Korean J Transplant.
2023 Jun;37(2):95-102. 10.4285/kjt.23.0020.
Safely navigating kidney transplantation during the COVID-19 pandemic: the Singapore General Hospital’s experience
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Renal Medicine, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore
- 2Renal Transplant Program, SingHealth Duke-NUS Transplant Centre, Singapore
- 3Department of Nursing, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore
- KMID: 2544113
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/kjt.23.0020
Abstract
- Background
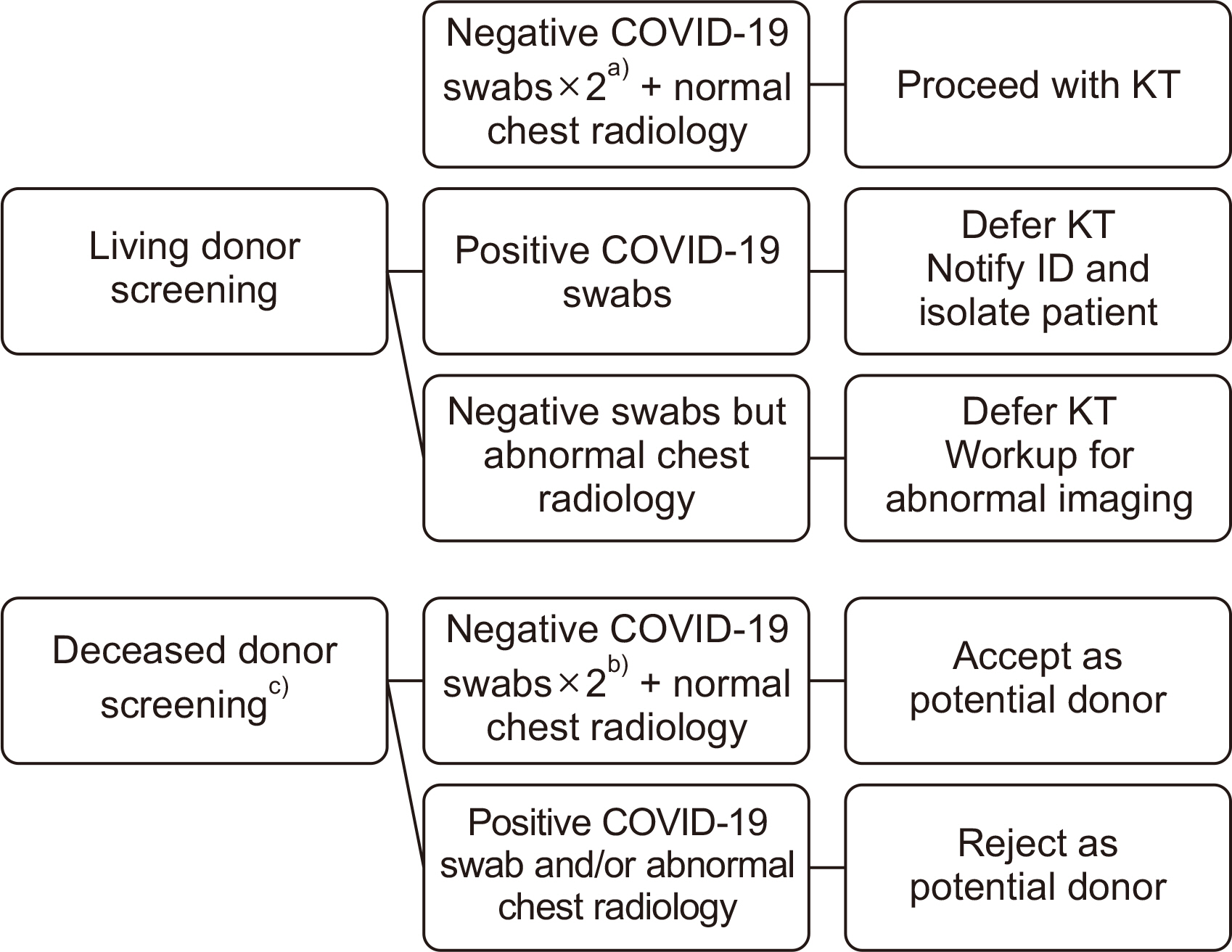
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic curtailed transplant activities worldwide, driven by concerns about increased COVID-19-related mortality among kidney transplant recipients (KTRs), infections originating from donors, and decreased availability of surgical and intensive care resources as healthcare resources are reallocated for pandemic response. We examined the outcomes of KTRs at our center before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective single-center cohort study examining the characteristics and outcomes of patients undergoing kidney transplantation during two periods: January 1, 2017 to December 31, 2019 (pre-COVID-19 era) and January 1, 2020 to June 30, 2022 (COVID-19 era). We reviewed perioperative and COVID-19 infection-related outcomes in both groups.
