J Breast Cancer.
2019 Jun;22(2):248-259. 10.4048/jbc.2019.22.e20.
High Survivin and Low Zinc Finger of the Cerebellum 1 Expression Indicates Poor Prognosis in Triple-negative Breast Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of General Surgery, Wuxi Xishan People's Hospital, Wuxi, China.
- 2Department of Urology, Kunshan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Kunshan, China.
- 3Department of Pathology, Wuxi Xishan People's Hospital, Wuxi, China.
- 4Department of Oncology, Wuxi Fifth People's Hospital, Wuxi, China. whn15066940731@163.com
- KMID: 2450119
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2019.22.e20
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Triple-negative breast carcinoma (TNBC) is accompanied with high risk of metastasis and recurrence. The present study aimed to explore the clinicopathological and prognostic roles of putative tumor-related genes in patients with TNBC.
METHODS
Thirty pairs of frozen-thawed tumors were used to select reliable indicators via real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). Then, 150 pathology specimens were used to evaluate the expression of proteins in TNBC through immunohistochemistry. In addition, Kaplan-Meier curves and Cox regression analysis were also performed to analyze the overall survival and disease-free survival.
RESULTS
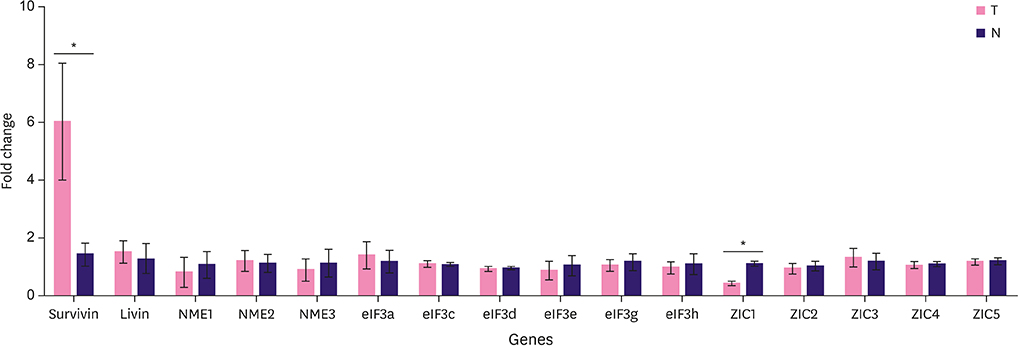
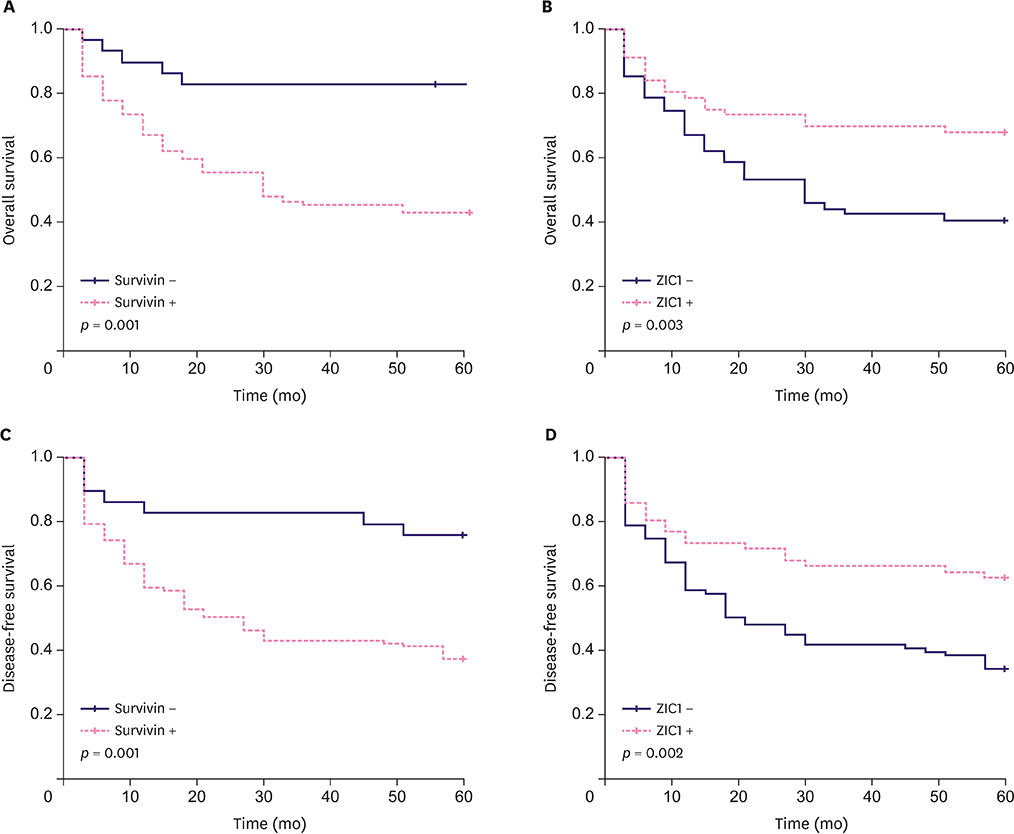
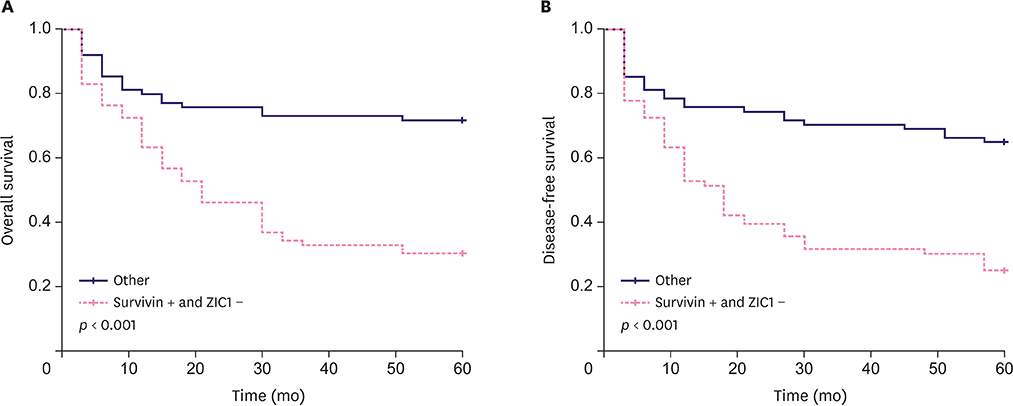
RT-qPCR results indicated that among all the proteins analyzed using fresh-frozen TNBC samples, the expression levels of only Survivin and zinc finger of the cerebellum 1 (ZIC1) were obviously different from those in the corresponding normal tissues. Survivin and ZIC1 expression had opposite effects on the clinicopathological diagnosis and prognostic assessment in TNBC patients. Further, there was a negative correlation between Survivin and ZIC1 expression. In addition, the "Survivin-positive ZIC1-negative group" was associated with histologic grade, lymph node metastasis, and TNM staging (p < 0.001) and this was also an independent factor for evaluating the prognosis of TNBC in patients.
CONCLUSION
In summary, the expression levels of Survivin and ZIC1 in TNBC are different from those in normal tissues and are negatively correlated mutually. The combined detection of Survivin and ZIC1 expression levels could allow better comprehensive diagnosis and prognostic evaluation for TNBC patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ritzwoller DP, Hassett MJ, Uno H, Cronin AM, Carroll NM, Hornbrook MC, et al. Development, validation, and dissemination of a breast cancer recurrence detection and timing informatics algorithm. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2018; 110:273–281.
