Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2023 Nov;16(4):369-379. 10.21053/ceo.2023.01214.
Comparative Effectiveness of Cryotherapy and Radiofrequency Ablation for Chronic Rhinitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea
- 2Department of Physiology and Biomedical Engineering, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA
- 3Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Bucheon St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea
- KMID: 2548365
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2023.01214
Abstract
Objectives
. Multiple minimally invasive techniques for chronic rhinitis treatment focus on posterior nasal nerve ablation. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy of cryotherapy and radiofrequency ablation for alleviating symptoms in patients with allergic and nonallergic rhinitis.
Methods
. We retrieved studies from PubMed, Scopus, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Database up to July 2023. Data on the impact of cryotherapy and radiofrequency ablation on quality of life and symptom ratings of rhinitis were extracted and evaluated.
Results
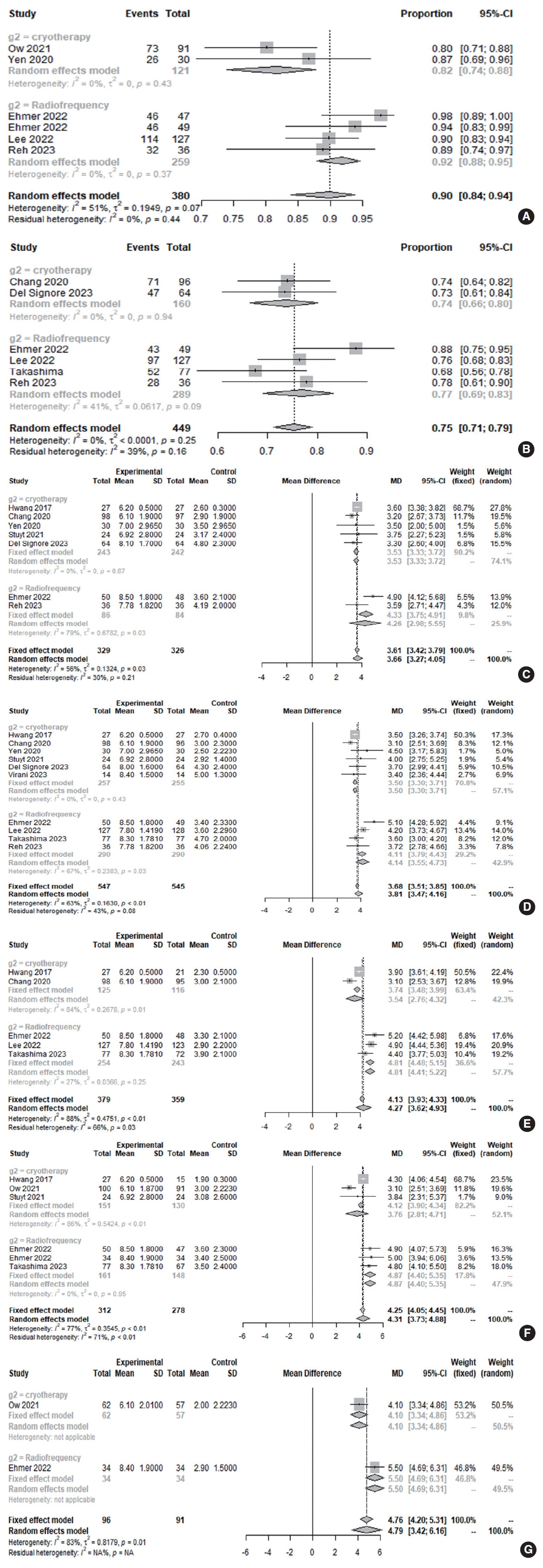
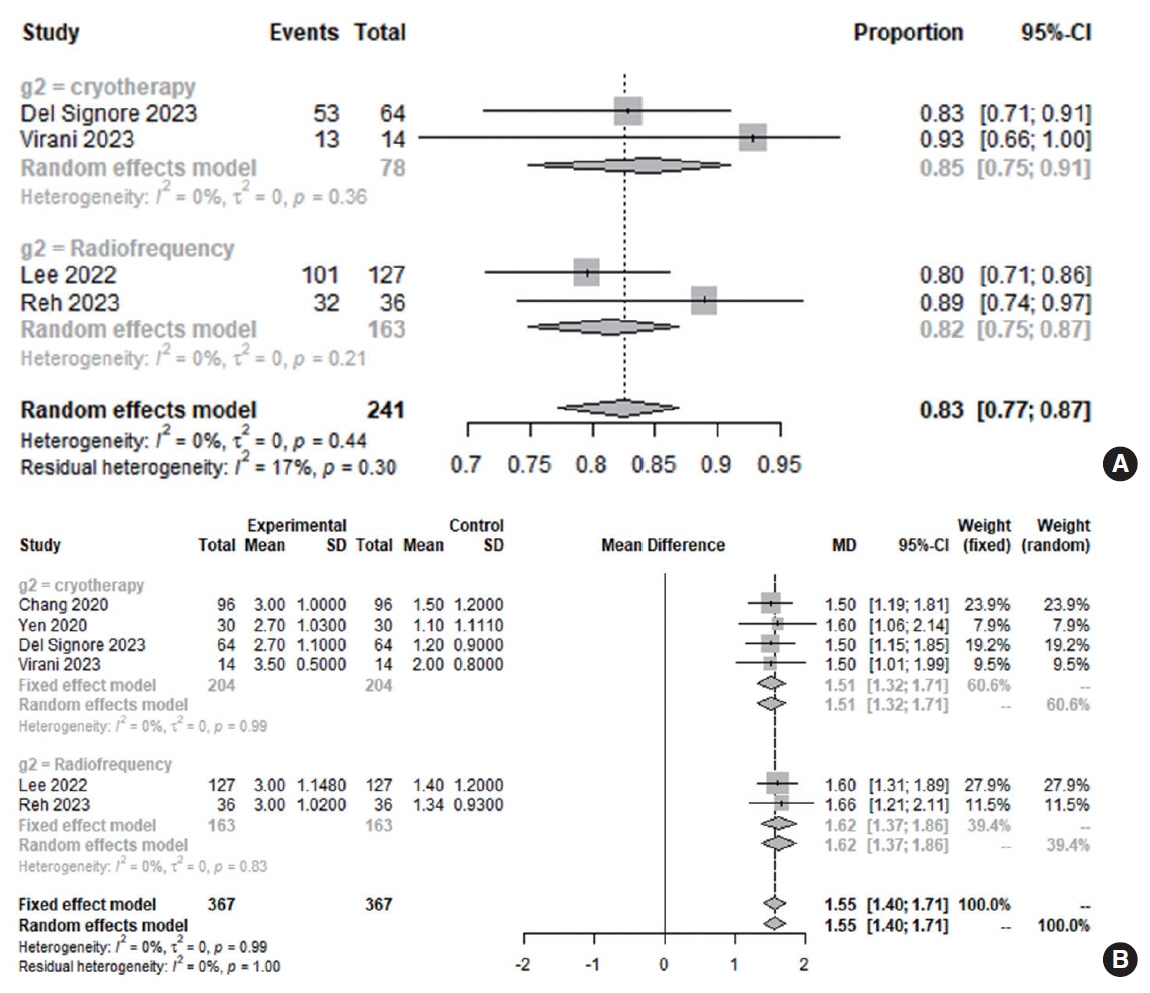
. An analysis of 12 studies involving 788 patients demonstrated significant improvements in quality of life and rhinitis-related symptoms (nasal obstruction, itching, rhinorrhea, and sneezing) in patients treated with cryotherapy or radiofrequency ablation (symptom score at 24 months and quality of life score at 3 months). However, radiofrequency ablation had a more positive effect on nasal symptoms after 3 months than cryotherapy. Nonallergic rhinitis patients responded more favorably to posterior nerve ablation than patients with allergic rhinitis. Both techniques enhanced disease-specific quality of life during the initial 3 months of treatment (cryotherapy, 84.6%; radiofrequency, 81.6%; P=0.564). After 3 months of treatment, a clinical improvement in all nasal symptoms (minimal clinically important difference in the total nasal symptom score: >1.0 points) was seen in 81.8% and 91.9% of patients who underwent cryotherapy and radiofrequency ablation, respectively (P=0.005), suggesting that radiofrequency is more likely to lead to clinical improvement.
