Int J Thyroidol.
2022 Nov;15(2):131-134. 10.11106/ijt.2022.15.2.131.
Effect of Afatinib for Lung Cancer on Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Yonsei University College of Medicine, Thyroid Cancer Center, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Surgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Institute of Refractory Thyroid Cancer, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2536500
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11106/ijt.2022.15.2.131
Abstract
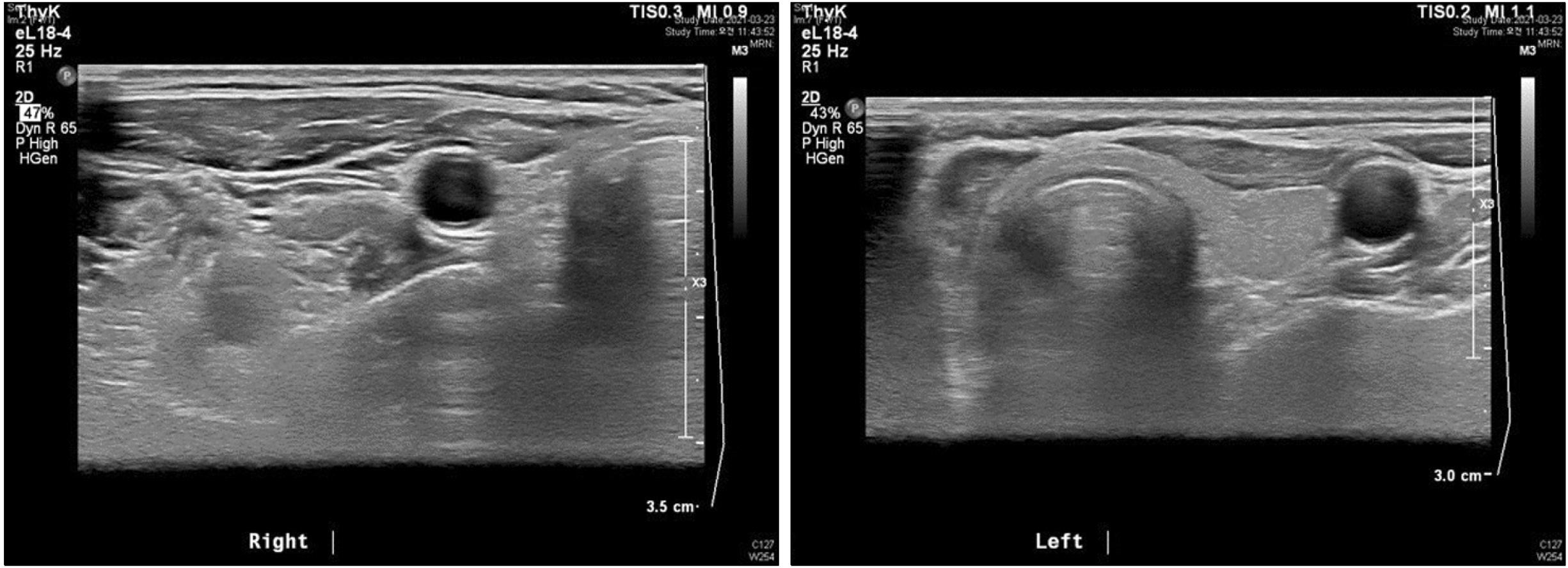
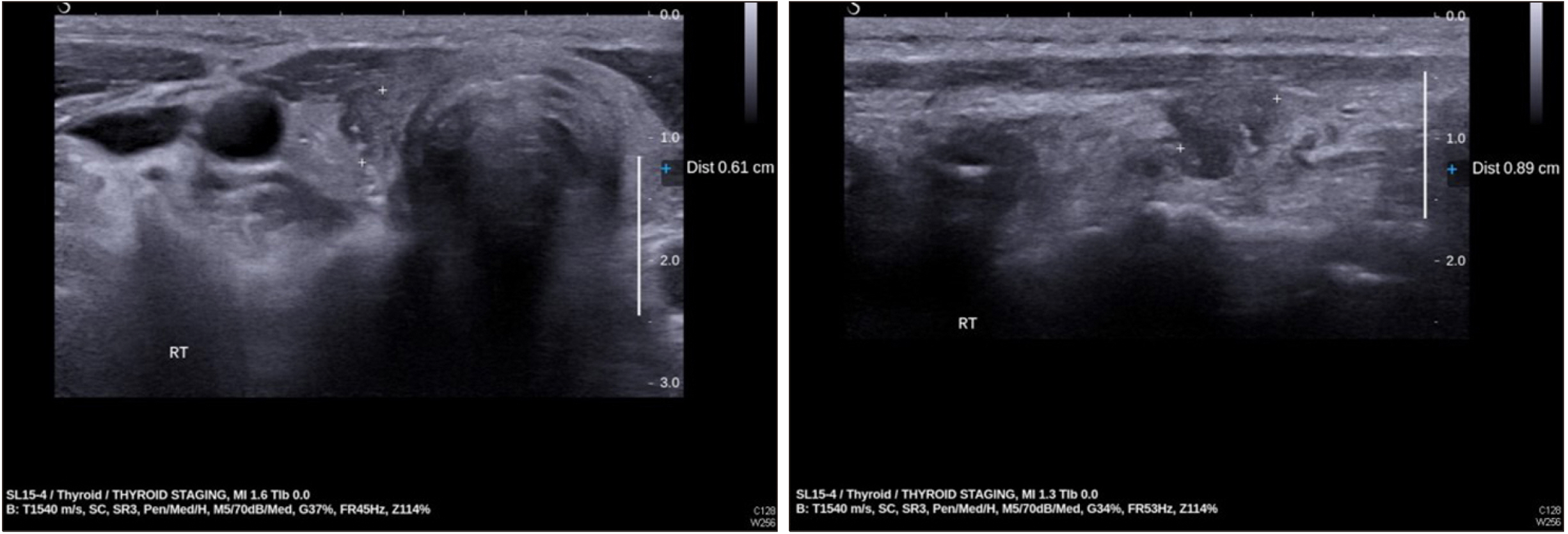
- Papillary thyroid carcinoma is the most common type of thyroid cancer, for which surgery following preoperative staging and risk assessment is the standard treatment. Afatinib is an orally active irreversible ErbB-family inhibitor that binds to the kinase domain of epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFRs), HER2, and HER4, and has been approved as monotherapy for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer with activated EGFR mutations. Recently, we observed an unexpected effect of afatinib administered to treat lung cancer on untreated papillary thyroid carcinoma.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Korea Central Cancer Registry. Annual report of cancer statistics in Korea in 2019. 2021; 2021:66.2. Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, Doherty GM, Mandel SJ, Nikiforov YE, et al. 2016; 2015 American Thyroid Association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: the American Thyroid Association guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 26(1):1–133. DOI: 10.1089/thy.2015.0020. PMID: 26462967. PMCID: PMC4739132.
