J Pathol Transl Med.
2020 Jan;54(1):119-122. 10.4132/jptm.2019.09.30.
Morule-like features in pulmonary adenocarcinoma associated with epidermal growth factor receptor mutations: two case reports with targeted next-generation sequencing analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Korea University Anam Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2501600
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.09.30
Abstract
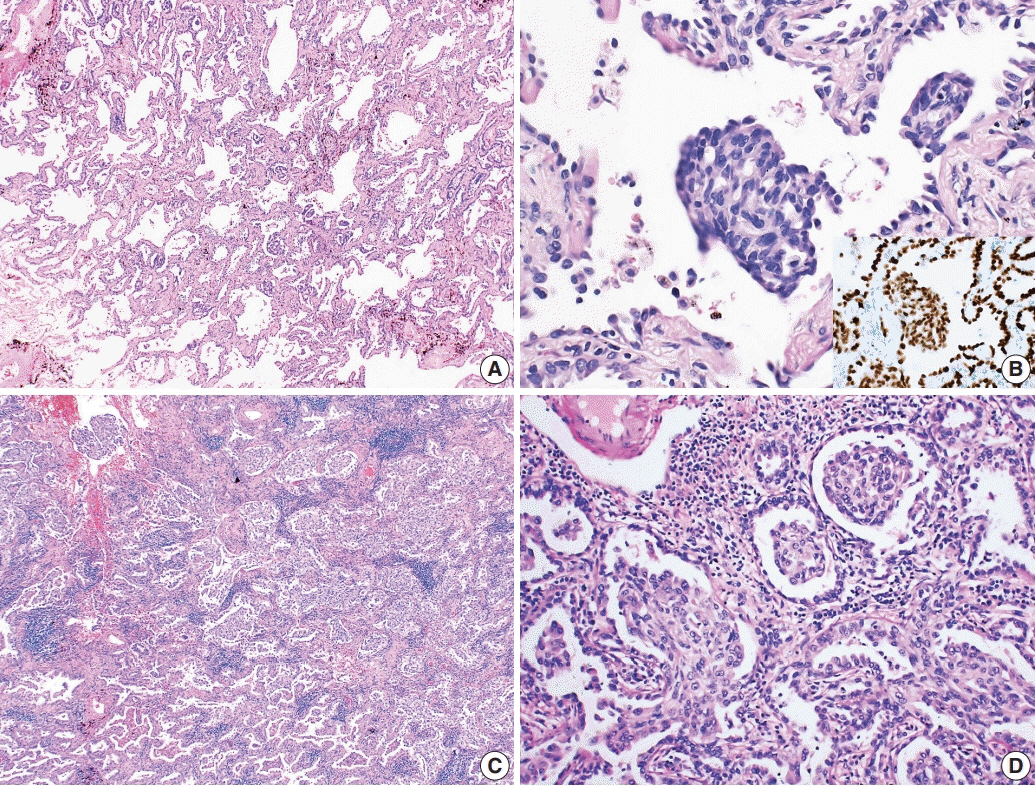
- Morules, or morule-like features, can be identified in benign and malignant lesions in various organs. Morular features are unusual in pulmonary adenocarcinoma cases with only 26 cases reported to date. Here, we describe two cases of pulmonary adenocarcinoma with morule-like features in Korean women. One patient had a non-mucinous-type adenocarcinoma in situ and the other had an acinarpredominant adenocarcinoma with a micropapillary component. Both patients showed multiple intra-alveolar, nodular, whorled proliferative foci composed of atypical spindle cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm. Targeted next-generation sequencing was performed on DNA extracted from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples of the tumors. Results showed unusual epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations, which are associated with drug resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, revealing the importance of identifying morule-like features in pulmonary adenocarcinoma and the need for additional study, since there are few reported cases.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Makishi S, Kinjo T, Sawada S, et al. Morules and morule-like features associated with carcinomas in various organs: report with immunohistochemical and molecular studies. J Clin Pathol. 2006; 59:95–100.
Article2. Tsuta K, Kawago M, Yoshida A, et al. Primary lung adenocarcinoma with morule-like components: a unique histologic hallmark of aggressive behavior and EGFR mutation. Lung Cancer. 2014; 85:12–8.3. Fornelli A, Cavazza A, Cancellieri A, Rossi G, De Marco L. Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma with nodular ("morule-like") features. Virchows Arch. 2003; 442:407–8.
Article4. Tajima S, Koda K. Transition between morule-like and solid components may occur in solid-predominant adenocarcinoma of the lung: report of 2 cases with EGFR and KRAS mutations. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015; 8:7475–81.5. Moran CA, Jagirdar J, Suster S. Papillary lung carcinoma with prominent “morular” component. Am J Clin Pathol. 2004; 122:106–9.
Article6. Nakatani Y, Masudo K, Miyagi Y, et al. Aberrant nuclear localization and gene mutation of beta-catenin in low-grade adenocarcinoma of fetal lung type: up-regulation of the Wnt signaling pathway may be a common denominator for the development of tumors that form morules. Mod Pathol. 2002; 15:617–24.7. Matsukuma S, Obara K, Kato K, et al. Non-sarcomatous spindle cell morphology in conventional lung adenocarcinoma: a clinicopathological study. Virchows Arch. 2014; 465:165–72.
Article8. Suda K, Mizuuchi H, Maehara Y, Mitsudomi T. Acquired resistance mechanisms to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer with activating epidermal growth factor receptor mutation: diversity, ductility, and destiny. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012; 31:807–14.9. Yamaguchi F, Fukuchi K, Yamazaki Y, et al. Acquired resistance L747S mutation in an epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor-naive patient: a report of three cases. Oncol Lett. 2014; 7:357–60.10. Yasuda H, Kobayashi S, Costa DB. EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer: preclinical data and clinical implications. Lancet Oncol. 2012; 13:e23–31.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Landscape of EGFR mutations in lung adenocarcinoma: a single institute experience with comparison of PANAMutyper testing and targeted next-generation sequencing
- Effect of intracelluar cyclic AMP on EGF receptor binding in human gastric adenocarcinoma cells
- Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutations in Colorectal Cancer Patients
- Amplification of epidermal growth factor receptor gene in primary cervical cancer
- Amplification of epidermal growth factor receptor gene in primary cervical cancer