Conclusion
. Rhinitis-associated subjective symptom scores and quality of life may be improved by both cryotherapy and radiofrequency ablation. Ablation was more efficacious than cryotherapy for nasal symptoms in patients with nonallergic rhinitis. To corroborate these findings, further randomized controlled studies directly comparing these two techniques are warranted.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Settipane RA. Epidemiology of vasomotor rhinitis. World Allergy Organ J. 2009; Jun. 2(6):115–8.2. Settipane RA, Charnock DR. Epidemiology of rhinitis: allergic and nonallergic. Clin Allergy Immunol. 2007; 19:23–34.3. Meltzer EO, Bukstein DA. The economic impact of allergic rhinitis and current guidelines for treatment. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2011; Feb. 106(2 Suppl):S12–6.4. Virani FR, Wilson MD, Beliveau AM, Gill AS, Strong EB, Steele TO. The impact of surgical posterior nasal nerve cryoablation on symptoms and disease-specific quality of life in patients with chronic rhinitis. Ear Nose Throat J. 2023; Oct. 102(10):654–60.5. Marple BF, Fornadley JA, Patel AA, Fineman SM, Fromer L, Krouse JH, et al. Keys to successful management of patients with allergic rhinitis: focus on patient confidence, compliance, and satisfaction. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007; Jun. 136(6 Suppl):S107–24.6. Reh DD, Lay K, Davis G, Dubin MG, Yen DM, O’Malley EM, et al. Clinical evaluation of a novel multipoint radiofrequency ablation device to treat chronic rhinitis. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2023; Mar. 8(2):367–72.7. Yan CH, Hwang PH. Surgical management of nonallergic rhinitis. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2018; Oct. 51(5):945–55.8. Del Signore AG, Greene JB, Russell JL, Yen DM, O’Malley EM, Schlosser RJ. Cryotherapy for treatment of chronic rhinitis: 3-month outcomes of a randomized, sham-controlled trial. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2022; Jan. 12(1):51–61.9. Ow RA, O’Malley EM, Han JK, Lam KK, Yen DM. Cryosurgical ablation for treatment of rhinitis: two-year results of a prospective multicenter study. Laryngoscope. 2021; Sep. 131(9):1952–7.10. Chang MT, Song S, Hwang PH. Cryosurgical ablation for treatment of rhinitis: a prospective multicenter study. Laryngoscope. 2020; Aug. 130(8):1877–84.11. Yen DM, Conley DB, O’Malley EM, Byerly TA, Johnson J. Multiple site cryoablation treatment of the posterior nasal nerve for treatment of chronic rhinitis: an observational feasibility study. Allergy Rhinol (Providence). 2020; Aug. 11:2152656720946996.12. Hwang PH, Lin B, Weiss R, Atkins J, Johnson J. Cryosurgical posterior nasal tissue ablation for the treatment of rhinitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2017; Oct. 7(10):952–6.13. Lee JT, Abbas GM, Charous DD, Cuevas PD, Goktas PD, Loftus PA, et al. Clinical and quality of life outcomes following temperaturecontrolled radiofrequency neurolysis of the posterior nasal nerve (RhinAer) for treatment of chronic rhinitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2022; Nov. 36(6):747–54.14. Ehmer D, McDuffie CM, Scurry WC Jr, McIntyre JB, Mehendale NH, Willis JH, et al. Temperature-controlled radiofrequency neurolysis for the treatment of rhinitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2022; Jan. 36(1):149–56.15. Stolovitzky JP, Ow RA, Silvers SL, Bikhazi NB, Johnson CD, Takashima M. Effect of radiofrequency neurolysis on the symptoms of chronic rhinitis: a randomized controlled trial. OTO Open. 2021; Sep. 5(3):2473974X211041124.16. Kim DH, Kim SW, Basurrah MA, Hwang SH. Clinical and laboratory features of various criteria of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2022; Aug. 15(3):230–46.17. Kim DH, Hwang SH. Effects of intraoperative saline-soaked pharyngeal packing on nausea, vomiting, and throat pain after nasal surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Rhinol. 2023; Mar. 30(1):6–14.18. Gerka Stuyt JA, Luk L, Keschner D, Garg R. Evaluation of in-office cryoablation of posterior nasal nerves for the treatment of rhinitis. Allergy Rhinol (Providence). 