Article3. Wind S, Schnell D, Ebner T, Freiwald M, Stopfer P. 2017; Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of afatinib. Clin Pharmacokinet. 56(3):235–50. DOI: 10.1007/s40262-016-0440-1. PMID: 27470518. PMCID: PMC5315738.
Article4. Keating GM. 2014; Afatinib: a review of its use in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Drugs. 74(2):207–21. DOI: 10.1007/s40265-013-0170-8. PMID: 24435321.
Article5. Fallahi P, Mazzi V, Vita R, Ferrari SM, Materazzi G, Galleri D, et al. 2015; New therapies for dedifferentiated papillary thyroid cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 16(3):6153–82. DOI: 10.3390/ijms16036153. PMID: 25789503. PMCID: PMC4394525.
Article6. Zhang H, Gao B, Shi B. 2016; Identification of differentially expressed kinase and screening potential anticancer drugs in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Dis Markers. 2016:2832980. DOI: 10.1155/2016/2832980. PMID: 27703281. PMCID: PMC5040815.
Article7. Dai Y-J, Qiu Y-B, Jiang R, Xu M, Zhao L, Chen GG, et al. 2017; Concomitant high expression of ERα36, EGFR and HER2 is associated with aggressive behaviors of papillary thyroid carcinomas. Sci Rep. 7(1):12279. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-12478-1. PMID: 28947799. PMCID: PMC5612999.
Article8. Tang C, Yang L, Wang N, Li L, Xu M, Chen GG, et al. 2014; High expression of GPER1, EGFR and CXCR1 is associated with lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7(6):3213–23.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Masquerading as Metastatic Papillary Thyroid Cancer
- Metastatic Lung Nodule of Thyroid Papillary Carcinoma, Mimicking Primary Lung Cancer
- Concurrent Medullay and Papillary Carcinoma of the Thyroid
- A Case of Ectopic Thyroid Papillary Carcinoma with Incidental Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
- Concurrent Papillary and Medullary Carcinoma of the Thyroid Gland