Anat Cell Biol.
2020 Dec;53(4):379-384. 10.5115/acb.20.199.
Direct drainage of the basal vein of Rosenthal into the superior petrosal sinus: a literature review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Pontificia Universidad Javeriana, Bogotá, Colombia
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, USA
- 3Department of Neurology, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, USA
- 4Department of Anatomical Sciences, St. George’s University, St. George’s, Grenada, West Indies,USA
- 5Department of Structural & Cellular Biology, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, USA
- 6Department of Neurosurgery and Ochsner Neuroscience Institute, Ochsner Health System, New Orleans, LA, USA
- KMID: 2509681
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.20.199
Abstract
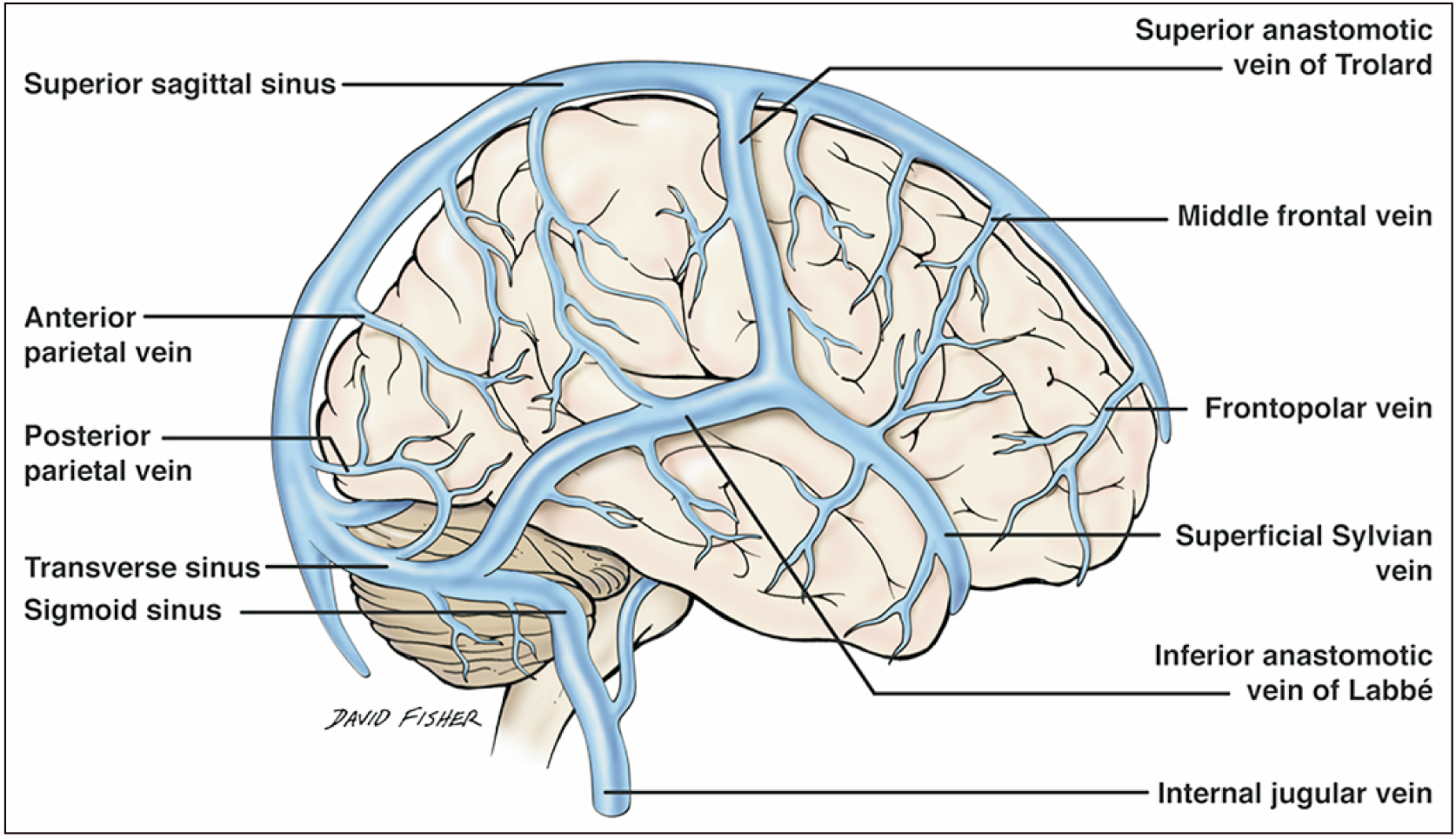
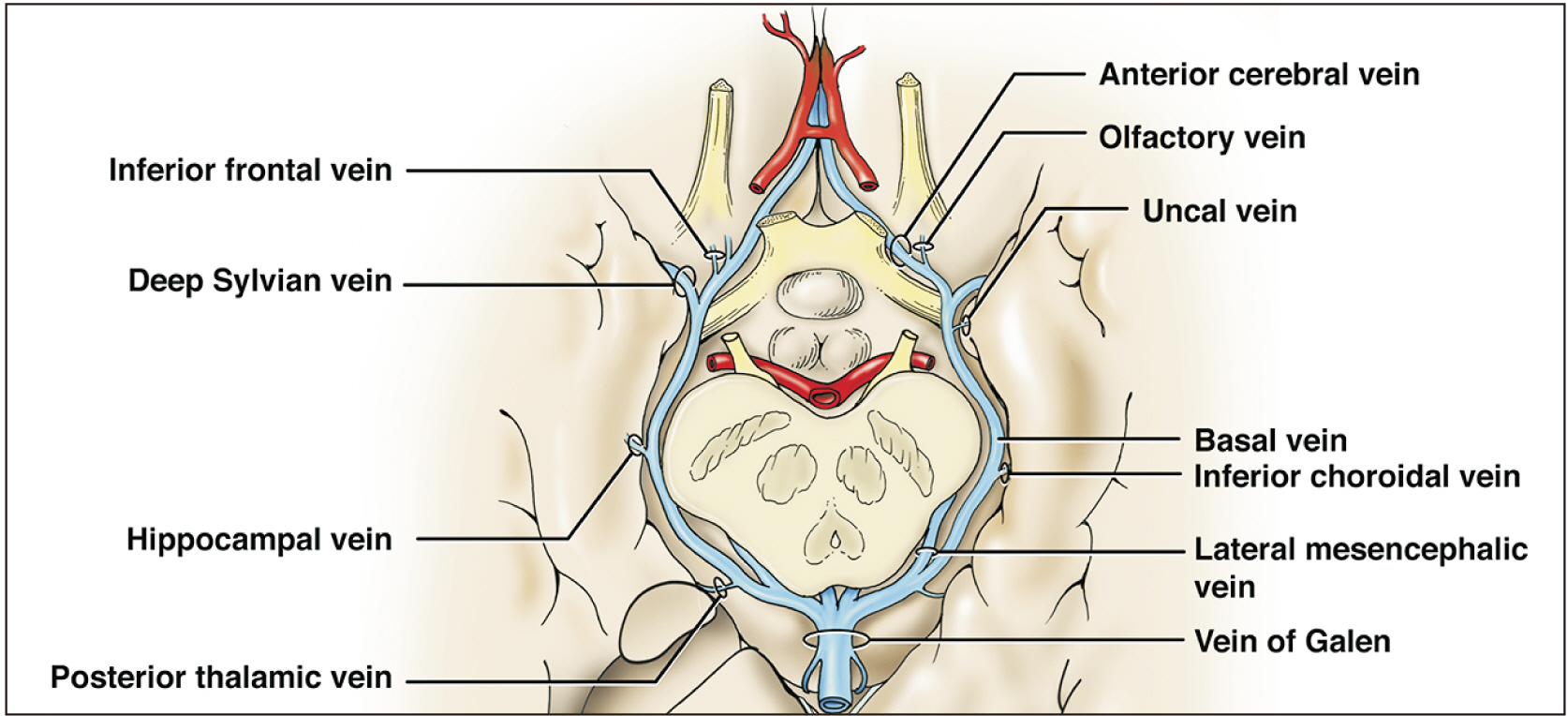
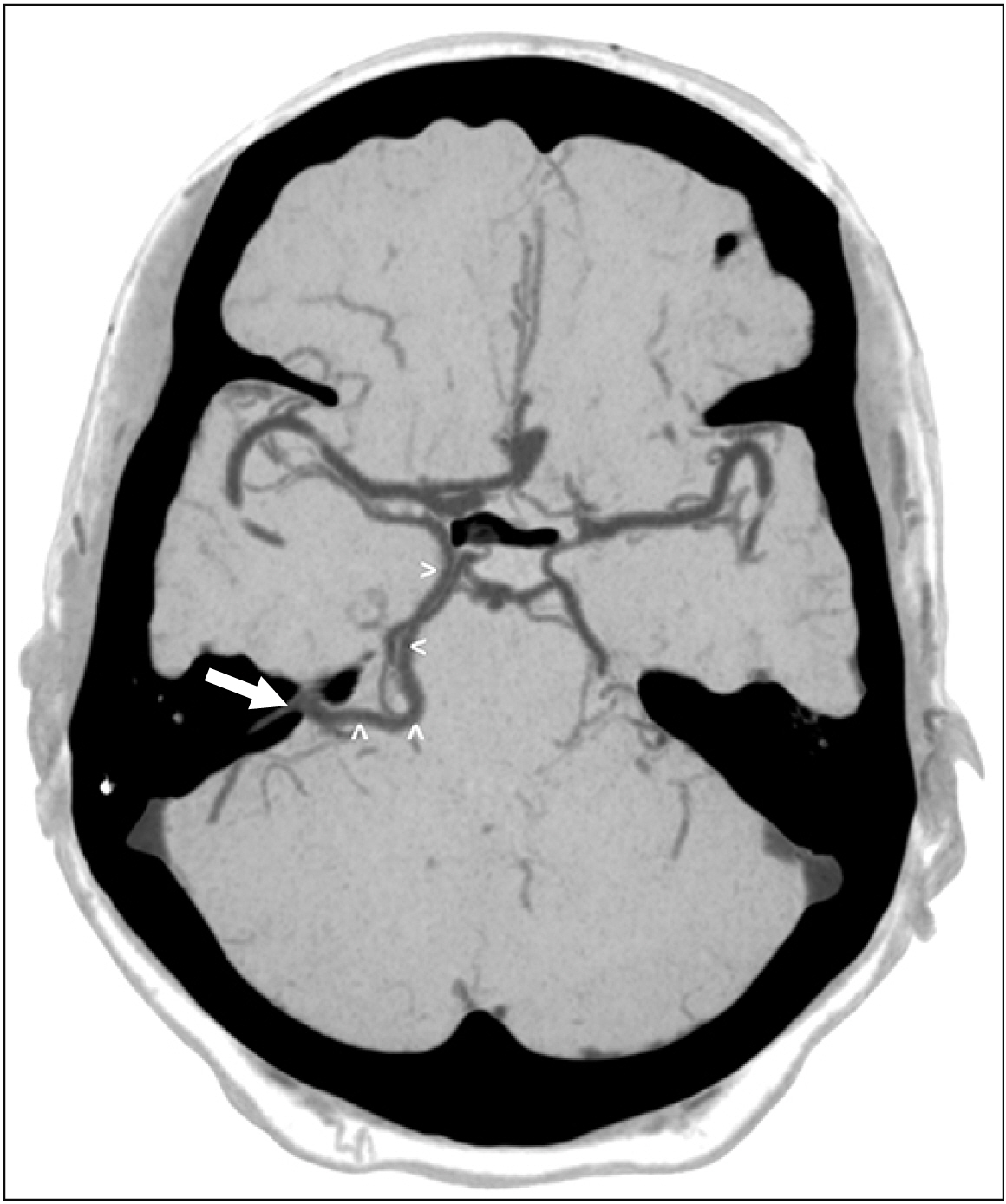
- An adult male was found to have a variation of the left basal vein of Rosenthal after presenting with complaints of headache and balance issues. In this case, the vein drained directly into the left superior petrosal sinus (SPS) instead of the great vein of Galen. Anatomical variation of the basal vein is likely due to embryonic development of the deep cerebral venous system as primitive structures either differentiate regress or further with age. These changes may result in the uncommon presentation seen in this case. To our knowledge, this is the first case that shows the basal vein drains into the SPS. The normal and variant anatomy of this vessel are discussed.
