J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Oct;31(10):1650-1655. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.10.1650.
Decreased Lumbar Lordosis and Deficient Acetabular Coverage Are Risk Factors for Subchondral Insufficiency Fracture
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The Catholic University of Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. WSLEEOS@yuhs.ac
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, International St. Mary's Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Seoul national University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2468258
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.10.1650
Abstract
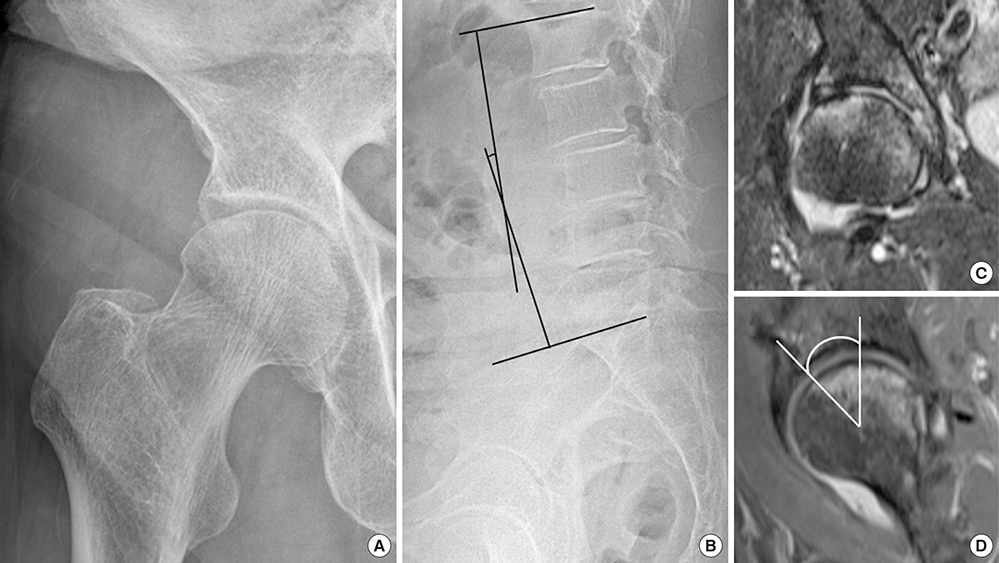
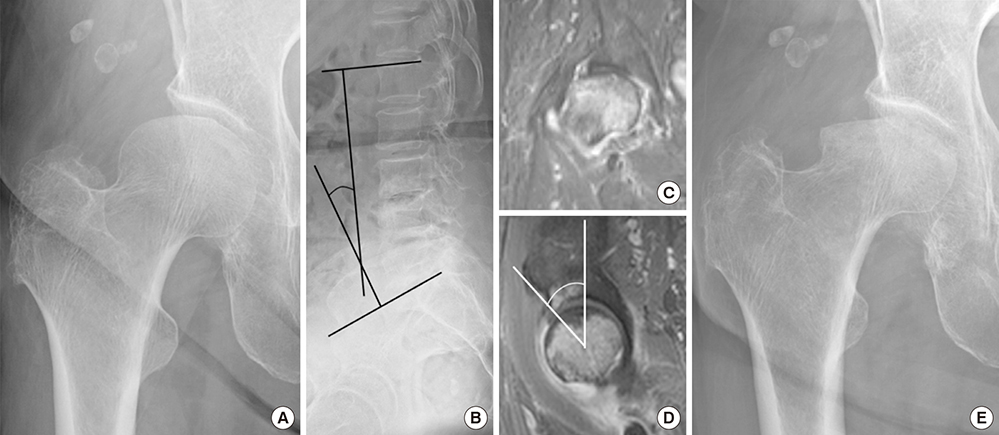
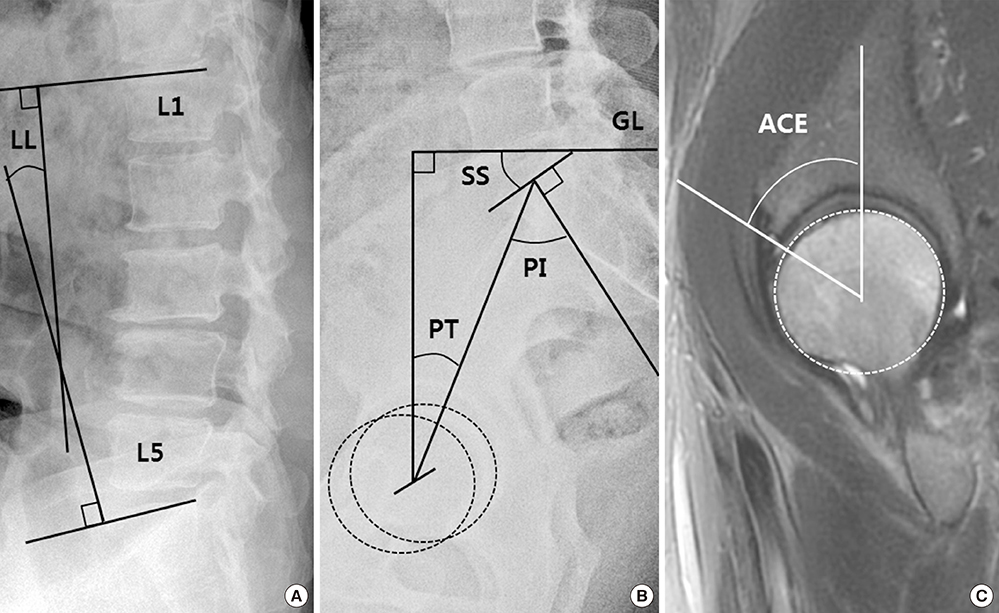
- Subchondral insufficiency fracture (SIF) of the femoral head occurs in the elderly and recipients of organ transplantation. Osteoporosis and deficient lateral coverage of the acetabulum are known risk factors for SIF. There has been no study about relation between spinopelvic alignment and anterior acetabular coverage with SIF. We therefore asked whether a decrease of lumbar lordosis and a deficiency in the anterior acetabular coverage are risk factors. We investigated 37 patients with SIF. There were 33 women and 4 men, and their mean age was 71.5 years (59-85 years). These 37 patients were matched with 37 controls for gender, age, height, weight, body mass index and bone mineral density. We compared the lumbar lordosis, pelvic incidence, pelvic tilt, sacral slope, acetabular index, acetabular roof angle, acetabular head index, anterior center-edge angle and lateral center-edge angle. Lumbar lordosis, pelvic tilt, sacral slope, lateral center edge angle, anterior center edge angle, acetabular index and acetabular head index were significantly different between SIF group and control group. Lumbar lordosis (OR = 1.11), lateral center edge angle (OR = 1.30) and anterior center edge angle (OR = 1.27) had significant associations in multivariate analysis. Decreased lumbar lordosis and deficient anterior coverage of the acetabulum are risk factors for SIF as well as decreased lateral coverage of the acetabulum.
MeSH Terms
-
Absorptiometry, Photon
Acetabulum/diagnostic imaging/*physiopathology
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Body Mass Index
Bone Density
Case-Control Studies
Female
Femur Head/diagnostic imaging
Fractures, Stress/*diagnosis/diagnostic imaging/etiology
Humans
Lordosis/diagnostic imaging/*physiopathology
