J Rheum Dis.
2022 Oct;29(4):223-231. 10.4078/jrd.22.0006.
Predictive Factors for Renal Response in Lupus Nephritis: A Single-center Prospective Cohort Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rheumatology, Hanyang University Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Korea
- 2Hanyang University Institute for Rheumatology, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2533623
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.22.0006
Abstract
Objective
To identify the predictive factors for renal response in patients with lupus nephritis (LN).
Methods
Patients and data were extracted from a prospective systemic lupus erythematosus cohort in Korea, in which clinical data were collected at 0, 3, 6, and 12 months after induction therapy. Treatment response of LN were evaluated as a complete response (CR), partial response (PR), or non-response (NR) at 3, 6, and 12 months, respectively. Predictive factors for CR at 6 months were evaluated using multivariable Poisson regression analysis.
Results
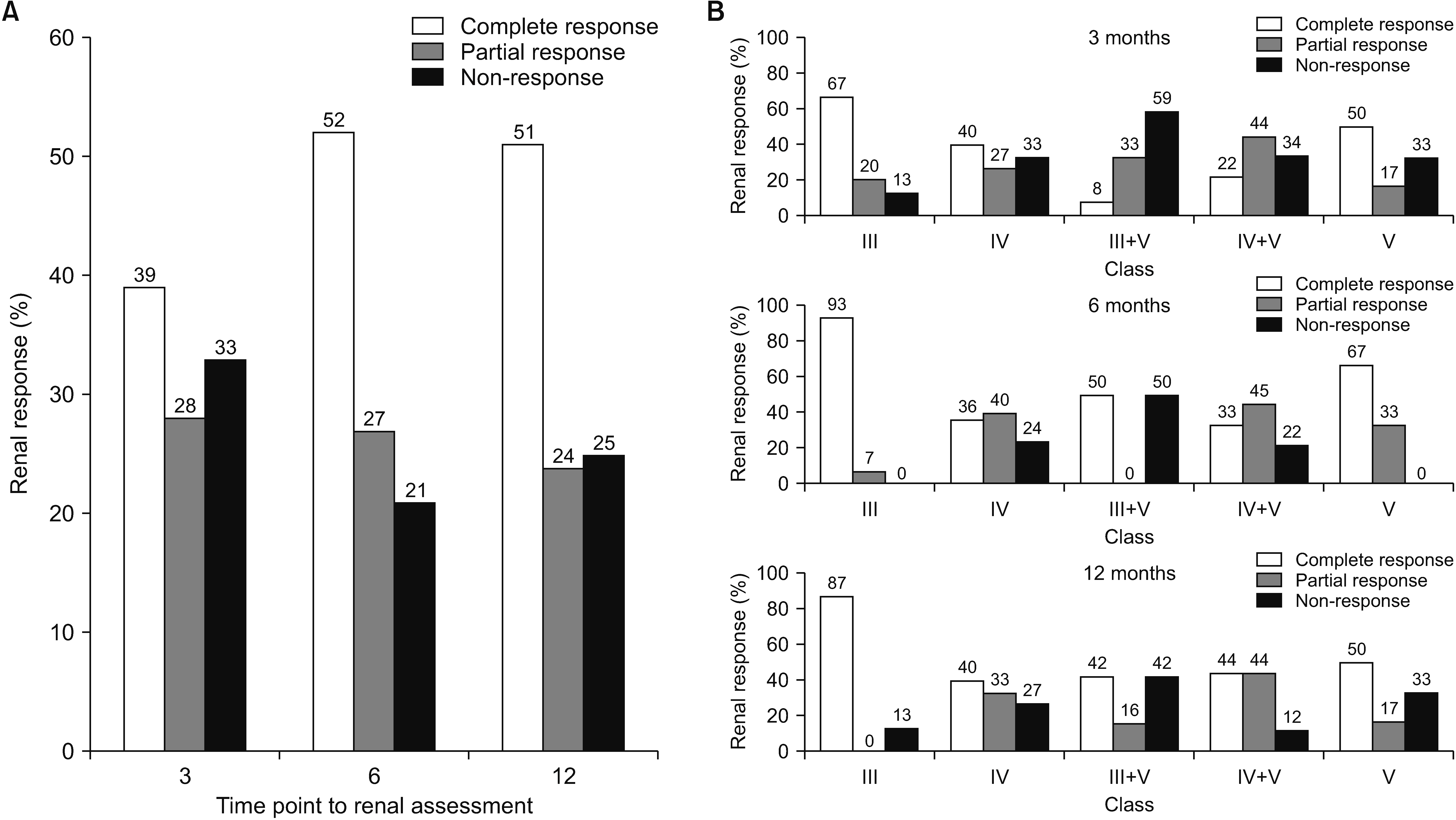
A total of 75 patients with LN who underwent biopsy was enrolled. The mean age at diagnosis of LN was 28.9±9.7 years, and 68 (90.7%) were female. The frequencies of classes III, IV, III+V, IV+V, and V were 20.0%, 44.0%, 16.0%, 12.0%, and 8.0%, respectively. Compared to relapsed LN, new-onset LN showed a lower percentage of glomerulosclerosis (45.5% vs. 76.2%, p=0.013). The overall proportions of CR, PR, and NR at 6 and 12 months were 52.0%, 26.7%, 21.3% and 50.7%, 24.0%, 25.3%, respectively. In multivariate analysis, age at enrollment (odds ratio [OR]=1.02, p=0.022), relapsed LN (OR=0.71, p=0.037), anti-Ro antibody (OR=0.67, p=0.014), and class III LN (OR=1.48, p=0.001) were associated with CR at 6 months.
