J Liver Cancer.
2022 Sep;22(2):183-187. 10.17998/jlc.2022.08.03.
Novel management of expected post-radiotherapy complications in hepatocellular carcinoma patients: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kangwon National University Hospital, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea
- 2Department of Radiology, Kangwon National University Hospital, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, Kangwon National University Hospital, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea
- KMID: 2534245
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.08.03
Abstract
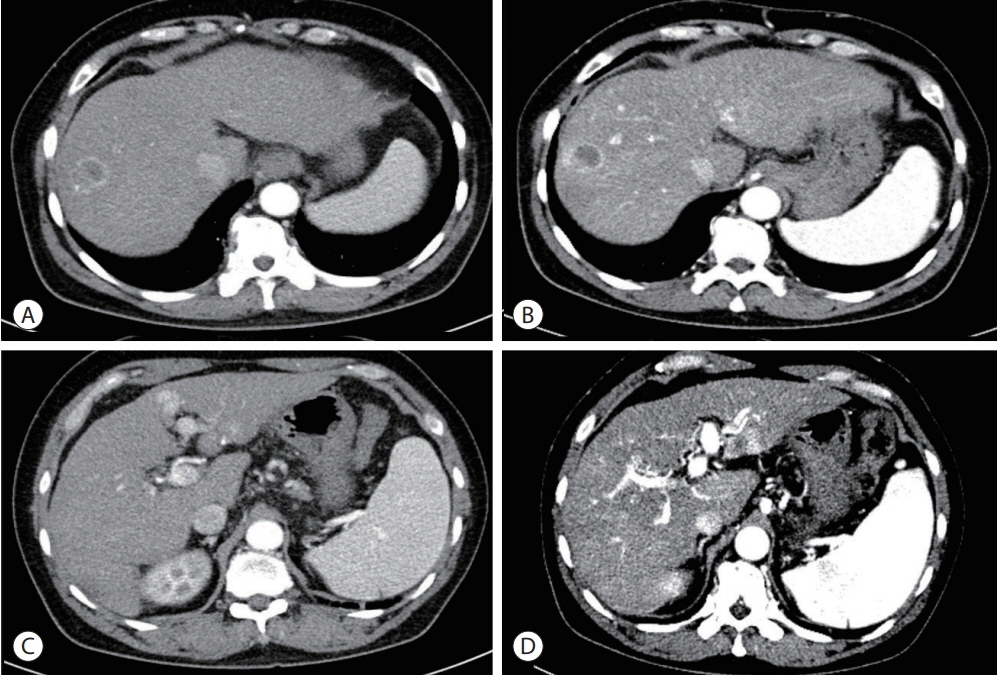
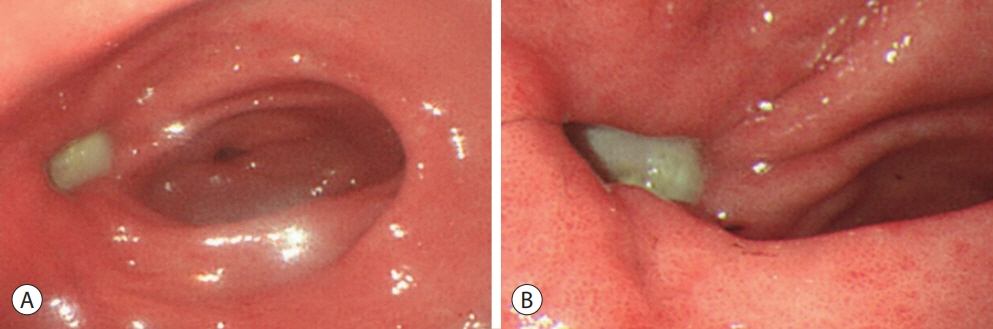
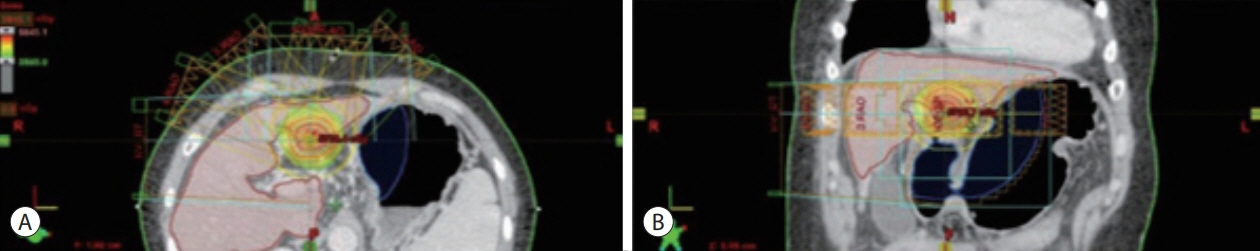
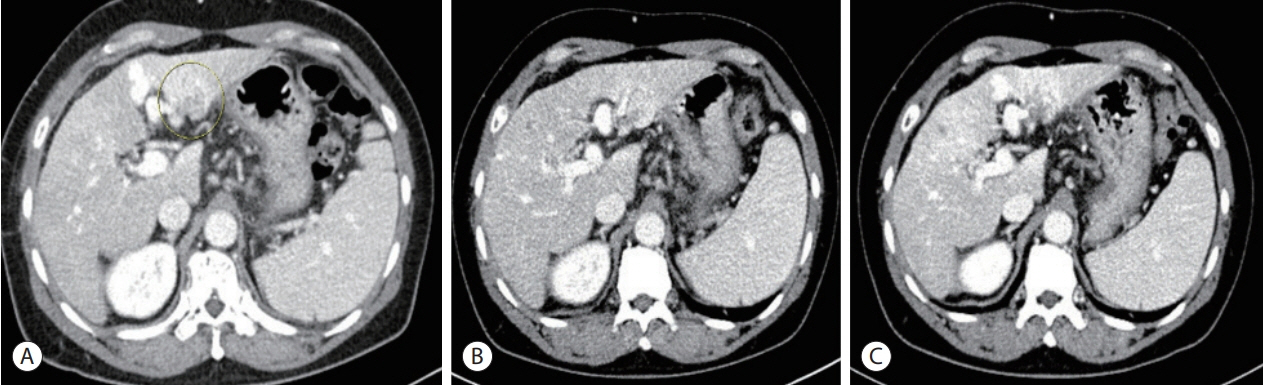
- In recent years, radiotherapy (RT) has been used to treat hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) at each stage. This clinical trend has developed with the increasing improvement of RT techniques, which show clinical results comparable to those of other treatment modalities. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy uses a high radiation dose to improve treatment effectiveness. However, the associated radiation toxicity can damage adjacent organs. Radiation-induced gastric damage with gastric ulcers is a complication of RT. This report presents a novel management strategy for preventing post-RT gastric ulcers. We present the case of a 53-year-old male patient diagnosed with HCC, who experienced gastric ulcer after RT. Before the second round of RT, the patient was administered a gas-foaming agent, which was effective in preventing RT complications.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021; 71:209–249.2. Hong S, Won YJ, Lee JJ, Jung KW, Kong HJ, Im JS, et al. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2018. Cancer Res Treat. 2021; 53:301–315.3. Delis SG, Dervenis C. Selection criteria for liver resection in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and chronic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14:3452–3460.4. Villanueva A. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:1450–1462.5. McKay MJ, Foster R. Pathobiology, irradiation dosimetric parameters and therapy of radiation-induced gastric damage: a narrative review. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021; 12:3115–3122.6. Kim BK, Kim SU, Park JY, Kim DY, Ahn SH, Park MS, et al. Applicability of BCLC stage for prognostic stratification in comparison with other staging systems: single centre experience from longterm clinical outcomes of 1717 treatment-naïve patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2012; 32:1120–1127.7. Hwang SY, Lee SM, Im JW, Kim JS, Ahn SB, Ji EK, et al. A case of perforation of gastric ulcer after complete remission of huge hepatocellular carcinoma invading main portal vein with combination therapy of stereotactic body radiation therapy and sorafenib. J Liver Cancer. 2014; 14:46–52.8. Lee KJ, Yoon HI, Chung MJ, Park JY, Bang S, Park SW, et al. A comparison of gastrointestinal toxicities between intensity-modulated radiotherapy and three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for pancreatic cancer. Gut Liver. 2016; 10:303–309.9. Andreyev J. Gastrointestinal symptoms after pelvic radiotherapy: a new understanding to improve management of symptomatic patients. Lancet Oncol. 2007; 8:1007–1017.10. Disher B, Hajdok G, Gaede S, Battista JJ. An in-depth Monte Carlo study of lateral electron disequilibrium for small fields in ultra-low density lung: implications for modern radiation therapy. Phys Med Biol. 2012; 57:1543–1559.11. Hannallah D, Zhu TC, Bjärngard BE. Electron disequilibrium in high-energy x-ray beams. Med Phys. 1996; 23:1867–1871.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Metastatic Omental Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Two Cases Report
- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis Treated by Hepatic Artery Injection Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy
- Recent developments in radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma
- Current status of stereotactic body radiotherapy for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- A case of metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma to orbit with superior orbital fissure syndrome