Yeungnam Univ J Med.
2019 Sep;36(3):192-200. 10.12701/yujm.2019.00269.
Current status of stereotactic body radiotherapy for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea. mkkang@knu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2460187
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00269
Abstract
- Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) is an advanced form of radiotherapy (RT) with a growing interest on its application in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). It can deliver ablative radiation doses to tumors in a few fractions without excessive doses to normal tissues, with the help of advanced modern RT and imaging technologies. Currently, SBRT is recommended as an alternative to curative treatments, such as surgery and radiofrequency ablation. This review discusses the current status of SBRT to aid in the decision making on how it is incorporated into the HCC management.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
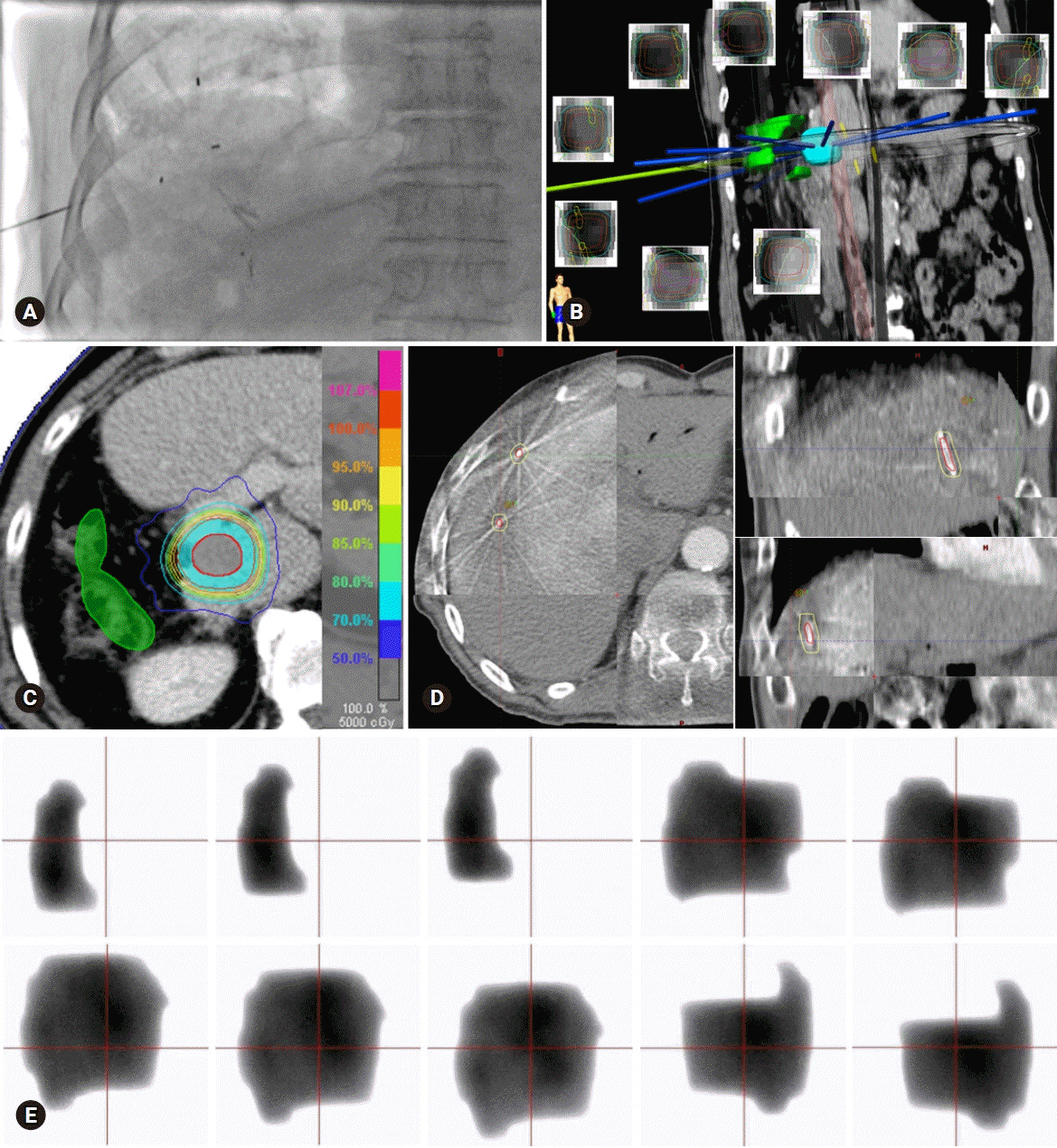
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Jung KW, Won YJ, Kong HJ, Lee ES; Community of Population-Based Regional Cancer Registries. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2015. Cancer Res Treat. 2018; 50:303–16.