Results
A total of 114 transplants were performed during the pre-COVID-19 era, while 74 transplants were conducted during the COVID-19 era. No differences in baseline demographics were observed. Additionally, there were no significant differences in perioperative outcomes, except for a longer cold ischemia time during the COVID-19 era. However, this did not result in an increased incidence of delayed graft function. Among the KTRs infected with COVID-19 during the pandemic era, no severe complications such as pneumonia, acute kidney injury, or death were reported.
Conclusions
With the global transition to an endemic phase of COVID-19, it is imperative to revitalize organ transplant activities. Effective containment workflow, good vaccination uptake, and prompt COVID-19 treatment are essential to ensure that transplants can proceed safely.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ministry of Health, Singapore (MOH). 2023. COVID-19 statistics [Internet]. MOH;Available from: https://www.moh.gov.sg. cited 2022 Dec 1.2. Kee T, Jeong JC, Ur-Rashid H, Begum NA, Arakama MH, Danguilan R, et al. 2021; Clinical characteristics, outcomes, and management of COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients across Asia: an ASTREGO report. Korean J Transplant. 35:218–29. DOI: 10.4285/kjt.21.0024. PMID: 35769859. PMCID: PMC9235460.
Article3. Kremer D, Pieters TT, Verhaar MC, Berger SP, Bakker SJ, van Zuilen AD, et al. 2021; A systematic review and meta-analysis of COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients: lessons to be learned. Am Transplant. 21:3936–45. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.16742. PMID: 34212499. PMCID: PMC9292797.
Article4. Ho QY, Sultana R, Lee TL, Thangaraju S, Kee T, Htay H. Coronavirus disease 2019 in kidney transplant recipients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Singapore Med J. 2021; Oct. 24. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.11622/smedj.2021171. DOI: 10.11622/smedj.2021171.
Article5. Mohamed IH, Chowdary PB, Shetty S, Sammartino C, Sivaprakasam R, Lindsey B, et al. 2021; Outcomes of renal transplant recipients with SARS-CoV-2 infection in the eye of the storm: a comparative study with waitlisted patients. Transplantation. 105:115–20. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003406. PMID: 33350626.
Article6. Jager KJ, Kramer A, Chesnaye NC, Couchoud C, Sánchez-Álvarez JE, Garneata L, et al. 2020; Results from the ERA-EDTA Registry indicate a high mortality due to COVID-19 in dialysis patients and kidney transplant recipients across Europe. Kidney Int. 98:1540–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.09.006. PMID: 32979369. PMCID: PMC7560263.
Article7. Goffin E, Candellier A, Vart P, Noordzij M, Arnol M, Covic A, et al. 2021; COVID-19-related mortality in kidney transplant and haemodialysis patients: a comparative, prospective registry-based study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 36:2094–105. DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfab200. PMID: 34132811. PMCID: PMC8394823.8. Meier-Kriesche HU, Port FK, Ojo AO, Rudich SM, Hanson JA, Cibrik DM, et al. 2000; Effect of waiting time on renal transplant outcome. Kidney Int. 58:1311–7. DOI: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.00287.x. PMID: 10972695.
Article9. Ho QY, Chung SJ, Gan VH, Ng LG, Tan BH, Kee TY. 2020; High-immunological risk living donor renal transplant during the COVID-19 outbreak: uncertainties and ethical dilemmas. Am J Transplant. 20:1949–51. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.15949. PMID: 32337825. PMCID: PMC7267290.
Article10. Tan EK, Koh YX, Kee T, Juhari JB, Tan TE, Sim DK, et al. 2020; Waitlisted transplant candidates' attitudes and concerns toward transplantation during COVID-19. Ann Transplant. 25:e926992. DOI: 10.12659/AOT.926992. PMID: 33289727. PMCID: PMC7735226.
