J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2021 Dec;23(4):348-353. 10.7461/jcen.2021.E2021.05.008.
Transvenous injection of n-butyl 2-cyanoacrylate to obliterate the pathologic cavernous sinus as a salvage technique for incompletely obliterated complex cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula after transvenous coil embolization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Hallym University Gangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2523893
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2021.E2021.05.008
Abstract
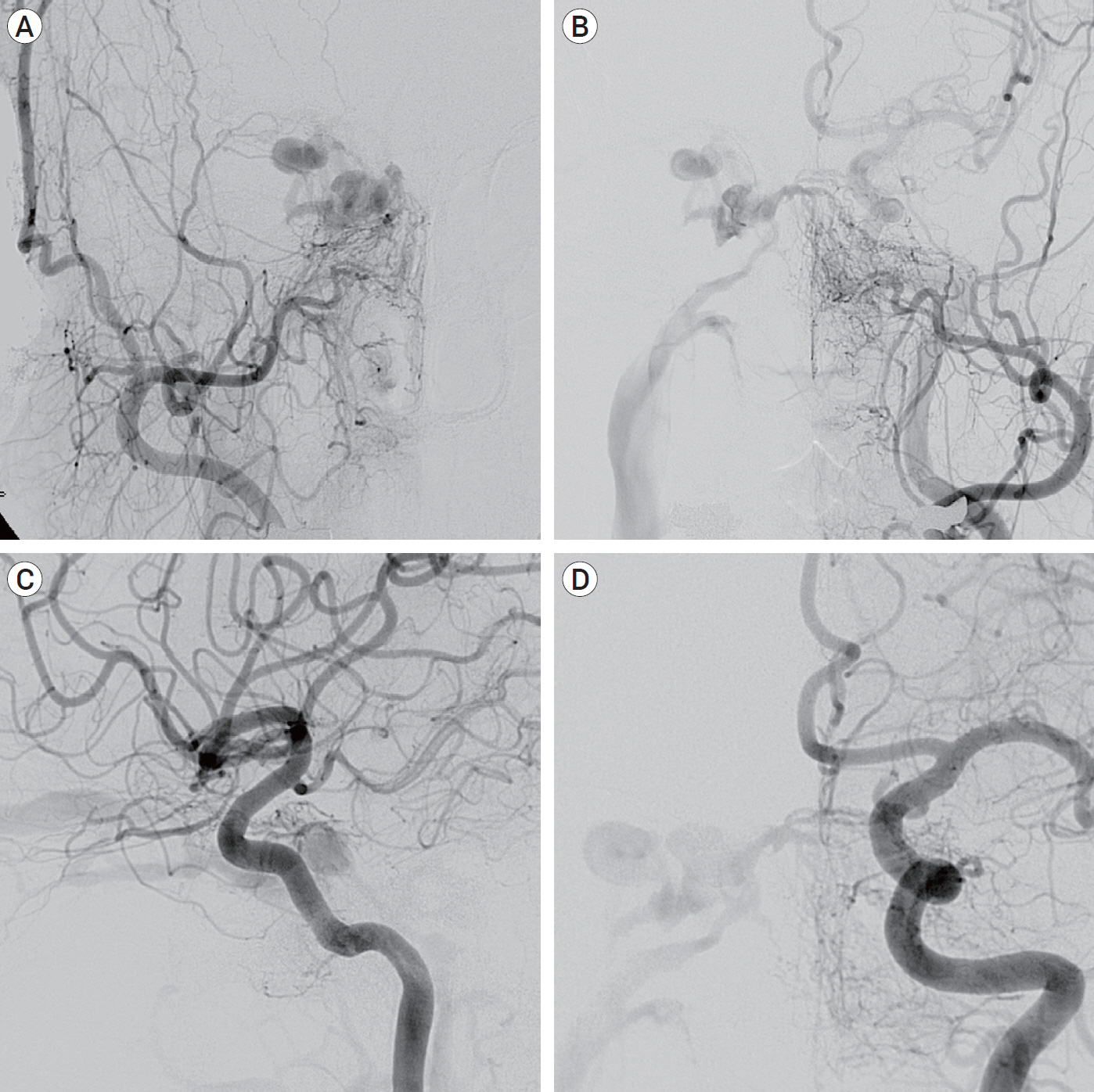
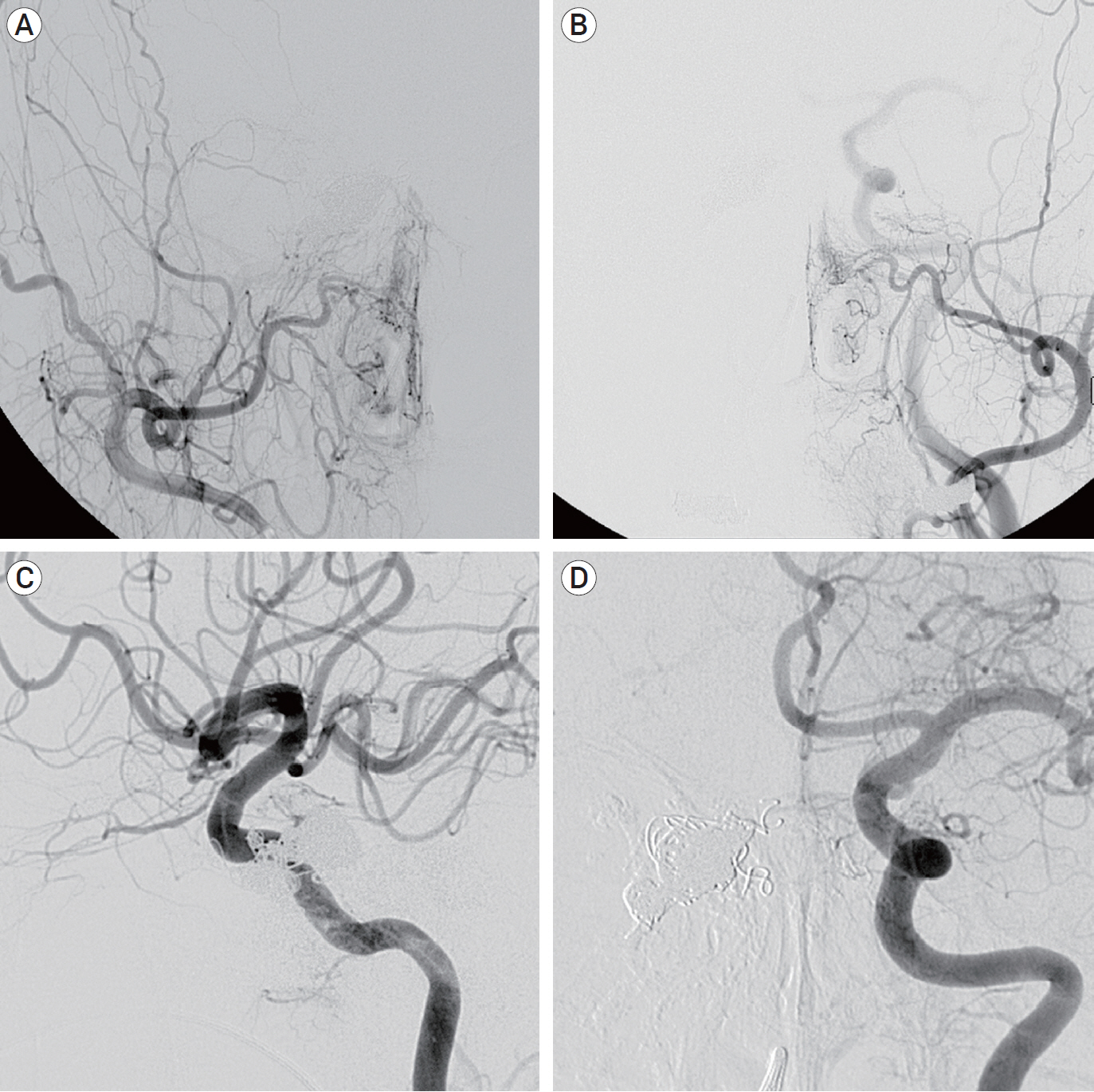
- A Barrow type D of complex cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula (CS-dAVF) was completely obliterated by using coils, n-butyl 2-cyanoacrylate (NBCA) and Onyx via transvenous approach. Especially in this case, after transvenous coil embolization of the pathologic cavernous sinus (CS), transvenous injection of NBCA was done to obliterate residual shunts recruited into CS. The complex CS-dAVF was completely obliterated without periprocedural complications. Transvenous injection of NBCA could be considered as a feasible option for obliteration of pathologic CS in a case of incompletely obliterated complex CS-dAVF after transvenous coil embolization.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Arat A, Cekirge S, Saatci I, Ozgen B. Transvenous injection of Onyx for casting of the cavernous sinus for the treatment of a carotid-cavernous fistula. Neuroradiology. 2004; Dec. 46(12):1012–5.
Article2. Berkmen T, Troffkin NA, Wakhloo AK. Transvenous sonographically guided percutaneous access for treatment of an indirect carotid cavernous fistula. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; Sep. 24(8):1548–51.
