Korean J Women Health Nurs.
2023 Sep;29(3):229-238. 10.4069/kjwhn.2023.09.12.
Effects of a virtual reality simulation integrated with problem-based learning on nursing students’ critical thinking ability, problem solving ability, and self-efficacy: a non-randomized trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Ansan University, Ansan, Korea
- KMID: 2547158
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4069/kjwhn.2023.09.12
Abstract
- Purpose
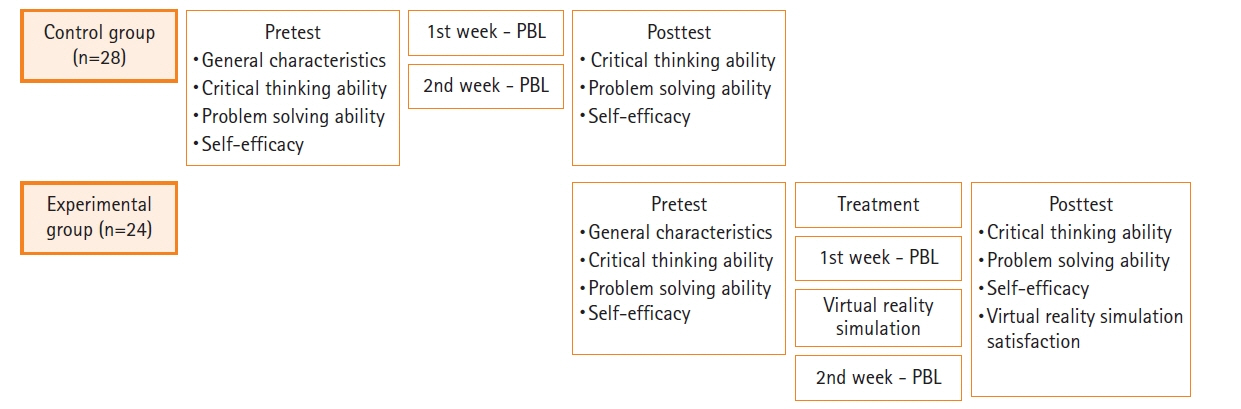
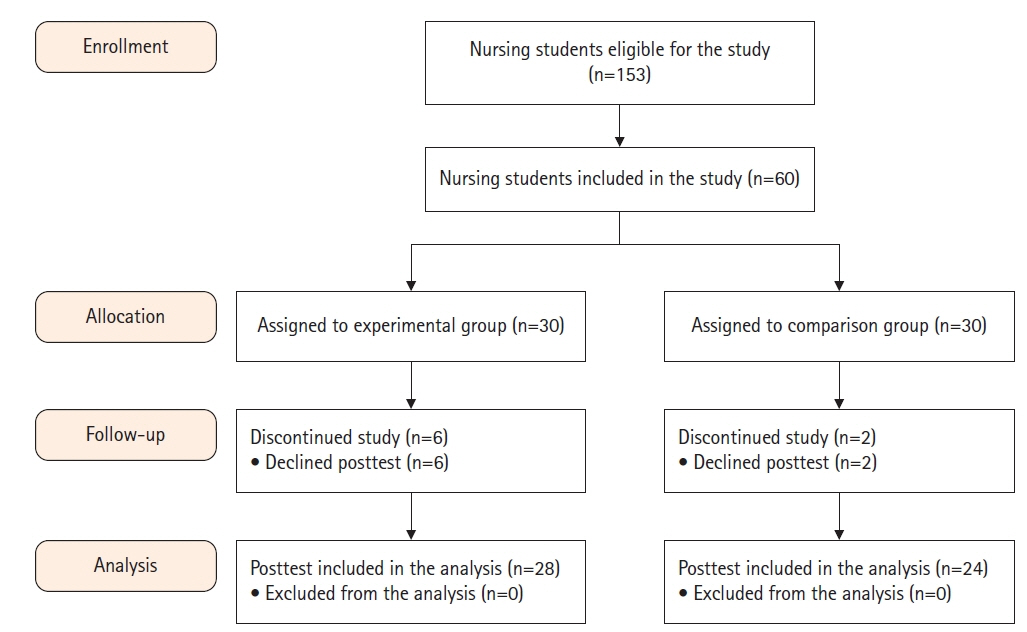
This study analyzed the effects of virtual reality simulation-based problem-based learning on nursing students’ critical thinking ability, problem-solving ability, and self-efficacy in the nursing care of women undergoing induction of labor. Methods: A nonequivalent control group pretest and posttest design was employed. The study participants included 52 nursing students (24 in the experimental group and 28 in the control group). The experimental group took a problem-based learning (PBL) class in the first week, and then engaged in self-directed learning using virtual reality simulation. In the second week, lectures about emergency nursing care for induction of labor and drug administration were given. The control group participated in PBL in the first week and lectures in the second week. The study was conducted from April 17 to May 19, 2023. Data were analyzed using the chi-square test, Fisher exact test, analysis of variance, and the independent t-test. Results: Before-and-after differences between the two groups were statistically significant in problem solving ability (t=–5.47, p<.001) and self-efficacy (t=–5.87, p<.001). Critical thinking ability did not show a statistically significant difference between the two groups. The score for satisfaction with the virtual reality simulation program was 3.64±5.88 out of 5 in the experimental group. Conclusion: PBL education using a virtual reality simulation was found to be an effective way of teaching. Although convenience sampling was used, PBL education using virtual reality can be used as an educational strategy to enhance nursing students’ problem-solving ability and self-efficacy
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim HJ, Park D. Effects of convergence education by Jigsaw Model and flipped learning in nursing students. J Converg Inform Technol. 2019; 9(3):36–43. https://doi.org/10.22156/CS4SMB.2019.9.3.036.
Article2. Lee S. The effect of Blended learning mode used in COVID-19 situation on learning motivation and attitude. J Educ Inform Media. 2022; 28(3):595–621. https://doi.org/10.15833/KAFEIAM.28.3.595.