Article2. Teles RH, Moralles HF, Cominetti MR. Global trends in nanomedicine research on triple negative breast cancer: a bibliometric analysis. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018; 13:2321–2336.
Article3. Darouich S, El Amine El Hadj O, Betaieb I, Goucha A, Dhiab T, Rahal K, et al. Triple negative breast cancer: a clinico-epidemiological and histopronostic study of 90 cases. Tunis Med. 2017; 95:37–44.4. Lyu H, Wang S, Huang J, Wang B, He Z, Liu B. Survivin-targeting miR-542-3p overcomes HER3 signaling-induced chemoresistance and enhances the antitumor activity of paclitaxel against HER2-overexpressing breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018; 420:97–108.
Article5. Ghebeh H, Al-Khaldi S, Olabi S, Al-Dhfyan A, Al-Mohanna F, Barnawi R, et al. Fascin is involved in the chemotherapeutic resistance of breast cancer cells predominantly via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Br J Cancer. 2014; 111:1552–1561.
Article6. Zhao W, Li X, Wang J, Wang C, Jia Y, Yuan S, et al. Decreasing Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 3C (EIF3C) suppresses proliferation and stimulates apoptosis in breast cancer cell lines through mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) pathway. Med Sci Monit. 2017; 23:4182–4191.
Article7. Okabe-Kado J, Hagiwara-Watanabe Y, Niitsu N, Kasukabe T, Kaneko Y. NM23 downregulation and lysophosphatidic acid receptor EDG2/lpa1 upregulation during myeloid differentiation of human leukemia cells. Leuk Res. 2018; 66:39–48.
Article8. Farkas Z, Fancsalszky L, Saskői É, Gráf A, Tárnok K, Mehta A, et al. The dosage-dependent effect exerted by the NM23-H1/H2 homolog NDK-1 on distal tip cell migration in C. elegans . Lab Invest. 2018; 98:182–189.
Article9. Nakakido M, Tamura K, Chung S, Ueda K, Fujii R, Kiyotani K, et al. Phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis, class X containing complex promotes cancer cell proliferation through suppression of EHD2 and ZIC1, putative tumor suppressors. Int J Oncol. 2016; 49:868–876.
Article10. Kim YJ, Sung M, Oh E, Vrancken MV, Song JY, Jung K, et al. Engrailed 1 overexpression as a potential prognostic marker in quintuple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2018; 19:335–345.
Article11. Han W, Zhang C, Cao FY, Cao F, Jiang L, Ding HZ. Prognostic and clinicopathological value of NM23 expression in patients with breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr Probl Cancer. 2017; 41:80–93.