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Cadaveric findings of a duplicated superior petrosal sinus
Tina K. Reddy, Łukasz Olewnik, Joe Iwanaga, Aaron S. Dumont, R. Shane Tubbs
Anat Cell Biol. 2022;55(3):384-389. doi: 10.5115/acb.22.012.Morphometric evaluation of great vein of Galen and its clinical implications
Grace Suganya. S, Ariharan. K, Raveendranath Veeramani, Dinesh Kumar. V, Nagarajan Krishnan
Anat Cell Biol. 2023;56(1):32-38. doi: 10.5115/acb.22.051.
Reference
-
References
1. Huang YP, Wolf BS. Newton TH, Potts DG, editors. 1974. The basal cerebral vein and its tributaries. Radiology of the Skull and Brain, Vol. 2: Angiography. Mosby;Saint Louis: p. 2111–54.2. Padget DH. 1956; The cranial venous system in man in reference to development, adult configuration, and relation to the arteries. Am J Anat. 98:307–55. DOI: 10.1002/aja.1000980302. PMID: 13362118.
Article3. Uddin MA, Haq TU, Rafique MZ. 2006; Cerebral venous system anatomy. J Pak Med Assoc. 56:516–9. PMID: 17183980.4. Chung JI, Weon YC. 2005; Anatomic variations of the deep cerebral veins, tributaries of basal vein of rosenthal: embryologic aspects of the regressed embryonic tentorial sinus. Interv Neuroradiol. 11:123–30. DOI: 10.1177/159101990501100202. PMID: 20584491. PMCID: PMC3399712.
Article5. Tubbs RS, Loukas M, Louis RG Jr, Shoja MM, Askew CS, Phantana-Angkool A, Salter EG, Oakes WJ. 2007; Surgical anatomy and landmarks for the basal vein of rosenthal. J Neurosurg. 106:900–2. DOI: 10.3171/jns.2007.106.5.900. PMID: 17542537.
Article6. Suzuki Y, Ikeda H, Shimadu M, Ikeda Y, Matsumoto K. 2001; Variations of the basal vein: identification using three-dimensional CT angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 22:670–6. PMID: 11290476.7. Ardeshiri A, Ardeshiri A, Tonn JC, Winkler PA. 2006; Microsurgical anatomy of the lateral mesencephalic vein and its meaning for the deep venous outflow of the brain. Neurosurg Rev. 29:154–8. discussion 158DOI: 10.1007/s10143-005-0016-2. PMID: 16534634.
Article8. Muthukumar N, Palaniappan P. 1998; Tentorial venous sinuses: an anatomic study. Neurosurgery. 42:363–71. DOI: 10.1097/00006123-199802000-00097. PMID: 9482188.
Article9. San Millán Ruíz D, Fasel JH, Reverdin A, Gailloud P. 2003; Bilateral tentorial sinus drainage of the basal vein (of Rosenthal). Clin Anat. 16:264–8. DOI: 10.1002/ca.10070. PMID: 12673824.