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Male
Middle Aged
Multivariate Analysis
Odds Ratio
Risk Factors
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yoon PW, Kwak HS, Yoo JJ, Yoon KS, Kim HJ. Subchondral insufficiency fracture of the femoral head in elderly people. J Korean Med Sci. 2014; 29:593–598.2. Ikemura S, Yamamoto T, Nakashima Y, Shuto T, Jingushi S, Iwamoto Y. Bilateral subchondral insufficiency fracture of the femoral head after renal transplantation: a case report. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52:1293–1296.3. Iwasaki K, Yamamoto T, Motomura G, Ikemura S, Yamaguchi R, Iwamoto Y. Radiologic measurements associated with the prognosis and need for surgery in patients with subchondral insufficiency fractures of the femoral head. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013; 201:W97-103.4. Yoshimoto H, Sato S, Masuda T, Kanno T, Shundo M, Hyakumachi T, Yanagibashi Y. Spinopelvic alignment in patients with osteoarthrosis of the hip: a radiographic comparison to patients with low back pain. Spine. 2005; 30:1650–1657.5. Tsuchie H, Yamada S, Tazawa H, Kijima H, Shimada Y. Anterior hip subluxation due to lumbar degenerative kyphosis and posterior pelvic tilt. Case Rep Orthop. 2014; 2014:806157.6. Jessel RH, Zurakowski D, Zilkens C, Burstein D, Gray ML, Kim YJ. Radiographic and patient factors associated with pre-radiographic osteoarthritis in hip dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009; 91:1120–1129.7. Rafii M, Mitnick H, Klug J, Firooznia H. Insufficiency fracture of the femoral head: MR imaging in three patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997; 168:159–163.8. Yamamoto T, Schneider R, Iwamoto Y, Bullough PG. Subchondral insufficiency fracture of the femoral head in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006; 65:837–838.9. Shibata A, Fukuda K, Inoue A, Higuchi F, Miyake H, Nishi M, Mori M, Ishii S, Nagao M, Yanagawa H. Flushing pattern and idiopathic avascular necrosis of the femoral head. J Epidemiol. 1996; 6:37–43.10. Sakata R. A case-control study of association between life-style, alcohol dehydrogenase 2 and aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 genotype and idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Kurume Med J. 2003; 50:121–130.11. Mont MA, Jones LC, Hungerford DS. Nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: ten years later. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88:1117–1132.12. Yamamoto T, Bullough PG. Subchondral insufficiency fracture of the femoral head: a differential diagnosis in acute onset of coxarthrosis in the elderly. Arthritis Rheum. 