Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2022 May;26(2):144-148. 10.14701/ahbps.21-130.
Elective splenectomy in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Does the size of the spleen affect surgical outcomes?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery, Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust, Exeter, United Kingdom
- 2Department of Medicine, Gemelli University Hospital, Rome, Italy
- 3Department of Surgery, Hospital Tor Vergata Roma, Rome, Italy
- KMID: 2530093
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.21-130
Abstract
- Backgrounds/Aims
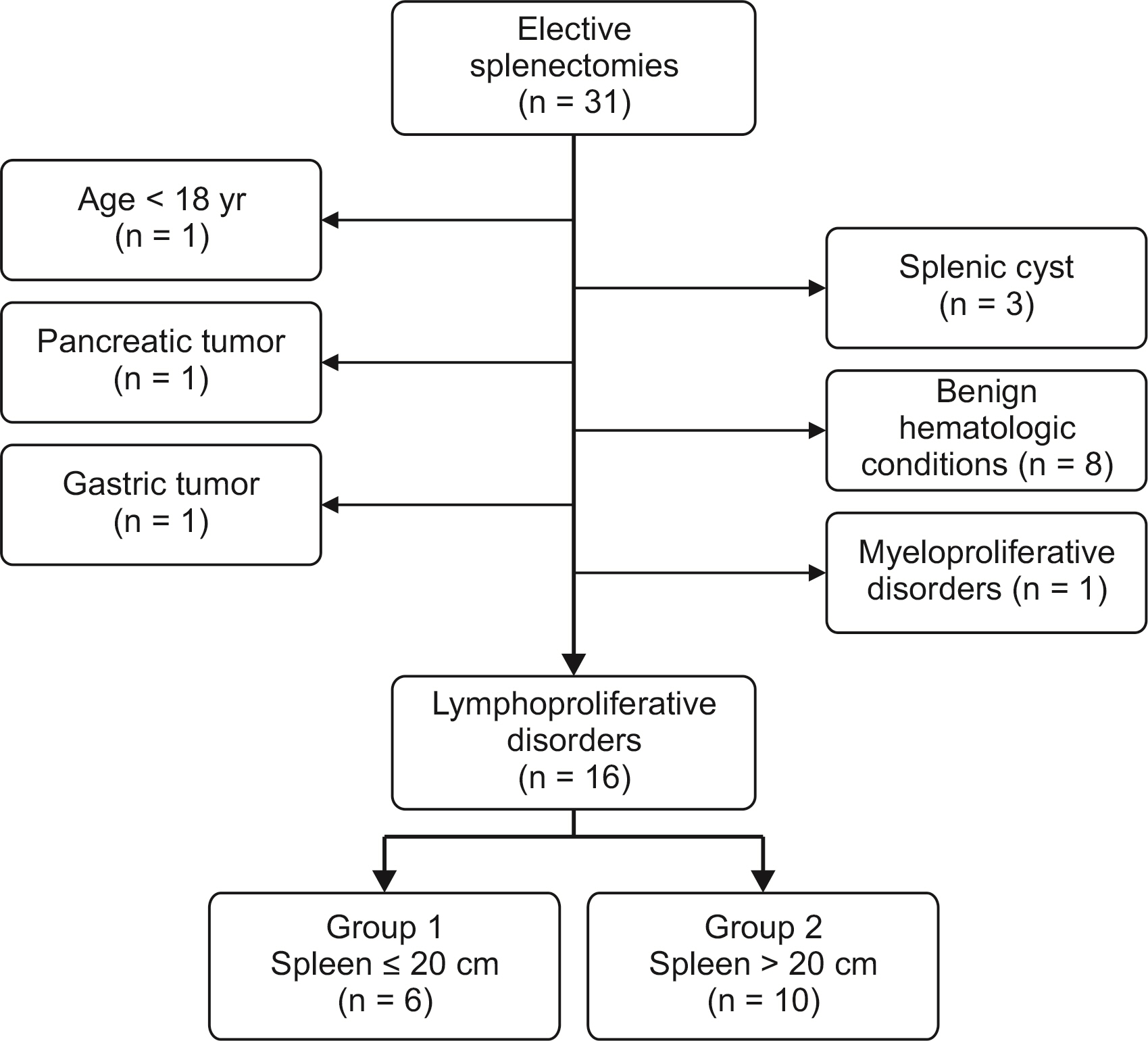
Splenectomy in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is performed to relieve abdominal symptoms, treat hypersplenism or confirm diagnosis. Excision of a very large spleen is technically challenging and data on outcomes of surgery in patients with NHL are scanty. The aim of study was to evaluate the impact of spleen size on the surgical outcome of splenectomy in patients with NHL.
