Imaging Sci Dent.
2018 Dec;48(4):261-268. 10.5624/isd.2018.48.4.261.
Image quality assessment of pre-processed and post-processed digital panoramic radiographs in paediatric patients with mixed dentition
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dentomaxillofacial Radiology, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta, Indonesia. isti.rahayu@ugm.ac.id
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Universidad de Los Andes, Santiago, Chile.
- 3OMFS IMPATH Research Group, Department of Imaging and Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, KU Leuven and Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, University Hospitals Leuven, Leuven, Belgium.
- 4Department of Dental Radiology, University of Padjajaran, Bandung, Indonesia.
- 5Division of Oral Diagnostics and Rehabilitation, Department of Dental Medicine, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden.
- KMID: 2450166
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2018.48.4.261
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To determine the impact of an image processing technique on diagnostic accuracy of digital panoramic radiographs for the assessment of anatomical structures in paediatric patients with mixed dentition.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
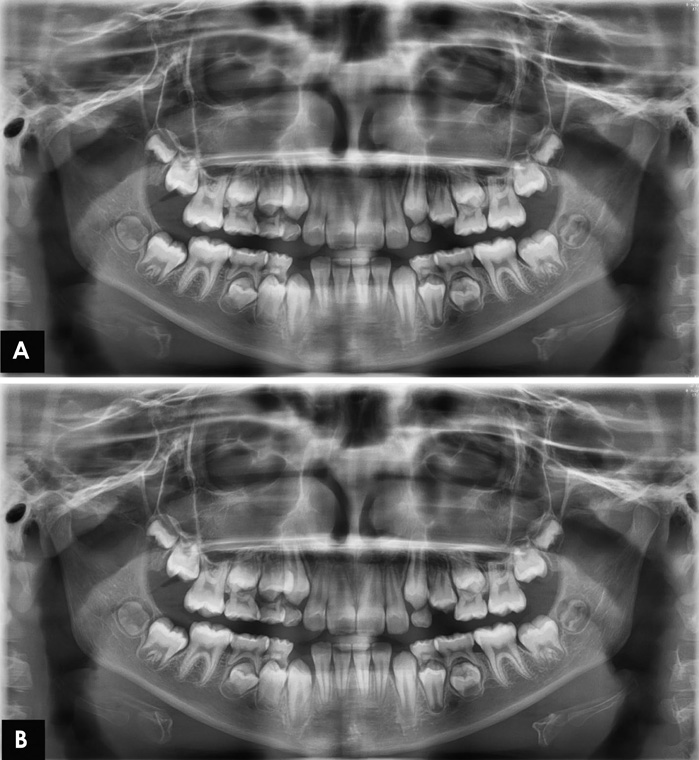
The study consisted of 50 digital panoramic radiographs of children aged from 6 to 12 years, which were later on processed using a dedicated image processing method. A modified clinical image quality evaluation chart was used to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of anatomical structures in maxillary and mandibular anterior and maxillary premolar region of processed images.
RESULTS
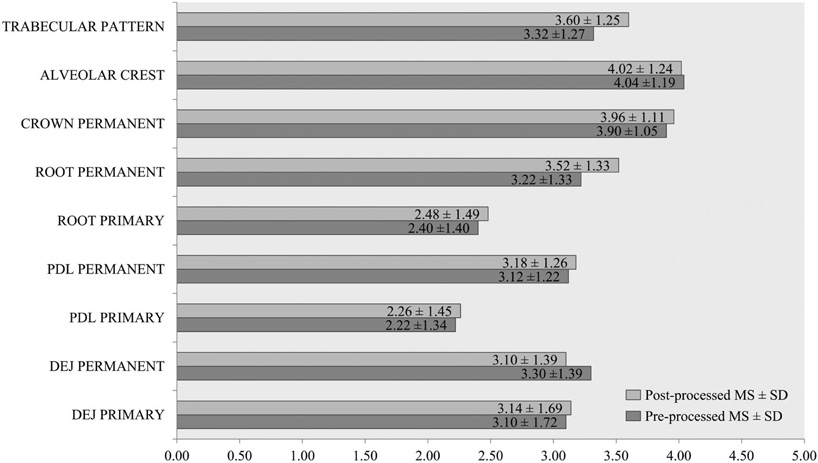
A statistically significant difference was observed between pre and post-processed evaluation of anatomical structures (P < 0.05) in the maxillary and mandibular anterior region. The anterior region was found to be more accurate in post-processed images. No significant difference was observed in the maxillary premolar region (P>0.05). The Inter-observer and intra-observer reliability of both pre and post processed images were excellent (>0.82) for anterior region and good (>0.63) for premolar region.