Conclusion
In our prospective cohort, class III LN was a good predictive factor for CR at 6 months in patients with LN, whereas younger age, relapsed LN, and anti-Ro antibody were poor predictive factors.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hanly JG, O'Keeffe AG, Su L, Urowitz MB, Romero-Diaz J, Gordon C, et al. 2016; The frequency and outcome of lupus nephritis: results from an international inception cohort study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 55:252–62. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev311. PMID: 26342222. PMCID: PMC4939728.2. Bastian HM, Roseman JM, McGwin G Jr, Alarcón GS, Friedman AW, Fessler BJ, et al. 2002; Systemic lupus erythematosus in three ethnic groups. XII. Risk factors for lupus nephritis after diagnosis. Lupus. 11:152–60. DOI: 10.1191/0961203302lu158oa. PMID: 12004788.
Article3. Kalloo S, Aggarwal N, Mohan P, Radhakrishnan J. 2013; Lupus nephritis: treatment of resistant disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 8:154–61. DOI: 10.2215/CJN.05870612. PMID: 23296380.
Article4. Ichinose K, Kitamura M, Sato S, Eguchi M, Okamoto M, Endo Y, et al. 2019; Complete renal response at 12 months after induction therapy is associated with renal relapse-free rate in lupus nephritis: a single-center, retrospective cohort study. Lupus. 28:501–9. DOI: 10.1177/0961203319829827. PMID: 30755146.
Article5. Vajgel G, Oliveira CBL, Costa DMN, Cavalcante MAGM, Valente LM, Sesso R, et al. 2020; Initial renal histology and early response predict outcomes of Brazilian lupus nephritis patients. Lupus. 29:83–91. DOI: 10.1177/0961203319890681. PMID: 31801041.
Article6. Davidson JE, Fu Q, Ji B, Rao S, Roth D, Magder LS, et al. 2018; Renal remission status and longterm renal survival in patients with lupus nephritis: a retrospective cohort analysis. J Rheumatol. 45:671–7. DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.161554. PMID: 29496892. PMCID: PMC5932209.
Article7. Luís MSF, Bultink IEM, da Silva JAP, Voskuyl AE, Inês LS. 2021; Early predictors of renal outcome in patients with proliferative lupus nephritis: a 36-month cohort study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 60:5134–41. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab126. PMID: 33560332.
Article8. Park DJ, Choi SE, Xu H, Kang JH, Lee KE, Lee JS, et al. 2018; Chronicity index, especially glomerular sclerosis, is the most powerful predictor of renal response following immunosuppressive treatment in patients with lupus nephritis. Int J Rheum Dis. 21:458–67. DOI: 10.1111/1756-185X.13254. PMID: 29314776.
Article9. Okamoto M, Kitamura M, Sato S, Fujikawa K, Horai Y, Matsuoka N, et al. 2021; Life prognosis and renal relapse after induction therapy in Japanese patients with proliferative and pure membranous lupus nephritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 60:2333–41. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa599. PMID: 33166998.
Article10. Liu G, Wang H, Le J, Lan L, Xu Y, Yang Y, et al. 2019; Early-stage predictors for treatment responses in patients with active lupus nephritis. Lupus. 28:283–9. DOI: 10.1177/0961203319826703. PMID: 30682900.
Article11. Hochberg MC. 1997; Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 40:1725. DOI: 10.1002/art.1780400928. PMID: 9324032.