Article3. Kiyosue H, Hori Y, Okahara M, Tanoue S, Sagara Y, Matsumoto S, et al. Treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: current strategies based on location and hemodynamics, and alternative techniques of transcatheter embolization. Radiographics. 2004; Nov-Dec. 24(6):1637–53.
Article4. Lv X, Jiang C, Li Y, Wu Z. Percutaneous transvenous packing of cavernous sinus with Onyx for cavernous dural arteriovenous fistula. Eur J Radiol. 2009; Aug. 71(2):356–62.
Article5. Nogueira RG, Dabus G, Rabinov JD, Eskey CJ, Ogilvy CS, Hirsch JA, et al. Preliminary experience with onyx embolization for the treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; Jan. 29(1):91–7.
Article6. Shi ZS, Loh Y, Gonzalez N, Tateshima S, Feng L, Jahan R, et al. Flow control techniques for Onyx embolization of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae. J Neurointerv Surg. 2013; Jul. 5(4):311–6.7. Suzuki S, Lee DW, Jahan R, Duckwiler GR, Viñuela F. Transvenous treatment of spontaneous dural carotid-cavernous fistulas using a combination of detachable coils and Onyx. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006; Jun-Jul. 27(6):1346–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Using the Direct Superior Ophthalmic Vein Approach: A Case Report
- Transvenous Coil Embolization for Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas of the Ophthalmic Sheath: Report of Two Cases and Review of the Literature
- Facilitated Retrograde Access via the Facial Vein for Transvenous Embolization of the Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula with Isolated Ophthalmic Venous Drainage
- Middle temporal vein access for transvenous embolization of Cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula: A case report and review of literature
- Intraoperative Embolization of Dural Carotid-Cavernous Fistula: Case Report