CONCLUSION
The application of image processing technique in digital panoramic radiography can be considered a reliable method for improving the quality of anatomical structures in paediatric patients with mixed dentition.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Clark HC, Curzon ME. A prospective comparison between findings from a clinical examination and results of bitewing and panoramic radiographs for dental caries diagnosis in children. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2004; 5:203–209.2. Abdinian M, Razavi SM, Faghihian R, Samety AA, Faghihian E. Accuracy of digital bitewing radiography versus different views of digital panoramic radiography for detection of proximal caries. J Dent (Tehran). 2015; 12:290–297.3. Barot AA, Chaturvedi MK, Butala PB, Rao VV, Patel PS, Barot AA. A study on changes in image quality with dose reduction in digital panoramic radiographs. J Int Oral Health. 2017; 9:174–179.4. Sabarudin A, Tiau YJ. Image quality assessment in panoramic dental radiography: a comparative study between conventional and digital systems. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2013; 3:43–48.5. Peker I, Toraman AM, Usalan G, Altunkaynak B. The comparison of subjective image quality in conventional and digital panoramic radiography. Indian J Dent Res. 2009; 20:21–25.
Article6. Parissis N, Angelopoulos C, Mantegari S, Karamanis S, Masood F, Tsirlis A. A comparison of panoramic image quality between a digital radiography storage phosphor system and a film-based system. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2010; 11:E009–E016.7. Amiri SA, Moudi E. Image quality enhancement in digital panoramic radiograph. J AI Data Min. 2014; 2:1–6.8. Kandan RS, John A, Kumar S. An improved contrast enhancement approach for panoramic dental x-ray images. ARPN J Eng App Sci. 2015; 10:1897–1901.9. Svenson B, Larsson L, Båth M. Optimization of exposure in panoramic radiography while maintaining image quality using adaptive filtering. Acta Odontol Scand. 2016; 74:229–235.
Article10. Baksi BG, Alpöz E, Sogur E, Mert A. Perception of anatomical structures in digitally filtered and conventional panoramic radiographs: a clinical evaluation. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2010; 39:424–430.
Article11. Gijbels F, De Meyer AM, Bou Serhal C, Van den Bossche C, Declerck J, Persoons M, et al. The subjective image quality of direct digital and conventional panoramic radiography. Clin Oral Investig. 2000; 4:162–167.
Article12. Choi BR, Choi DH, Huh KH, Yi WJ, Heo MS, Choi SC, et al. Clinical image quality evaluation for panoramic radiography in Korean dental clinics. Imaging Sci Dent. 2012; 42:183–190.
Article13. Altman DG, Machin D, Bryant TN, Gardner MJ. Statistics with confidence. 2nd ed. London: BMJ Books;2003.14. Angelopoulos C, Bedard A, Katz JO, Karamanis S, Parissis N. Digital panoramic radiography: an overview. Semin Orthod. 2004; 10:194–203.
Article15. Ahmad SA, Taib MN, Khalid NE, Taib H. Correlation between quantitative and qualitative analysis on image quality of digital dental X-ray images. J Comput Sci Comput Math. 2012; 2:43–51.16. Yalcinkaya S, Künzel A, Willers R, Thoms M, Becker J. Subjective image quality of digitally filtered radiographs acquired by the Dürr Vistascan system compared with conventional radiographs. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006; 101:643–651.
Article17. Kaeppler G, Axmann-Krcmar D, Reuter I, Meyle J, Gómez-Román G. A clinical evaluation of some factors affecting image quality in panoramic radiography. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2000; 29:81–84.
Article18. Lehmann TM, Troeltsch E, Spitzer K. Image processing and enhancement provided by commercial dental software programs. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2002; 31:264–272.
Article19. Batista SS, Panzarella FK, Tavano O, Filho AM, Junqueira JL. Image adjustments on digital panoramic radiographs using Adobe Photoshop CS3 software. Rev Sul-Bras Odontol. 2013; 10:394–401.20. Gijbels F, Sanderink G, Pauwels H, Jacobs R. Subjective image quality of digital panoramic radiographs displayed on monitor and printed on various hardcopy media. Clin Oral Investig. 2004; 8:25–29.21. Bekiroglu N, Mete S, Ozbay G, Yalcinkaya S, Kargul B. Evaluation of panoramic radiographs taken from 1,056 Turkish children. Niger J Clin Pract. 2015; 18:8–12.22. Temmerman A, Hertelé S, Teughels W, Dekeyser C, Jacobs R, Quirynen M. Are panoramic images reliable in planning sinus augmentation procedures? Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011; 22:189–194.
Article23. Rushton VE, Horner K, Worthington HV. The quality of panoramic radiographs in a sample of general dental practices. Br Dent J. 1999; 186:630–633.
Article24. Kayal RA. Distortion of digital panoramic radiographs used for implant site assessment. J Orthod Sci. 2016; 5:117–120.
Article25. Vazquez L, Nizamaldin Y, Combescure C, Nedir R, Bischof M, Dohan Ehrenfest DM, et al. Accuracy of vertical height measurements on direct digital panoramic radiographs using posterior mandibular implants and metal balls as reference objects. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2013; 42:20110429.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Image enhancement of digital periapical radiographs according to diagnostic tasks
- Abdominal Digital Radiography with a Novel Post-Processing Technique: Phantom and Patient Studies
- Reproducibility of lateral cephalometric landmarks on conventional radiographs and spatial frequency-processed digital images
- Effects of digital image processing on the detection of simulated lesion in chest radiographs: an experimental study
- Clinical image quality evaluation for panoramic radiography in Korean dental clinics