Article12. Vucemilo T, Skoko M, Sarcević B, Puljiz M, Alvir I, Turudić TP, et al. The level of serum pro-matrix metalloproteinase-2 as a prognostic factor in patients with invasive ductal breast cancer. Coll Antropol. 2014; 38:135–140.13. Li F, Yin X, Luo X, Li HY, Su X, Wang XY, et al. Livin promotes progression of breast cancer through induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and activation of AKT signaling. Cell Signal. 2013; 25:1413–1422.
Article14. Han W, Zhang C, Gao XJ, Wang HB, Chen F, Cao F, et al. Clinicopathologic and prognostic significance of the zinc finger of the cerebellum family in invasive breast cancer. J Breast Cancer. 2018; 21:51–61.
Article15. Werner TA, Dizdar L, Nolten I, Riemer JC, Mersch S, Schütte SC, et al. Survivin and XIAP - two potential biological targets in follicular thyroid carcinoma. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:11383.
Article16. Wang QP, Wang Y, Wang XD, Mo XM, Gu J, Lu ZY, et al. Survivin up-regulates the expression of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) through attenuating the suppression of p53 on NF-κB expression in MCF-7/5-FU cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013; 45:2036–2044.
Article17. Jin Q, Feng L, Behrens C, Bekele BN, Wistuba II, Hong WK, et al. Implication of AMP-activated protein kinase and Akt-regulated survivin in lung cancer chemopreventive activities of deguelin. Cancer Res. 2007; 67:11630–11639.
Article18. Siddharth S, Das S, Nayak A, Kundu CN. SURVIVIN as a marker for quiescent-breast cancer stem cells-An intermediate, adherent, pre-requisite phase of breast cancer metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2016; 33:661–675.
Article19. Grzmil M, Rzymski T, Milani M, Harris AL, Capper RG, Saunders NJ, et al. An oncogenic role of eIF3e/INT6 in human breast cancer. Oncogene. 2010; 29:4080–4089.
Article20. Zheng Q, Liu H, Ye J, Zhang H, Jia Z, Cao J. Nuclear distribution of eIF3g and its interacting nuclear proteins in breast cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 2016; 13:2973–2980.
Article21. Mahmood SF, Gruel N, Chapeaublanc E, Lescure A, Jones T, Reyal F, et al. A siRNA screen identifies RAD21, EIF3H, CHRAC1 and TANC2 as driver genes within the 8q23, 8q24.3 and 17q23 amplicons in breast cancer with effects on cell growth, survival and transformation. Carcinogenesis. 2014; 35:670–682.
Article22. Wakefield A, Soukupova J, Montagne A, Ranger J, French R, Muller WJ, et al. Bcl3 selectively promotes metastasis of ERBB2-driven mammary tumors. Cancer Res. 2013; 73:745–755.
Article23. Aruga J, Yokota N, Hashimoto M, Furuichi T, Fukuda M, Mikoshiba K. A novel zinc finger protein, zic, is involved in neurogenesis, especially in the cell lineage of cerebellar granule cells. J Neurochem. 1994; 63:1880–1890.
Article24. Li Y, Ma X, Wu X, Liu X, Liu L. Prognostic significance of survivin in breast cancer: meta-analysis. Breast J. 2014; 20:514–524.
Article25. Stache C, Bils C, Fahlbusch R, Flitsch J, Buchfelder M, Stefanits H, et al. Drug priming enhances radiosensitivity of adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma via downregulation of survivin. Neurosurg Focus. 2016; 41:E14.
Article26. Yang YL, Ji C, Bi ZG, Lu CC, Wang R, Gu B, et al. Deguelin induces both apoptosis and autophagy in cultured head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e54736.
Article27. Wilson JM, Kunnimalaiyaan S, Kunnimalaiyaan M, Gamblin TC. Inhibition of the AKT pathway in cholangiocarcinoma by MK2206 reduces cellular viability via induction of apoptosis. Cancer Cell Int. 2015; 15:13.
Article28. Du L, Qian X, Dai C, Wang L, Huang D, Wang S, et al. Screening the molecular targets of ovarian cancer based on bioinformatics analysis. Tumori. 2015; 101:384–389.
Article29. Qiang W, Zhao Y, Yang Q, Liu W, Guan H, Lv S, et al. ZIC1 is a putative tumor suppressor in thyroid cancer by modulating major signaling pathways and transcription factor FOXO3a. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014; 99:E1163–72.
Article30. Han W, Cao F, Gao XJ, Wang HB, Chen F, Cai SJ, et al. ZIC1 acts a tumor suppressor in breast cancer by targeting survivin. Int J Oncol. 2018; 53:937–948.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognosis of Early Stage Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Comparison with Non-triple Negative Group
- Prognostic Value of TZAP Expression in Various Cancers: TCGA Data Analysis
- Expression of Survivin According to Malignant Progression of Breast Lesions
- Expression of Survivin in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma: Relationship to Tumor Biology and Prognosis in Surgically Treated Patients
- The Prognostic Significance of Survivin Expression in Breast Cancer