Article2. Perz JF, Armstrong GL, Farrington LA, Hutin YJ, Bell BP. The contributions of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infections to cirrhosis and primary liver cancer worldwide. J Hepatol. 2006; 45:529–38.
Article3. Ock M, Choi WJ, Jo MW. Trend analysis of major cancer statistics according to sex and severity levels in Korea. PLoS One. 2018; 13:e0203110.
Article4. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2018; 69:182–236.5. Korean Liver Cancer Association; National Cancer Center. 2018 Korean Liver Cancer Association-National Cancer Center Korea Practice Guidelines for the management of hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gut Liver. 2019; 13:227–99.6. Delis SG, Dervenis C. Selection criteria for liver resection in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and chronic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14:3452–60.
Article7. Tiong L, Maddern GJ. Systematic review and meta-analysis of survival and disease recurrence after radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Surg. 2011; 98:1210–24.
Article8. Benedict SH, Yenice KM, Followill D, Galvin JM, Hinson W, Kavanagh B, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy: the report of AAPM Task Group 101. Med Phys. 2010; 37:4078–101.
Article9. Rim CH, Kim HJ, Seong J. Clinical feasibility and efficacy of stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Radiother Oncol. 2019; 131:135–44.
Article10. Vogel A, Cervantes A, Chau I, Daniele B, Llovet J, Meyer T, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2018; 29(Suppl 4):iv238–55.
Article11. Murray LJ, Dawson LA. Advances in stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2017; 27:247–55.
Article12. Yoon SM, Lim YS, Park MJ, Kim SY, Cho B, Shim JH, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy as an alternative treatment for small hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e79854.
Article13. Sanuki N, Takeda A, Oku Y, Mizuno T, Aoki Y, Eriguchi T, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for small hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective outcome analysis in 185 patients. Acta Oncol. 2014; 53:399–404.
Article14. Sanuki N, Takeda A, Kunieda E. Role of stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:3100–11.
Article15. Dawson LA, Brock KK, Kazanjian S, Fitch D, McGinn CJ, Lawrence TS, et al. The reproducibility of organ position using active breathing control (ABC) during liver radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001; 51:1410–21.
Article16. Herfarth KK, Debus J, Lohr F, Bahner ML, Fritz P, Höss A, et al. Extracranial stereotactic radiation therapy: set-up accuracy of patients treated for liver metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000; 46:329–35.
Article17. Brock KK. Imaging and image-guided radiation therapy in liver cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2011; 21:247–55.
Article18. Park SH, Kim JC, Kang MK. Technical advances in external radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2016; 22:7311–21.
Article19. Scorsetti M, Comito T, Cozzi L, Clerici E, Tozzi A, Franzese C, et al. The challenge of inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): results of a single-institutional experience on stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT). J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015; 141:1301–9.
Article20. Lee KH, Yu JI, Park HC, Park SY, Shin JS, Shin EH, et al. Is higher dose always the right answer in stereotactic body radiation therapy for small hepatocellular carcinoma? Radiat Oncol J. 2018; 36:129–38.