Methods
Patients with NHL who underwent splenectomy, between 2006 and 2017, were included and divided into two groups: group 1, spleen ≤ 20 cm; group 2, spleen > 20 cm. Surgical approach, operative time, postoperative morbidity, mortality, hospital stay and re-admission rates were retrospectively compared between groups. Non-parametric data were evaluated with the Mann-Whitney U test. Differences in frequencies were analyzed with Fisher’s exact test.
Results
Sixteen patients were included (group 1, 6; group 2, 10). Laparoscopy was successful in three patients of group 1, none of group 2 (p = 0.035), the intraoperative time did not differ significantly between groups. One patient in each group developed postoperative complications. The patient in group 1 died of pneumonia. Median length of stay was 8 days (range, 3–16 days) for group 1, 5.5 days (range, 3–10 days) for group 2, showing no significant difference between the two groups. No patient was readmitted to hospital.
Conclusions
Spleen size does not affect the outcome of splenectomy in patients with NHL. If a mini-invasive approach is to be chosen, laparoscopy may not be feasible when the spleen size is > 20 cm.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Xiros N, Economopoulos T, Christodoulidis C, Dervenoulas J, Papageorgiou E, Mellou S, et al. 2000; Splenectomy in patients with malignant non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Eur J Haematol. 64:145–150. DOI: 10.1034/j.1600-0609.2000.90079.x. PMID: 10997879.
Article2. Brodsky J, Abcar A, Styler M. 1996; Splenectomy for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Am J Clin Oncol. 19:558–561. DOI: 10.1097/00000421-199612000-00004. PMID: 8931670.
Article3. Walsh RM, Heniford BT. 1999; Laparoscopic splenectomy for non-Hodgkin lymphoma. J Surg Oncol. 70:116–121. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9098(199902)70:2<116::AID-JSO10>3.0.CO;2-Y. PMID: 10084655.
Article4. Horowitz J, Smith JL, Weber TK, Rodriguez-Bigas MA, Petrelli NJ. 1996; Postoperative complications after splenectomy for hematologic malignancies. Ann Surg. 223:290–296. DOI: 10.1097/00000658-199603000-00010. PMID: 8604910. PMCID: PMC1235118.
Article5. Edgren G, Almqvist R, Hartman M, Utter GH. 2014; Splenectomy and the risk of sepsis: a population-based cohort study. Ann Surg. 260:1081–1087. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000439. PMID: 24374533.6. Bickenbach KA, Gonen M, Labow DM, Strong V, Heaney ML, Zelenetz AD, et al. 2013; Indications for and efficacy of splenectomy for haematological disorders. Br J Surg. 100:794–800. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.9067. PMID: 23436638.
Article7. Balagué C, Targarona EM, Cerdán G, Novell J, Montero O, Bendahan G, et al. 2004; Long-term outcome after laparoscopic splenectomy related to hematologic diagnosis. Surg Endosc. 18:1283–1287. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-003-9092-y. PMID: 15457387.
Article8. Uranues S, Alimoglu O. 2005; Laparoscopic surgery of the spleen. Surg Clin North Am. 85:75–90. ixDOI: 10.1016/j.suc.2004.09.003. PMID: 15619530.
Article9. Lewis KM, Li Q, Jones DS, Corrales JD, Du H, Spiess PE, et al. 2017; Development and validation of an intraoperative bleeding severity scale for use in clinical studies of hemostatic agents. Surgery. 161:771–781. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2016.09.022. PMID: 27839931.
Article10. Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. 2004; Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 240:205–213. DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000133083.54934.ae. PMID: 15273542. PMCID: PMC1360123.11. Lemaire J, Rosière A, Bertrand C, Bihin B, Donckier JE, Michel LA. 2017; Surgery for massive splenomegaly. BJS Open. 1:11–17. DOI: 10.1002/bjs5.1. PMID: 29951600. PMCID: PMC5989945.