2021; Jan. 12:2152656720988565.19. Takashima M, Stolovitzky JP, Ow RA, Silvers SL, Bikhazi NB, Johnson CD. Temperature-controlled radiofrequency neurolysis for treatment of chronic rhinitis: 12-month outcomes after treatment in a randomized controlled trial. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2023; Feb. 13(2):107–15.20. Ehmer D, McDuffie CM, McIntyre JB, Davis BM, Mehendale NH, Willis JH, et al. Long-term outcomes following temperature-controlled radiofrequency neurolysis for the treatment of chronic rhinitis. Allergy Rhinol (Providence). 2022; May. 13:21526575221096045.21. Klimek L, Bergmann KC, Biedermann T, Bousquet J, Hellings P, Jung K, et al. Visual analogue scales (VAS): measuring instruments for the documentation of symptoms and therapy monitoring in cases of allergic rhinitis in everyday health care: position paper of the German Society of Allergology (AeDA) and the German Society of Allergy and Clinical Immunology (DGAKI), ENT Section, in collaboration with the working group on Clinical Immunology, Allergology and Environmental Medicine of the German Society of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery (DGHNOKHC). Allergo J Int. 2017; Jan. 26(1):16–24.22. Barnes ML, Vaidyanathan S, Williamson PA, Lipworth BJ. The minimal clinically important difference in allergic rhinitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010; Feb. 40(2):242–50.23. Juniper EF, Thompson AK, Ferrie PJ, Roberts JN. Development and validation of the mini Rhinoconjunctivitis Quality of Life Questionnaire. Clin Exp Allergy. 2000; Jan. 30(1):132–40.24. Senanayake P, Wong E, McBride K, Singh N. Efficacy of vidian neurectomy and posterior nasal neurectomy in the management of nonallergic rhinitis: a systematic review. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2022; Nov. 36(6):849–71.25. Girdhar-Gopal H, Okurowski L, Strome M. An assessment of postganglionic cryoneurolysis for managing vasomotor rhinitis. Am J Rhinol. 1994; Jul. 8(4):157–64.26. Robinson SR, Wormald PJ. Endoscopic vidian neurectomy. Am J Rhinol. 2006; Mar-Apr. 20(2):197–202.27. Konno A. Historical, pathophysiological, and therapeutic aspects of vidian neurectomy. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2010; Mar. 10(2):105–12.28. Ogi K, Valentine R, Suzuki M, Fujieda S, Psaltis AJ, Wormald PJ. The anatomy of the foramina and efferent nerve fibers from the pterygopalatine ganglion in posterolateral nasal wall. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2022; May. 7(3):679–83.29. Kikawada T. Endoscopic posterior nasal neurectomy: an alternative to vidian neurectomy. Oper Tech Otolayngol Head Neck Surg. 2007; Dec. 18(4):297–301.30. Fan T, Chandna M, Gorelik D, Takashima M, Yim MT, Rowan NR, et al. Correlation between middle turbinate insertion in relation to sphenopalatine foramen and failure rates of cryotherapy and radiofrequency treatment for chronic rhinitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2023; Jan. 13(1):88–91.31. Ikeda K, Yokoi H, Saito T, Kawano K, Yao T, Furukawa M. Effect of resection of the posterior nasal nerve on functional and morphological changes in the inferior turbinate mucosa. Acta Otolaryngol. 2008; 128(12):1337–41.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of intracanal cryotherapy on postendodontic pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Comparative Efficacy of Clinical Interventions for Sacroiliac Joint Pain: Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis With Preliminary Design of Treatment Algorithm
- Cryotherapy versus radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of dysplastic Barrett’s esophagus with or without early esophageal neoplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- A Case of Chronic Radiodermatitis following Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation
- Effect of intracanal cryotherapy on postoperative pain after endodontic treatment: systematic review with meta-analysis