Article21. Jang WI, Kim MS, Bae SH, Cho CK, Yoo HJ, Seo YS, et al. High-dose stereotactic body radiotherapy correlates increased local control and overall survival in patients with inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiat Oncol. 2013; 8:250.
Article22. Mizumoto M, Okumura T, Hashimoto T, Fukuda K, Oshiro Y, Fukumitsu N, et al. Proton beam therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a comparison of three treatment protocols. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011; 81:1039–45.
Article23. Kasuya G, Kato H, Yasuda S, Tsuji H, Yamada S, Haruyama Y, et al. Progressive hypofractionated carbon-ion radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: combined analyses of 2 prospective trials. Cancer. 2017; 123:3955–65.
Article24. Toramatsu C, Katoh N, Shimizu S, Nihongi H, Matsuura T, Takao S, et al. What is the appropriate size criterion for proton radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma? A dosimetric comparison of spot-scanning proton therapy versus intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Radiat Oncol. 2013; 8:48.
Article25. Gandhi SJ, Liang X, Ding X, Zhu TC, Ben-Josef E, Plastaras JP, et al. Clinical decision tool for optimal delivery of liver stereotactic body radiation therapy: Photons versus protons. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2015; 5:209–18.
Article26. Blomgren H, Lax I, Näslund I, Svanström R. Stereotactic high dose fraction radiation therapy of extracranial tumors using an accelerator. Clinical experience of the first thirty-one patients. Acta Oncol. 1995; 34:861–70.
Article27. Shiozawa K, Watanabe M, Ikehara T, Matsukiyo Y, Kogame M, Kishimoto Y, et al. Comparison of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and CyberKnife® for initial solitary hepatocellular carcinoma: A pilot study. World J Gastroenterol. 2015; 21:13490–9.
Article28. Wahl DR, Stenmark MH, Tao Y, Pollom EL, Caoili EM, Lawrence TS, et al. Outcomes after stereotactic body radiotherapy or radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2016; 34:452–9.
Article29. Bujold A, Massey CA, Kim JJ, Brierley J, Cho C, Wong RK, et al. Sequential phase I and II trials of stereotactic body radiotherapy for locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31:1631–9.
Article30. Rhim H, Yoon KH, Lee JM, Cho Y, Cho JS, Kim SH, et al. Major complications after radio-frequency thermal ablation of hepatic tumors: spectrum of imaging findings. Radiographics. 2003; 23:123–34.
Article31. Rice SL, Bale R, Breen DJ, de Baere T, Denys A, Guiu B, et al. The management of colorectal cancer liver metastases: the interventional radiology viewpoint. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019; 103:537–9.
Article32. Lee S, Kim H, Ji Y, Cho B, Kim SS, Jung J, et al. Evaluation of hepatic toxicity after repeated stereotactic body radiation therapy for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma using deformable image registration. Sci Rep. 2018; 8:16224.
Article33. Rajyaguru DJ, Borgert AJ, Smith AL, Thomes RM, Conway PD, Halfdanarson TR, et al. Radiofrequency ablation versus stereotactic body radiotherapy for localized hepatocellular carcinoma in nonsurgically managed patients: analysis of the national cancer database. J Clin Oncol. 2018; 36:600–8.
Article34. Nakano R, Ohira M, Kobayashi T, Ide K, Tahara H, Kuroda S, et al. Hepatectomy versus stereotactic body radiotherapy for primary early hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity-matched analysis in a single institution. Surgery. 2018; 164:219–26.
Article35. Su TS, Liang P, Liang J, Lu HZ, Jiang HY, Cheng T, et al. Long-term survival analysis of stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus liver resection for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017; 98:639–46.
Article36. Pan CC, Kavanagh BD, Dawson LA, Li XA, Das SK, Miften M, et al. Radiation-associated liver injury. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010; 76(3 Suppl):S94–100.