Article3. Kuo Y, Belland BR, Schroder KE, Walker AE. K-12 teachers’ perceptions of and their satisfaction with interaction type in blended learning environments. Distance Educ. 2014; 35(3):360–381.
Article4. Hung W, Jonassen DH, Liu R. Problem-based learning. In : Spector JM, editor. Handbook of research on educational communications and technology. 3rd ed. New York: Routledge;2008. p. 485–506.5. Barrows HS. Problem-based learning in medicine and beyond: a brief overview. New Dir Teach Learn. 1996; (68):3–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/tl.37219966804.
Article6. Borhan MT. Problem based learning (PBL) in Malaysian higher education: a review of research on learners’ experience and issues of implementations. Asian J Eng Educ. 2012; 1(1):48–53.7. Yun SY. Song CE. Changes in problem solving ability, clinical competency and self-confidence in learning of nursing students in simulation integrated with problem based learning: focusing on cancer care scenarios. J Korea Acad-Ind Coop Soc. 2021; 22(8):312–319. https://doi.org/10.5762/KAIS.2021.22.8.312.
Article8. Kim JS, Kim YH. The effects of simulation practice education applying problem-based learning on problem solving ability, critical thinking and learning satisfaction of nursing students. J Korea Contents Assoc. 2016; 16(12):203–212. https://dx.doi.org/10.5392/JKCA.2016.16.12.203.
Article9. Park IS. The effect of problem-based learning strategies (PBL) on problem solving skill: a meta-analysis. J Korea Converg Soc. 2019; 10(10):197–205. https://doi.org/10.15207/JKCS.2019.10.10.197.
Article10. Kim HY, Kim MS, Jung HC. Effect of smart PBL on meta-cognition, academic self-efficacy, and practice satisfaction in nursing students taking fundamental nursing skills and applying flipped learning. J Korean Soc Simul Nurs. 2020; 8(1):57–67. https://doi.org/10.17333/JKSSN.2020.8.1.57.
Article11. You HE, Yang BS. The effects of virtual reality simulation scenario application on clinical competency, problem solving ability and nursing performance confidence. J Korea Acade-Ind Coop Soc. 2021; 22(9):116–126. https://doi.org/10.5762/KAIS.2021.22.9.116.
Article12. Kim MK, Kim HY. The effects of classes using virtual reality simulations of the hospital environment on knowledge of the hospital environment, academic self-efficacy, learning flow, educational satisfaction and academic achievement in nursing students. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 2021; 28(4):520–529. https://doi.org/10.7739/jkafn.2021.28.4.520.