1999; 42:2719–2723.13. Stelzeneder D, Hingsammer A, Bixby SD, Kim YJ. Can radiographic morphometric parameters for the hip be assessed on MRI? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013; 471:989–999.14. Botser IB, Ozoude GC, Martin DE, Siddiqi AJ, Kuppuswami S, Domb BG. Femoral anteversion in the hip: comparison of measurement by computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and physical examination. Arthroscopy. 2012; 28:619–627.15. Yamamoto T. Subchondral insufficiency fractures of the femoral head. Clin Orthop Surg. 2012; 4:173–180.16. Offierski CM, MacNab I. Hip-spine syndrome. Spine. 1983; 8:316–321.17. Ishihara K, Miyanishi K, Ihara H, Jingushi S, Torisu T. Subchondral insufficiency fracture of the femoral head may be associated with hip dysplasia: a pilot study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010; 468:1331–1335.18. Mankin HJ. Nontraumatic necrosis of bone (osteonecrosis). N Engl J Med. 1992; 326:1473–1479.19. Yamamoto T, Schneider R, Bullough PG. Insufficiency subchondral fracture of the femoral head. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000; 24:464–468.20. Yamamoto T, Schneider R, Bullough PG. Subchondral insufficiency fracture of the femoral head: histopathologic correlation with MRI. Skeletal Radiol. 2001; 30:247–254.21. Ikemura S, Yamamoto T, Motomura G, Nakashima Y, Mawatari T, Iwamoto Y. MRI evaluation of collapsed femoral heads in patients 60 years old or older: differentiation of subchondral insufficiency fracture from osteonecrosis of the femoral head. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 195:W63-8.22. Song WS, Yoo JJ, Koo KH, Yoon KS, Kim YM, Kim HJ. Subchondral fatigue fracture of the femoral head in military recruits. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004; 86-A:1917–1924.23. Yamamoto T, Iwamoto Y, Schneider R, Bullough PG. Histopathological prevalence of subchondral insufficiency fracture of the femoral head. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008; 67:150–153.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Posterior Acetabular Coverage of the Femoral Head in Sport-Related Posterior Hip Dislocation or Subluxation
- Interface Stability on Insufficient Coverage of Non-cemented Acetabular Cup with Screw Fixations
- Subchondral Stress Fracture of the Femoral Head
- Medialization of Cementless Acetabular Components after the Removal of Subchondral Bone in Total Hip Arthroplasty
- Subchondral Insufficiency Fractures of the Femoral Head