Article37. Liang SX, Zhu XD, Xu ZY, Zhu J, Zhao JD, Lu HJ, et al. Radiation-induced liver disease in three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy for primary liver carcinoma: the risk factors and hepatic radiation tolerance. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006; 65:426–34.
Article38. Jung J, Yoon SM, Kim SY, Cho B, Park JH, Kim SS, et al. Radiation-induced liver disease after stereotactic body radiotherapy for small hepatocellular carcinoma: clinical and dose-volumetric parameters. Radiat Oncol. 2013; 8:249.
Article39. Culleton S, Jiang H, Haddad CR, Kim J, Brierley J, Brade A, et al. Outcomes following definitive stereotactic body radiotherapy for patients with Child-Pugh B or C hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiother Oncol. 2014; 111:412–7.
Article40. Su TS, Liang P, Lu HZ, Liang J, Gao YC, Zhou Y, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for small primary or recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma in 132 Chinese patients. J Surg Oncol. 2016; 113:181–7.
Article41. Dawson LA. Overview: where does radiation therapy fit in the spectrum of liver cancer local-regional therapies? Semin Radiat Oncol. 2011; 21:241–6.
Article42. Kavanagh BD, Pan CC, Dawson LA, Das SK, Li XA, Ten Haken RK, et al. Radiation dose-volume effects in the stomach and small bowel. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010; 76(3 Suppl):S101–7.
Article43. Bae SH, Kim MS, Kim SY, Jang WI, Cho CK, Yoo HJ, et al. Severe intestinal toxicity after stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for abdominopelvic malignancies. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2013; 28:1707–13.
Article44. LaCouture TA, Xue J, Subedi G, Xu Q, Lee JT, Kubicek G, et al. Small bowel dose tolerance for stereotactic body radiation therapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2016; 26:157–64.
Article45. Goldsmith C, Price P, Cross T, Loughlin S, Cowley I, Plowman N. Dose-volume histogram analysis of stereotactic body radiotherapy treatment of pancreatic cancer: a focus on duodenal dose constraints. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2016; 26:149–56.
Article46. Yamashita H, Onishi H, Murakami N, Matsumoto Y, Matsuo Y, Nomiya T, et al. Survival outcomes after stereotactic body radiotherapy for 79 Japanese patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Radiat Res. 2015; 56:561–7.
Article47. Sapir E, Tao Y, Schipper MJ, Bazzi L, Novelli PM, Devlin P, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy as an alternative to transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018; 100:122–30.
Article48. Jeong Y, Jung J, Cho B, Kwak J, Jeong C, Kim JH, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy using a respiratory-gated volumetric-modulated arc therapy technique for small hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2018; 18:416.
Article49. Eriguchi T, Takeda A, Sanuki N, Oku Y, Aoki Y, Shigematsu N, et al. Acceptable toxicity after stereotactic body radiation therapy for liver tumors adjacent to the central biliary system. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013; 85:1006–11.
Article50. Toesca DA, Osmundson EC, Eyben RV, Shaffer JL, Lu P, Koong AC, et al. Central liver toxicity after SBRT: an expanded analysis and predictive nomogram. Radiother Oncol. 2017; 122:130–6.
Article51. O'Connor JK, Trotter J, Davis GL, Dempster J, Klintmalm GB, Goldstein RM. Long-term outcomes of stereotactic body radiation therapy in the treatment of hepatocellular cancer as a bridge to transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2012; 18:949–54.52. Andolino DL, Johnson CS, Maluccio M, Kwo P, Tector AJ, Zook J, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011; 81:e447–53.
Article53. Sapisochin G, Barry A, Doherty M, Fischer S, Goldaracena N, Rosales R, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy vs. TACE or RFA as a bridge to transplant in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. An intention-to-treat analysis. J Hepatol. 2017; 67:92–9.