Article12. Saboo SS, Krajewski KM, O'Regan KN, Giardino A, Brown JR, Ramaiya N, et al. 2012; Spleen in haematological malignancies: spectrum of imaging findings. Br J Radiol. 85:81–92. DOI: 10.1259/bjr/31542964. PMID: 22096219. PMCID: PMC3473934.
Article13. Grahn SW, Alvarez J 3rd, Kirkwood K. 2006; Trends in laparoscopic splenectomy for massive splenomegaly. Arch Surg. 141:755–761. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.141.8.755. PMID: 16924082.
Article14. Targarona EM, Balagué C, Trías M. 2002; Laparoscopic splenectomy for splenomegaly. Probl Gen Surg. 19:58–64. DOI: 10.1097/00013452-200209000-00010. PMID: 30720697.
Article15. Delpero JR, Houvenaeghel G, Gastaut JA, Orsoni P, Blache JL, Guerinel G, et al. 1990; Splenectomy for hypersplenism in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and malignant non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Br J Surg. 77:443–449. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.1800770427. PMID: 2340397.
Article16. Walsh RM, Brody F, Brown N. 2004; Laparoscopic splenectomy for lymphoproliferative disease. Surg Endosc. 18:272–275. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-003-8916-0. PMID: 14691699.
Article17. Tsamalaidze L, Stauffer JA, Permenter SL, Asbun HJ. 2017; Laparoscopic splenectomy for massive splenomegaly: does size matter? J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 27:1009–1014. DOI: 10.1089/lap.2017.0384. PMID: 28799827.
Article18. Klingler PJ, Tsiotos GG, Glaser KS, Hinder RA. 1999; Laparoscopic splenectomy: evolution and current status. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 9:1–8. DOI: 10.1097/00019509-199901000-00001. PMID: 9950119.19. Habermalz B, Sauerland S, Decker G, Delaitre B, Gigot JF, Leandros E, et al. 2008; Laparoscopic splenectomy: the clinical practice guidelines of the European Association for Endoscopic Surgery (EAES). Surg Endosc. 22:821–848. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-007-9735-5. PMID: 18293036.
Article20. Knauer EM, Ailawadi G, Yahanda A, Obermeyer RJ, Millie MP, Ojeda H, et al. 2003; 101 laparoscopic splenectomies for the treatment of benign and malignant hematologic disorders. Am J Surg. 186:500–504. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2003.07.026. PMID: 14599614.
Article21. Bagrodia N, Button AM, Spanheimer PM, Belding-Schmitt ME, Rosenstein LJ, Mezhir JJ. 2014; Morbidity and mortality following elective splenectomy for benign and malignant hematologic conditions: analysis of the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program data. JAMA Surg. 149:1022–1029. DOI: 10.1001/jamasurg.2014.285. PMID: 25143027.
Article22. Kavic SM, Segan RD, Park AE. 2005; Laparoscopic splenectomy in the elderly: a morbid procedure? Surg Endosc. 19:1561–1564. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-005-0125-6. PMID: 16189722.
Article23. Targarona EM, Espert JJ, Cerdán G, Balagué C, Piulachs J, Sugrañes G, et al. 1999; Effect of spleen size on splenectomy outcome. A comparison of open and laparoscopic surgery. Surg Endosc. 13:559–562. DOI: 10.1007/s004649901040. PMID: 10347290.24. Ohta M, Nishizaki T, Matsumoto T, Shimabukuro R, Sasaki A, Shibata K, et al. 2005; Analysis of risk factors for massive intraoperative bleeding during laparoscopic splenectomy. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 12:433–437. DOI: 10.1007/s00534-005-1027-7. PMID: 16365814.
Article25. Wysocki M, Radkowiak D, Zychowicz A, Rubinkiewicz M, Kulawik J, Major P, et al. 2018; Prediction of technical difficulties in laparoscopic splenectomy and analysis of risk factors for postoperative complications in 468 cases. J Clin Med. 7:547. DOI: 10.3390/jcm7120547. PMID: 30558132. PMCID: PMC6306709.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Primary Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma of the Spleen Associated with Hepatitis B Virus Infection
- Primary Lymphoma of the Spleen: A case report
- Gastrosplenic Fistula Complicated in a Patient with Non- Hodgkin's Lymphoma
- Hamartoma of the Spleen
- Three Cases of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Presenting as Primary Splenic Lymphoma