J Liver Cancer.
2019 Mar;19(1):64-68. 10.17998/jlc.19.1.64.
Liver Transplantation after Successful Downstaging with Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy in a Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. yoonsk@catholic.ac.kr
- 2The Catholic Liver Research Center, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2448279
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.1.64
Abstract
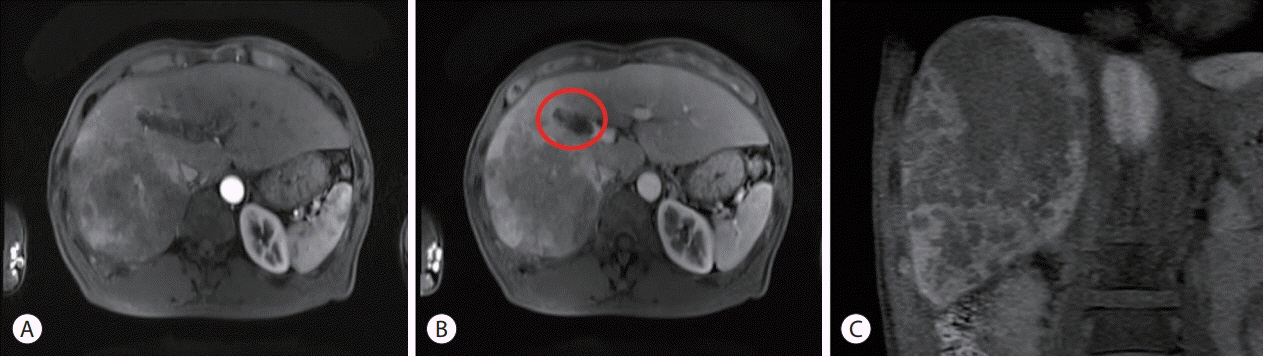
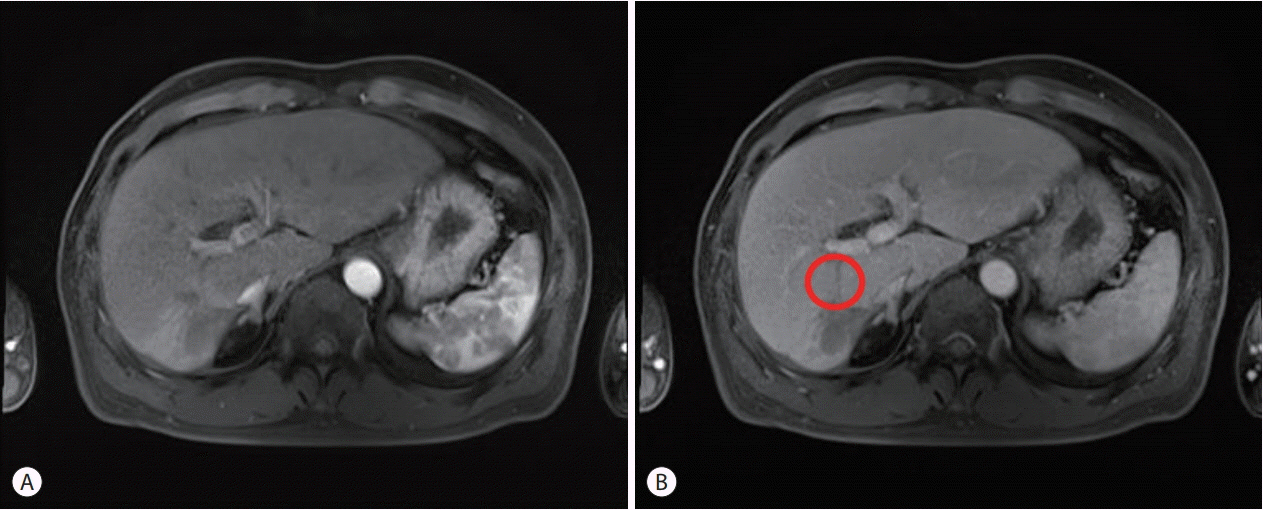
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common cancers worldwide. The majority of patients with HCC are diagnosed at advanced disease stages with vascular invasion, where curative approaches are often not feasible. Currently, sorafenib is the only available standard therapy for HCC with portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT). However, in many cases, sorafenib therapy fails to achieve satisfactory results in clinical practice. We present a case of advanced HCC with PVTT that was treated with hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) followed by liver transplantation. Three cycles of HAIC treatment resulted in necrotic changes in most of the tumors, and PVTT was reduced to an extent at which liver transplantation was possible. Further studies are required to determine the treatment strategies for advanced HCC with PVTT that can improve prognosis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Heimbach JK, Kulik LM, Finn RS, Sirlin CB, Abecassis MM, Roberts LR, et al. AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2018; 67:358–380.2. Pinter M, Peck-Radosavljevic M. Review article: systemic treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018; 48:598–609.3. Finn RS, Zhu AX, Farah W, Almasri J, Zaiem F, Prokop LJ, et al. Therapies for advanced stage hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion or metastatic disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology. 2018; 67:422–435.4. European Association for the Study of the Liver, Galle PR, Forner A, Llovet JM, Mazzaferro V, Piscaglia F, et al. EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2018; 69:182–236.5. Omata M, Cheng AL, Kokudo N, Kudo M, Lee JM, Jia J, et al. Asia-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: a 2017 update. Hepatol Int. 2017; 11:317–370.6. Kim DY, Kim HJ, Han KH, Han SY, Heo J, Woo HY, et al. Real-life experience of sorafenib treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma in Korea: from GIDEON data. Cancer Res Treat. 2016; 48:1243–1252.7. Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009; 10:25–34.8. Choi JH, Chung WJ, Bae SH, Song DS, Song MJ, Kim YS, et al. Randomized, prospective, comparative study on the effects and safety of sorafenib vs. hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018; 82:469–478.9. Onishi H, Nouso K, Nakamura S, Katsui K, Wada N, Morimoto Y, et al. Efficacy of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy in combination with irradiation for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein invasion. Hepatol Int. 2015; 9:105–112.10. Song DS, Bae SH, Song MJ, Lee SW, Kim HY, Lee YJ, et al. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:4679–4688.11. Song MJ. Hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2015; 21:3843–3849.12. Bruix J, Sherman M; American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology. 2011; 53:1020–1022.13. Parikh ND, Waljee AK, Singal AG. Downstaging hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and pooled analysis. Liver Transpl. 2015; 21:1142–1152.14. Sung PS, Park HL, Yang K, Hwang S, Song MJ, Jang JW, et al. 18Ffluorodeoxyglucose uptake of hepatocellular carcinoma as a prognostic predictor in patients with sorafenib treatment. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2018; 45:384–391.15. Llovet JM, Zucman-Rossi J, Pikarsky E, Sangro B, Schwartz M, Sherman M, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016; 2:16018.16. Jeong SW, Jang JY, Shim KY, Lee SH, Kim SG, Cha SW, et al. Practical effect of sorafenib monotherapy on advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein tumor thrombosis. Gut Liver. 2013; 7:696–703.17. Park JG. Long-term outcomes of patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma who achieved complete remission after sorafenib therapy. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2015; 21:287–294.18. Moriguchi M, Aramaki T, Nishiofuku H, Sato R, Asakura K, Yamaguchi K, et al. Sorafenib versus hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy as initial treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma with advanced portal vein tumor thrombosis. Liver Cancer. 2017; 6:275–286.19. Dasari S, Tchounwou PB. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014; 740:364–378.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis
- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis Treated by Hepatic Artery Injection Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy
- A Case of Successful Living Donor Liver Transplantation after Down-staging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with the Beyond Milan Criteria by Radioembolization, Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy, and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis Treated by Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy
- Pathological Complete Remission of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Main Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis by Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy