver E, Phoa KN, et al. Radiofrequency ablation for low-grade dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus: long-term outcome of a randomized trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020; 92:569–574.5. Sawas T, Alsawas M, Bazerbachi F, et al. Persistent intestinal metaplasia after endoscopic eradication therapy of neoplastic Barrett’s esophagus increases the risk of dysplasia recurrence: meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019; 89:913–925.6. De Souza TF, Artifon EL, Mestieri LH, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of endoscopic ablative treatment of Barrett’s esophagus. Rev Gastroenterol Peru. 2014; 34:217–224.7. Weusten B, Bisschops R, Coron E, et al. Endoscopic management of Barrett’s esophagus: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Position Statement. Endoscopy. 2017; 49:191–198.8. Orman ES, Li N, Shaheen NJ. Efficacy and durability of radiofrequency ablation for Barrett’s Esophagus: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 11:1245–1255.9. Pandey G, Mulla M, Lewis WG, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the effectiveness of radiofrequency ablation in low grade dysplastic Barrett’s esophagus. Endoscopy. 2018; 50:953–960.10. Wolfson P, Ho KMA, Wilson A, et al. Endoscopic eradication therapy for Barrett’s esophagus-related neoplasia: a final 10-year report from the UK National HALO Radiofrequency Ablation Registry. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022; 96:223–233.11. Barret M, Pioche M, Terris B, et al. Endoscopic radiofrequency ablation or surveillance in patients with Barrett’s oesophagus with confirmed low-grade dysplasia: a multicentre randomised trial. Gut. 2021; 70:1014–1022.12. Hamade N, Desai M, Thoguluva Chandrasekar V, et al. Efficacy of cryotherapy as first line therapy in patients with Barrett’s neoplasia: a systematic review and pooled analysis. Dis Esophagus. 2019; 32:doz040.13. Tariq R, Enslin S, Hayat M, et al. Efficacy of cryotherapy as a primary endoscopic ablation modality for dysplastic Barrett’s esophagus and early esophageal neoplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Control. 2020; 27:1073274820976668.14. Visrodia K, Zakko L, Singh S, et al. Cryotherapy for persistent Barrett’s esophagus after radiofrequency ablation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018; 87:1396–1404.15. Trindade AJ, Inamdar S, Kothari S, et al. Feasibility of liquid nitrogen cryotherapy after failed radiofrequency ablation for Barrett’s esophagus. Dig Endosc. 2017; 29:680–685.16. Solomon SS, Kothari S, Smallfield GB, et al. Liquid nitrogen spray cryotherapy is associated with less postprocedural pain than radiofrequency ablation in Barrett’s esophagus: a multicenter prospective study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2019; 53:e84–e90.17. Canto MI, Trindade AJ, Abrams J, et al. Multifocal cryoballoon ablation for eradication of Barrett’s esophagus-related neoplasia: a prospective multicenter clinical trial. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020; 115:1879–1890.18. The Cochrane Collaboration. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.0 [Internet]. The Cochrane Collaboration;2019. [cited 2023 Jan 31]. Available from: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook.19. GRADEpro. Guideline Development Tool software [Internet]. McMaster University;2023. [cited 2023 Jan 31]. Available from: https://gdt.gradepro.org/app/.20. Agarwal S, Alshelleh M, Scott J, et al. Comparative outcomes of radiofrequency ablation and cryoballoon ablation in dysplastic Barrett’s esophagus: a propensity score-matched cohort study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022; 95:422–431.21. Fasullo M, Shah T, Patel M, et al. Outcomes of radiofrequency ablation compared to liquid nitrogen spray cryotherapy for the eradication of dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus. Dig Dis Sci. 2022; 67:2320–2326.22. Thota PN, Arora Z, Dumot JA, et al. Cryotherapy and radiofrequency ablation for eradication of Barrett’s esophagus with dysplasia or intramucosal cancer. Dig Dis Sci. 2018; 63:1311–1319.23. van Munster SN, Overwater A, Haidry R, et al. Focal cryoballoon versus radiofrequency ablation of dysplastic Barrett’s esophagus: impact on treatment response and postprocedural pain. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018; 88:795–803.24. Canto MI, Shaheen NJ, Almario JA, et al. Multifocal nitrous oxide cryoballoon ablation with or without EMR for treatment of neoplastic Barrett’s esophagus (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2018; 88:438–446.25. Cotton CC, Wolf WA, Overholt BF, et al. Late recurrence of Barrett’s esophagus after complete eradication of intestinal metaplasia is rare: final report from ablation in Intestinal Metaplasia Containing Dysplasia Trial. Gastroenterology. 2017; 153:681–688.26. Shaheen NJ, Falk GW, Iyer PG, et al. Diagnosis and management of Barrett’s esophagus: an updated ACG guideline. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022; 117:559–587.27. Standards of Practice Committee, Wani S, Qumseya B, et al. Endoscopic eradication therapy for patients with Barrett’s esophagus-associated dysplasia and intramucosal cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018; 87:907–931.28. Wani S, Muthusamy VR, Shaheen NJ, et al. Development of quality indicators for endoscopic eradication therapies in Barrett’s esophagus: the TREAT-BE (Treatment with Resection and Endoscopic Ablation Techniques for Barrett’s Esophagus) Consortium. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 86:1–17.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Buried Barrett's Esophagus with High-Grade Dysplasia after Radiofrequency Ablation
- Comparative Effectiveness of Cryotherapy and Radiofrequency Ablation for Chronic Rhinitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Role of artificial intelligence in diagnosing Barrett’s esophagus-related neoplasia
- Hybrid argon plasma coagulation in Barrett’s esophagus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Photodynamic Therapy for Barrett's Esophagus and Esophageal Carcinoma