Article12. Petri M, Orbai AM, Alarcón GS, Gordon C, Merrill JT, Fortin PR, et al. 2012; Derivation and validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 64:2677–86. DOI: 10.1002/art.34473. PMID: 22553077. PMCID: PMC3409311.13. Gladman DD, Ibañez D, Urowitz MB. 2002; Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000. J Rheumatol. 29:288–91.14. Bajema IM, Wilhelmus S, Alpers CE, Bruijn JA, Colvin RB, Cook HT, et al. 2018; Revision of the International Society of Nephrology/Renal Pathology Society classification for lupus nephritis: clarification of definitions, and modified National Institutes of Health activity and chronicity indices. Kidney Int. 93:789–96. DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2017.11.023. PMID: 29459092.
Article15. Fanouriakis A, Kostopoulou M, Cheema K, Anders HJ, Aringer M, Bajema I, et al. 2020; 2019 Update of the Joint European League Against Rheumatism and European Renal Association-European Dialysis and Transplant Association (EULAR/ERA-EDTA) recommendations for the management of lupus nephritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 79:713–23. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-216924. PMID: 32220834.16. Hahn BH, McMahon MA, Wilkinson A, Wallace WD, Daikh DI, Fitzgerald JD, et al. 2012; American College of Rheumatology guidelines for screening, treatment, and management of lupus nephritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 64:797–808. DOI: 10.1002/acr.21664. PMID: 22556106. PMCID: PMC3437757.
Article17. Renal Disease Subcommittee of the American College of Rheumatology Ad Hoc Committee on Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Response Criteria. 2006; The American College of Rheumatology response criteria for proliferative and membranous renal disease in systemic lupus erythematosus clinical trials. Arthritis Rheum. 54:421–32. DOI: 10.1002/art.21625. PMID: 16453282.18. Cattran DC, Feehally J, Cook HT, Liu ZH, Fervenza FC, Mezzano SA, et al. 2012; Kidney disease: improving global outcomes (KDIGO) glomerulonephritis work group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int Suppl. 2:139–274.19. Choi SE, Park DJ, Kang JH, Lee KE, Xu H, Lee JS, et al. 2019; Comparison of renal responses to cyclophosphamide and mycophenolate mofetil used as induction therapies in Korean patients with lupus nephritis. J Rheum Dis. 26:57–65. DOI: 10.4078/jrd.2019.26.1.57.
Article20. Korbet SM, Lewis EJ. 2012; Complete remission in severe lupus nephritis: assessing the rate of loss in proteinuria. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 27:2813–9. DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfr741. PMID: 22199359.
Article21. Mok CC, To CH, Yu KL, Ho LY. 2013; Combined low-dose mycophenolate mofetil and tacrolimus for lupus nephritis with suboptimal response to standard therapy: a 12-month prospective study. Lupus. 22:1135–41. DOI: 10.1177/0961203313502864. PMID: 23995863.
Article22. Marinaki S, Kapsia E, Liapis G, Gakiopoulou H, Skalioti C, Kolovou K, et al. 2020; Clinical impact of repeat renal biopsies in patients with lupus nephritis: renal biopsy is essential especially later in the course of the disease. Eur J Rheumatol. 7:2–8. DOI: 10.5152/eurjrheum.2019.18146. PMID: 31782721. PMCID: PMC7001996.
Article23. Korbet SM, Lewis EJ, Schwartz MM, Reichlin M, Evans J, Rohde RD. 2000; Factors predictive of outcome in severe lupus nephritis. Lupus Nephritis Collaborative Study Group. Am J Kidney Dis. 35:904–14. DOI: 10.1016/S0272-6386(00)70262-9.24. Moon SJ, Park HS, Kwok SK, Ju JH, Choi BS, Park KS, et al. 2013; Predictors of renal relapse in Korean patients with lupus nephritis who achieved remission six months following induction therapy. Lupus. 22:527–37. DOI: 10.1177/0961203313476357. PMID: 23423249.
Article25. Sule SD, Moodalbail DG, Burnham J, Fivush B, Furth SL. 2015; Predictors of kidney disease in a cohort of pediatric patients with lupus. Lupus. 24:862–8. DOI: 10.1177/0961203315570162. PMID: 25680740. PMCID: PMC4466076.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Outcome and Predictive Factors for Remission and Relapse of Proliferative Lupus Nephritis after Intravenous Cyclophosphamide Pulse Therapy
- A case of Lupus Nephritis
- Clinical Outcome and Prognostic Factors of Biopsy-proven Diffuse Proliferative Lupus Nephritis
- A Case of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Involving the Kidneys in a Patient with IgA Nephropathy
- Initial Preserved Renal Function as a Predictor of Favorable Renal Response to Rituximab in Refractory or Relapsing Lupus Nephritis: A Single-center Cohort Study in Korea