Article11. Couzi L, Manook M, Caillard S, Épailly É, Barrou B, Anglicheau D, et al. 2021; Impact of Covid-19 on kidney transplant and waiting list patients: lessons from the first wave of the pandemic. Nephrol Ther. 17:245–51. DOI: 10.1016/j.nephro.2020.12.004. PMID: 33541842. PMCID: PMC7791308.
Article12. Thind AK, Beckwith H, Dattani R, Dhutia A, Gleeson S, Martin P, et al. 2021; Resuming deceased donor kidney transplantation in the COVID-19 era: what do patients want? Transplant Direct. 7:e678. DOI: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000001126. PMID: 33688577. PMCID: PMC7935425.
Article13. Heldman MR, Kates OS, Safa K, Kotton CN, Georgia SJ, Steinbrink JM, et al. 2022; Changing trends in mortality among solid organ transplant recipients hospitalized for COVID-19 during the course of the pandemic. Am J Transplant. 22:279–88. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.16840. PMID: 34514710. PMCID: PMC8653312.
Article14. Cochran W, Shah P, Barker L, Langlee J, Freed K, Boyer L, et al. 2022; COVID-19 clinical outcomes in solid organ transplant recipients during the Omicron surge. Transplantation. 106:e346–7. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000004162. PMID: 35404880. PMCID: PMC9213060.
Article15. Ministry of Health, Singapore. Advisory on health measures for organ and tissue recovery and transplantation: COVID-19 Dorscon Orange. Ministry of Health, Singapore;2020.16. Ministry of Health, Singapore. Update to booster vaccine recommendations. Ministry of Health, Singapore;2022.17. Liew IT, Kadir HA, Thangaraju S, Ho QY, Ng E, Foo F, et al. COVID-19 vaccine acceptance among kidney transplant recipients in Singapore. Singapore Med J. 2023; Apr. 26. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.4103/singaporemedj.SMJ-2021-332. DOI: 10.4103/singaporemedj.SMJ-2021-332. PMID: 37171427.
Article18. Liew IT, Tan WJ, Ho QY, Thangaraju S, Yong JH, Ng E, et al. 2022; COVID-19 infected kidney transplant patients outpatient management-a single-center experience with a hospital-at-home program. Transplantation. 106:e525–7. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000004379. PMID: 36173624. PMCID: PMC9696754.
Article19. Lee J, Kim EJ, Ihn K, Lee JG, Joo DJ, Kim MS, et al. 2020; The feasibility of organ transplantation during the COVID-19 outbreak: experiences from South Korea. Korean J Transplant. 34:257–64. DOI: 10.4285/kjt.20.0048. PMID: 35770112. PMCID: PMC9187045.
Article20. Jha PK, Yadav DK, Siddini V, Bansal SB, Sharma R, Anandh U, et al. 2021; A retrospective multi-center experience of renal transplants from India during COVID-19 pandemic. Clin Transplant. 35:e14423. DOI: 10.1111/ctr.14423. PMCID: PMC8420412.
Article21. Tsapepas D, Paget K, Mohan S, Cohen DJ, Husain SA. 2021; Clinically significant COVID-19 following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in kidney transplant recipients. Am J Kidney Dis. 78:314–7. DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.05.004. PMID: 34019949. PMCID: PMC8129995.
Article22. Ravanan R, Mumford L, Ushiro-Lumb I, Callaghan C, Pettigrew G, Thorburn D, et al. 2021; Two doses of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines reduce risk of death due to COVID-19 in solid organ transplant recipients: preliminary outcomes from a UK registry linkage analysis. Transplantation. 105:e263–4. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003908. PMID: 34310530. PMCID: PMC8549134.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Insights and pearls of healthcare systems management of COVID-19 in Asia and its relevance to Asian transplant services
- COVID -19: Protection of Workers at the Workplace in Singapore
- The Safe Conduct of Echocardiographic Studies During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Perspectives and Experience from a Tertiary Echocardiography Laboratory in Singapore
- Surviving the COVID-19 pandemic: early response of a gynecologic oncology unit in Singapore
- Comparison of kidney transplant outcomes before and after COVID-19 pandemic: a single-institution experience