Ann Clin Neurophysiol.
2020 Apr;22(1):33-36. 10.14253/acn.2020.22.1.33.
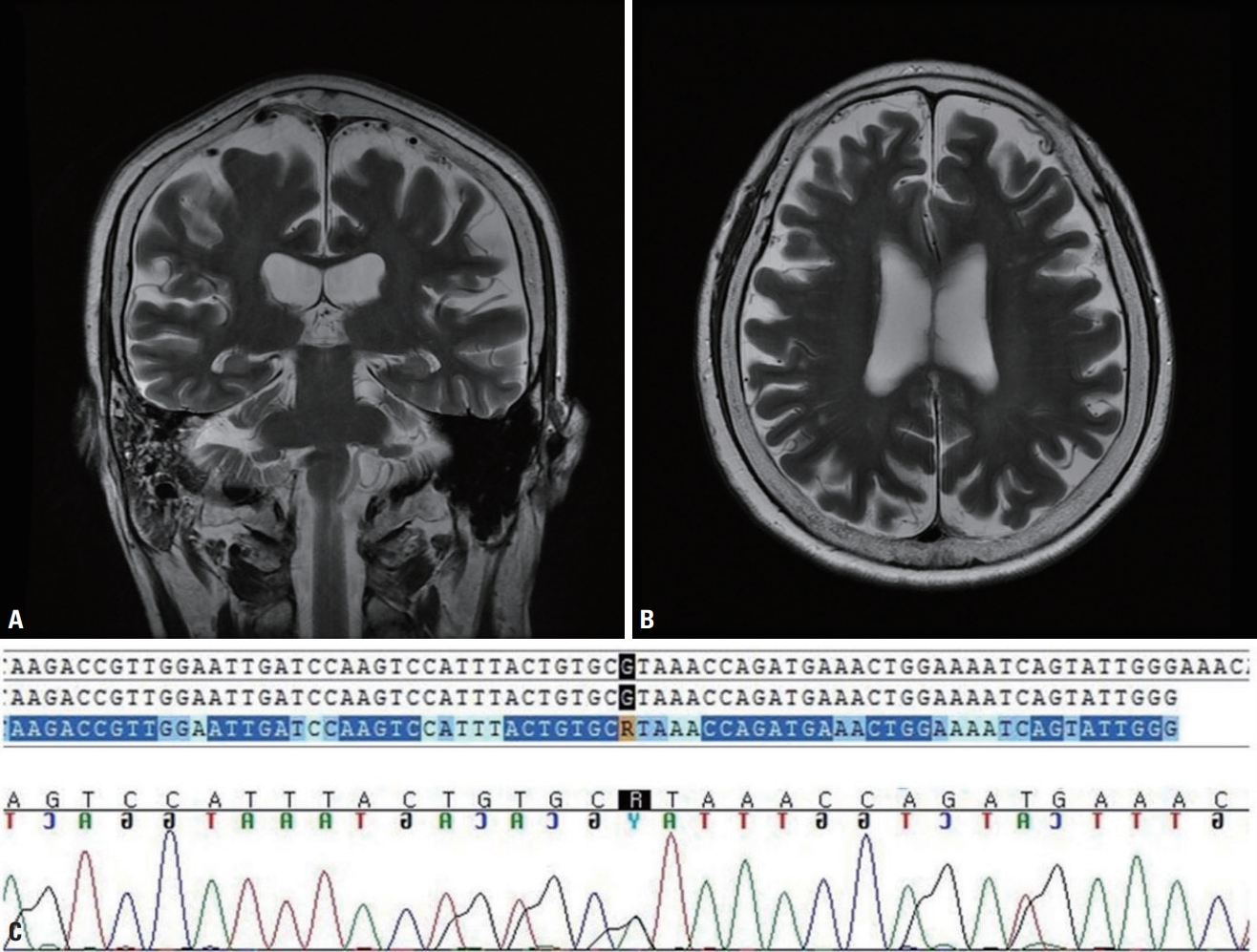
Likely pathogenic FIG4 related amyotrophiclateral sclerosis patient whocorrelated with clinical, imaging andneuropsychological studies
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Kyungpook National University Chilgok Hospital, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea
- 2Department of Rehabilitation, Kyungpook National University Chilgok Hospital, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2500302
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14253/acn.2020.22.1.33
Abstract
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder with numerous causes that include genetic factors. Efforts to reveal the genetics of ALS have identified several candidate genes that are associated with familial and sporadic ALS. Here we report a Korean ALS patient who showed prominent upper motor-neuron-related symptoms with marked brain atrophy and neuropsychological deficits. The findings were highly suggestive of ALS in a patient with a likely pathogenic FIG4 variant.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Renton AE, Chiò A, Traynor BJ. State of play in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis genetics. Nat Neurosci. 2014; 17:17–23.
Article2. Kim HJ, Oh KW, Kwon MJ, Oh SI, Park JS, Kim YE, et al. Identification of mutations in Korean patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using multigene panel testing. Neurobiol Aging. 2016; 37:209.e9–e16.
Article3. Chow CY, Zhang Y, Dowling JJ, Jin N, Adamska M, Shiga K, et al. Mutation of FIG4 causes neurodegeneration in the pale tremor mouse and patients with CMT4J. Nature. 2007; 448:68–72.
Article4. Chow CY, Landers JE, Bergren SK, Sapp PC, Grant AE, Jones JM, et al. Deleterious variants of FIG4, a phosphoinositide phosphatase, in patients with ALS. Am J Hum Genet. 2009; 84:85–88.
Article5. Campeau PM, Lenk GM, Lu JT, Bae Y, Burrage L, Turnpenny P, et al. Yunis-Varon syndrome is caused by mutations in FIG4, encoding a phosphoinositide phosphatase. Am J Hum Genet. 2013; 92:781–791.6. Osmanovic A, Rangnau I, Kosfeld A, Abdulla S, Janssen C, Auber B, et al. FIG4 variants in central European patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a whole-exome and targeted sequencing study. Eur J Hum Genet. 2017; 25:324–331.
Article7. Massman PJ, Sims J, Cooke N, Haverkamp LJ, Appel V, Appel SH. Prevalence and correlates of neuropsychological deficits in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1996; 61:450–455.
Article8. Ringholz GM, Appel SH, Bradshaw M, Cooke NA, Mosnik DM, Schulz PE. Prevalence and patterns of cognitive impairment in sporadic ALS. Neurology. 2005; 65:586–590.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Novel Variants in the FIG4 Gene Associated With Chinese Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis With Slow Progression
- Multiple Sclerosis and Peripheral Multifocal Demyelinating Neuropathies Occurring in a Same Patient
- Balo's Concentric Sclerosis in a Patient with Previous Recurrent Optic Neuritis
- Diagnosis and Therapeutic Strategies of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- Tuberous Sclerosis with Aortic Aneurysm and Rib Changes