Article13. Lee EJ, Baek GL. The effects of nursing education program combined virtual reality simulation for enhancing critical performance: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Learn-Cent Curric Instr. 2022; 22(11):303–313. https://doi.org/10.22251/jlcci.2022.22.11.303.
Article14. Hwang S, Kim HK. The effects of maternal-child nursing clinical practicum using virtual reality on nursing students’ competencies: a systematic review. Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2022; 28(3):174–186. https://doi.org/10.4069/kjwhn.2022.09.13.
Article15. Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd ed. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates;1988. p. 52.16. Yang SH, Hong S. Development and effects of simulation practice program about family centered delivery care. Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2017; 23(1):52–61. https://doi.org/10.4069/kjwhn.2017.23.1.52.
Article17. Yoon J. Development of an instrument for the measurement of critical thinking disposition: in nursing [doctoral dissertation]. Seoul: Catholic University;2004. 64.18. Lee SJ, Jang YK, Lee HN, Bang GY. Study on the development of life-skills : communication, problem solving, and self-directed learning. Jincheon, Korea: Korean Educational Development Institute;2003. Report No. RR 2003-15-3.19. DiIorio C, Price ME. Description and use of the neuroscience nursing self-efficacy scale. J Neurosci Nurs. 2001; 33(3):130–135. https://doi.org/10.1097/01376517-200106000-00004.
Article20. Kim HY. Development and application of phased nursing simulation modules: based on a conceptual framework of 3-D nursing simulation education [dissertation]. Seoul: Seoul National University;2013. 168.21. Oh SY, Kim HS. The effect of virtual simulation learning experience on self-directed learning ability, self-efficacy, and educational satisfaction of nursing students. J Learn-Cent Curric Instr. 2020; 21(24):547–557. https://doi.org/10.22251/jlcci.2021.21.24.547.
Article22. Kim M, Kim S, Lee WS. Effects of a virtual reality simulation and a blended simulation of care for pediatric patient with asthma. Child Health Nurs Res. 2019; 25(4):496–506. https://doi.org/10.4094/chnr.2019.25.4.496.
Article23. Kim HY. Self-directed learning ability, confidence in nursing skills and learning satisfaction according to web-based pre-learning of nursing students [masters’ thesis]. Gwangju: Nambu University;2017. 60.24. Jho MY. Effects of writing reflective journal on meta-cognition and problem solving ability in nursing students taking a fundamental nursing skills course applying blended learning. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 2016; 23(4):430–439. https://doi.org/10.7739/jkafn.2016.23.4.430.
Article25. Bandura A. Self-efficacy: toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychol Rev. 1977; 84(2):191–215. https://doi.org/10.1037//0033-295x.84.2.191.
Article26. Verkuyl M, Romaniuk D, Atack L, Mastrilli P. Virtual gaming simulation for nursing education: an experiment. Clin Simul Nurs. 2017; 13(5):238–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecns.2017.02.004.
Article27. Kim SH. Effects of the self-regulated learning in the mathematics class to the academic achievement levels, academic self-efficacy and self-determination motivation. J Curric Instr Stud. 2016; 9(2):15–38.28. Song MS, Cho H. Structural equation model of self-regulated learning among nursing students for convergence education. J Korea Converg Soc. 2019; 10(11):533–541. https://doi.org/10.15207/JKCS.2019.10.11.533.
Article29. Seo YS. Effects of blended simulation on normal neonatal nursing. J Korea Entertain Ind Assoc. 2022; 16(7):259–267. https://doi.org/10.21184/jkeia.2022.10.16.7.259.
Article30. Kim S, Kim MJ. Effect of learner-centered virtual reality simulation education. J Digit Converg. 2022; 20(4):705–713. https://doi.org/10.14400/JDC.2022.20.4.705.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects of Jigsaw Cooperation Learning on Communication Ability, Problem Solving Ability, Critical Thinking Disposition, Self-directed Learning Ability and Cooperation of Nursing Students
- Metacognition, Learning Flow and Problem Solving Ability in Nursing Simulation Learning
- Effects of integrative simulation practice on nursing knowledge, critical thinking, problem-solving ability, and immersion in problem-based learning among nursing students
- Planning and Applying Simulation-based Practice for the Achievement of Program Outcomes in Nursing Students
- The Relationship of Core Competencies(Problem Solving Ability, Communication Ability, Self-directed Learning Ability) to Critical Thinking