Article10. Watanabe A, Hirano K, Kamada M, Imamura K, Ishii N, Sekihara Y, Suzuki Y, Ishii R. 2002; Perimesencephalic nonaneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage and variations in the veins. Neuroradiology. 44:319–25. DOI: 10.1007/s00234-001-0741-3. PMID: 11914808.
Article11. Linn J, Strueder K, Winkler PA, Brückmann H. 2009; The value of contrast-enhanced MR angiography in visualization of the basal vein of rosenthal and the lateral mesencephalic vein and their intra- and interindividual variations. Skull Base. 19:A293. DOI: 10.1055/s-2009-1222404.
Article12. Karakas AB, Govsa F, Ozer MA, Eraslan C. 2019; 3D brain imaging in vascular segmentation of cerebral venous sinuses. J Digit Imaging. 32:314–21. DOI: 10.1007/s10278-018-0125-4. PMID: 30242780. PMCID: PMC6456638.
Article13. Suzuki Y, Nakajima M, Ikeda H, Abe T. 2005; Three-dimensional computed tomography angiography of the galenic system for the occipital transtentorial approach. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 45:387–93. discussion 393–4. DOI: 10.2176/nmc.45.387. PMID: 16127255.
Article14. Kouzmitcheva E, Andrade A, Muthusami P, Shroff M, MacGregor DL, deVeber G, Dlamini N, Moharir M. 2019; Anatomical venous variants in children with cerebral sinovenous thrombosis. Stroke. 50:178–80. DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.023482. PMID: 30580715.
Article15. Ract I, Drier A, Leclercq D, Sourour N, Gabrieli J, Yger M, Nouet A, Dormont D, Chiras J, Clarençon F. 2014; Extensive basal ganglia edema caused by a traumatic carotid-cavernous fistula: a rare presentation related to a basal vein of Rosenthal anatomical variation. J Neurosurg. 121:63–6. DOI: 10.3171/2014.1.JNS132016. PMID: 24527815.
Article16. Nishino K, Hasegawa H, Morita K, Fukuda M, Ito Y, Fujii Y, Sato M. 2017; Clinical characteristics of arteriovenous malformations in the cerebellopontine angle cistern. J Neurosurg. 126:60–8. DOI: 10.3171/2015.12.JNS152190. PMID: 27035170.
Article17. Cannizzaro D, Rammos SK, Peschillo S, El-Nashar AM, Grande AW, Lanzino G. 2016; The lateral mesencephalic vein: surgical anatomy and its role in the drainage of tentorial dural arteriovenous fistulae. World Neurosurg. 85:163–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.wneu.2015.08.060. PMID: 26341441.
Article18. Kiyosue H, Mori H, Sagara Y, Hori Y, Okahara M, Nagatomi H, Abe T. 2009; Basal cerebral venous drainage from cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas. Neuroradiology. 51:175–81. DOI: 10.1007/s00234-008-0486-3. PMID: 19104792.
Article19. Shimada R, Kiyosue H, Tanoue S, Mori H, Abe T. 2013; Superior petrosal sinus: hemodynamic features in normal and cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 34:609–15. DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A3252. PMID: 22954738.
Article20. Porter RW, Detwiler PW, Spetzler RF. 2000; Surgical approaches to the brain stem. Oper Tech Neurosurg. 3:114–23. DOI: 10.1053/oy.2000.6576. PMID: 8353444.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Persistent fetal superficial middle cerebral vein: an anatomical study
- Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Using the Direct Superior Ophthalmic Vein Approach: A Case Report
- Cerebellar Hemorrhage due to a Direct Carotid–Cavernous Fistula after Surgery for Maxillary Cancer
- Drainage of the basal vein of Rosenthal into the confluence of sinuses
- Middle temporal vein access for transvenous embolization of Cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula: A case report and review of literature