Article54. Mohamed M, Katz AW, Tejani MA, Sharma AK, Kashyap R, Noel MS, et al. Comparison of outcomes between SBRT, yttrium-90 radioembolization, transarterial chemoembolization, and radiofrequency ablation as bridge to transplant for hepatocellular carcinoma. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2015; 1:35–42.
Article55. Kim JY, Chung SM, Choi BO, Kay CS. Hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: Improved treatment outcomes with external beam radiation therapy. Hepatol Res. 2011; 41:813–24.
Article56. Im JH, Yoon SM, Park HC, Kim JH, Yu JI, Kim TH, et al. Radiotherapeutic strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumour thrombosis in a hepatitis B endemic area. Liver Int. 2017; 37:90–100.
Article57. Bae SH, Kim MS, Jang WI, Kim JH, Kim WC, Kim JH, et al. Multicenter planning comparison of stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with major portal vein tumor thrombosis (KROG 16-17). J Liver Cancer. 2018; 18:130–41.
Article58. Xi M, Zhang L, Zhao L, Li QQ, Guo SP, Feng ZZ, et al. Effectiveness of stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein and/or inferior vena cava tumor thrombosis. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e63864.
Article59. Kang J, Nie Q, DU R, Zhang L, Zhang J, Li Q, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy combined with transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. Mol Clin Oncol. 2014; 2:43–50.
Article60. Shui Y, Yu W, Ren X, Guo Y, Xu J, Ma T, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy based treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma with extensive portal vein tumor thrombosis. Radiat Oncol. 2018; 13:188.
Article61. Meng MB, Cui YL, Lu Y, She B, Chen Y, Guan YS, et al. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in combination with radiotherapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiother Oncol. 2009; 92:184–94.
Article62. Jacob R, Turley F, Redden DT, Saddekni S, Aal AK, Keene K, et al. Adjuvant stereotactic body radiotherapy following transarterial chemoembolization in patients with non-resectable hepatocellular carcinoma tumours of ≥3 cm. HPB (Oxford). 2015; 17:140–9.63. Paik EK, Kim MS, Jang WI, Seo YS, Cho CK, Yoo HJ, et al. Benefits of stereotactic ablative radiotherapy combined with incomplete transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiat Oncol. 2016; 11:22.
Article64. Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:378–90.
Article65. Yu W, Gu K, Yu Z, Yuan D, He M, Ma N, et al. Sorafenib potentiates irradiation effect in hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett. 2013; 329:109–17.
Article66. Barney BM, Markovic SN, Laack NN, Miller RC, Sarkaria JN, Macdonald OK, et al. Increased bowel toxicity in patients treated with a vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor (VEGFI) after stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013; 87:73–80.
Article67. Brade AM, Ng S, Brierley J, Kim J, Dinniwell R, Ringash J, et al. Phase 1 trial of sorafenib and stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016; 94:580–7.
Article68. Kang J, Demaria S, Formenti S. Current clinical trials testing the combination of immunotherapy with radiotherapy. J Immunother Cancer. 2016; 4:51.
Article69. Bernstein MB, Krishnan S, Hodge JW, Chang JY. Immunotherapy and stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (ISABR): a curative approach? Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2016; 13:516–24.
Article70. Formenti SC. Optimizing dose per fraction: a new chapter in the story of the abscopal effect? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017; 99:677–9.
Article71. Vanpouille-Box C, Formenti SC, Demaria S. Toward precision radiotherapy for use with immune checkpoint blockers. Clin Cancer Res. 2018; 24:259–65.
Article72. Kim KJ, Kim JH, Lee SJ, Lee EJ, Shin EC, Seong J. Radiation improves antitumor effect of immune checkpoint inhibitor in murine hepatocellular carcinoma model. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:41242–55.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma Who Showed Complete Response by Combined Therapy of Transarterial Chemoembolization and Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy
- Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy: Does It Have a Role in Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma?
- Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Early Stage Lung Cancer
- Differences in radiotherapy application according to regional disease characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Recent developments in radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma