J Breast Cancer.
2019 Mar;22(1):109-119. 10.4048/jbc.2019.22.e7.
Immediate Breast Reconstruction Does Not Have a Clinically Significant Impact on Adjuvant Treatment Delay and Subsequent Survival Outcomes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. gsjjoon@yuhs.ac
- 2Departments of Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2441856
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2019.22.e7
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The use of immediate breast reconstruction (IBR) has been debated because it may be a causative factor in adjuvant treatment delay and may subsequently increase the probability of recurrence. We investigated whether IBR was related to adjuvant treatment delay and survival outcomes.
METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed the duration from operation to adjuvant treatment administration and survival outcomes according to IBR status among patients with breast cancer who underwent mastectomy followed by adjuvant chemotherapy from January 2005 to December 2014. Propensity score matching was performed to balance the clinicopathologic baseline characteristics between patients who did and did not undergo IBR.
RESULTS
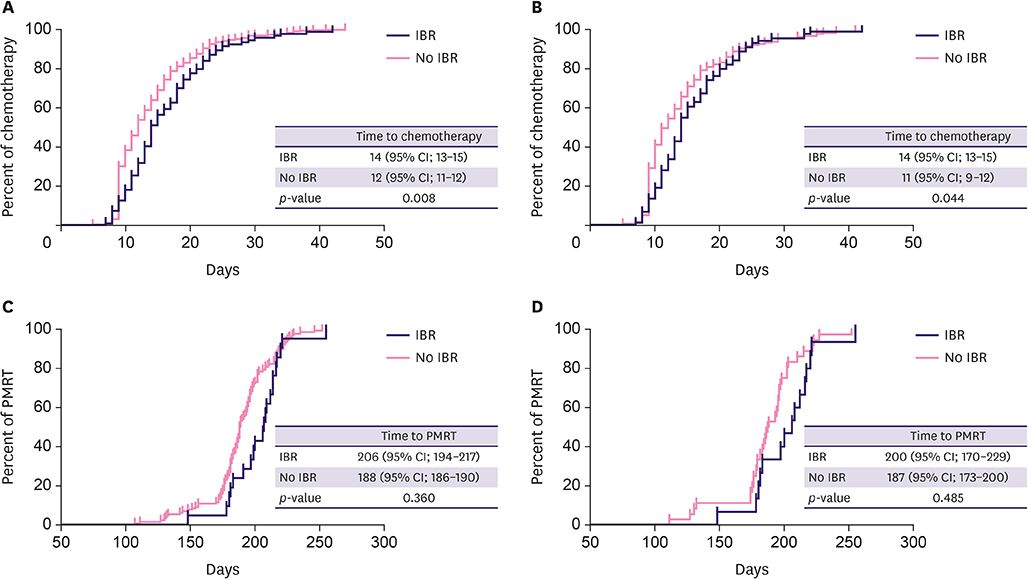
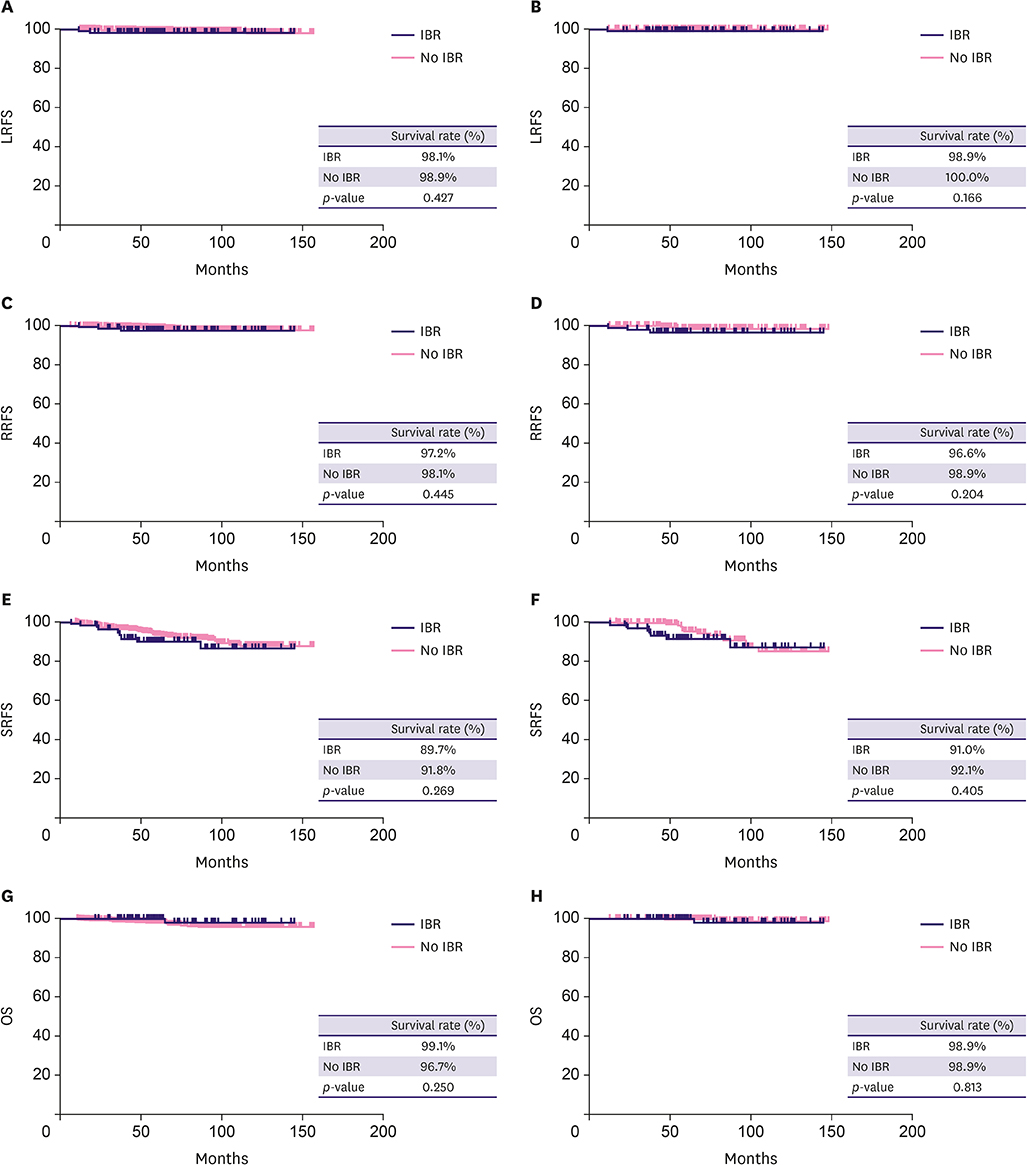
Of 646 patients, 107 (16.6%) underwent IBR, and the median follow-up was 72 months. The median duration from surgery to adjuvant chemotherapy was significantly longer in patients who underwent IBR than in those who did not (14 vs. 12 days, respectively, p = 0.008). Based on propensity score matching, patients who underwent IBR received adjuvant therapy 3 days later than those who did not (14 vs. 11 days, respectively, p = 0.044). The duration from surgery to post-mastectomy radiation therapy (PMRT) did not significantly differ between the 2 groups. Local recurrence-free survival, regional recurrence-free survival, systemic recurrence-free survival, and overall survival were also not significantly different between the 2 groups (p = 0.427, p = 0.445, p = 0.269, and p = 0.250, respectively). In the case-matched cohort, survival outcomes did not change.
CONCLUSION
IBR was associated with a modest increase in the duration from surgery to chemotherapy that was statistically but not clinically significant. Moreover, IBR had no influence on PMRT delay or survival outcomes, suggesting that it is an acceptable option for patients with non-metastatic breast cancer undergoing mastectomy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Masetti R, Di Leone A, Franceschini G, Magno S, Terribile D, Fabbri MC, et al. Oncoplastic techniques in the conservative surgical treatment of breast cancer: an overview. Breast J. 2006; 12:S174–S180.
Article2. Dragun AE, Huang B, Tucker TC, Spanos WJ. Increasing mastectomy rates among all age groups for early stage breast cancer: a 10-year study of surgical choice. Breast J. 2012; 18:318–325.
Article3. Rowland JH, Desmond KA, Meyerowitz BE, Belin TR, Wyatt GE, Ganz PA. Role of breast reconstructive surgery in physical and emotional outcomes among breast cancer survivors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000; 92:1422–1429.
Article4. Kiebert GM, de Haes JC, van de Velde CJ. The impact of breast-conserving treatment and mastectomy on the quality of life of early-stage breast cancer patients: a review. J Clin Oncol. 1991; 9:1059–1070.
Article5. Moyer A. Psychosocial outcomes of breast-conserving surgery versus mastectomy: a meta-analytic review. Health Psychol. 1997; 16:284–298.
Article6. Albornoz CR, Bach PB, Mehrara BJ, Disa JJ, Pusic AL, McCarthy CM, et al. A paradigm shift in U.S. breast reconstruction: increasing implant rates. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013; 131:15–23.7. Min SY, Kim Z, Hur MH, Yoon CS, Park EH, Jung KW, et al. The basic facts of Korean breast cancer in 2013: results of a nationwide survey and breast cancer registry database. J Breast Cancer. 2016; 19:1–7.
Article8. Cemal Y, Albornoz CR, Disa JJ, McCarthy CM, Mehrara BJ, Pusic AL, et al. A paradigm shift in U.S. breast reconstruction. Part 2. The influence of changing mastectomy patterns on reconstructive rate and method. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013; 131:320e–326e.9. Nguyen AT, Chang DW. Discussion: a paradigm shift in U.S. breast reconstruction: increasing implant rates. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013; 131:24–25.10. Zhong T, Hofer SO, McCready DR, Jacks LM, Cook FE, Baxter N. A comparison of surgical complications between immediate breast reconstruction and mastectomy: the impact on delivery of chemotherapy--an analysis of 391 procedures. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012; 19:560–566.
Article11. Rainsbury RM. Skin-sparing mastectomy. Br J Surg. 2006; 93:276–281.
Article12. Gagliato DM, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Lei X, Theriault RL, Giordano SH, Valero V, et al. Clinical impact of delaying initiation of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2014; 32:735–744.
Article13. Huang J, Barbera L, Brouwers M, Browman G, Mackillop WJ. Does delay in starting treatment affect the outcomes of radiotherapy? A systematic review. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21:555–563.
Article14. Alderman AK, Collins ED, Schott A, Hughes ME, Ottesen RA, Theriault RL, et al. The impact of breast reconstruction on the delivery of chemotherapy. Cancer. 2010; 116:1791–1800.
Article15. Zhang P, Li CZ, Wu CT, Jiao GM, Yan F, Zhu HC, et al. Comparison of immediate breast reconstruction after mastectomy and mastectomy alone for breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2017; 43:285–293.
Article16. Ryu JM, Paik HJ, Park S, Yi HW, Nam SJ, Kim SW, et al. Oncologic outcomes after immediate breast reconstruction following total mastectomy in patients with breast cancer: a matched case-control study. J Breast Cancer. 2017; 20:74–81.
Article17. Ryu JM, Park S, Paik HJ, Nam SJ, Kim SW, Lee SK, et al. Oncologic safety of immediate breast reconstruction in breast cancer patients who underwent neoadjuvant chemotherapy: short-term outcomes of a matched case-control study. Clin Breast Cancer. 2017; 17:204–210.
Article18. Reuben BC, Manwaring J, Neumayer LA. Recent trends and predictors in immediate breast reconstruction after mastectomy in the United States. Am J Surg. 2009; 198:237–243.
Article19. Joslyn SA. Patterns of care for immediate and early delayed breast reconstruction following mastectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005; 115:1289–1296.
Article20. Kronowitz SJ, Kuerer HM. Advances and surgical decision-making for breast reconstruction. Cancer. 2006; 107:893–907.
Article21. Morrow M, Scott SK, Menck HR, Mustoe TA, Winchester DP. Factors influencing the use of breast reconstruction postmastectomy: a national cancer database study. J Am Coll Surg. 2001; 192:1–8.
Article22. Lohrisch C, Paltiel C, Gelmon K, Speers C, Taylor S, Barnett J, et al. Impact on survival of time from definitive surgery to initiation of adjuvant chemotherapy for early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:4888–4894.
Article23. Senkus E, Kyriakides S, Ohno S, Penault-Llorca F, Poortmans P, Rutgers E, et al. Primary breast cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2015; 26:Suppl 5. v8–v30.
Article24. Recht A, Edge SB, Solin LJ, Robinson DS, Estabrook A, Fine RE, et al. Postmastectomy radiotherapy: clinical practice guidelines of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. J Clin Oncol. 2001; 19:1539–1569.
Article25. Overgaard M, Nielsen HM, Overgaard J. Is the benefit of postmastectomy irradiation limited to patients with four or more positive nodes, as recommended in international consensus reports? A subgroup analysis of the DBCG 82 b&c randomized trials. Radiother Oncol. 2007; 82:247–253.
Article26. Clarke M, Collins R, Darby S, Davies C, Elphinstone P, Evans V, et al. Effects of radiotherapy and of differences in the extent of surgery for early breast cancer on local recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005; 366:2087–2106.
Article27. Wright JL, Cordeiro PG, Ben-Porat L, Van Zee KJ, Hudis C, Beal K, et al. Mastectomy with immediate expander-implant reconstruction, adjuvant chemotherapy, and radiation for stage II–III breast cancer: treatment intervals and clinical outcomes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008; 70:43–50.
Article28. Albright EL, Schroeder MC, Foster K, Sugg SL, Erdahl LM, Weigel RJ, et al. Nipple-sparing mastectomy is not associated with a delay of adjuvant treatment. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018; 25:1928–1935.
Article29. Jabo B, Lin AC, Aljehani MA, Ji L, Morgan JW, Selleck MJ, et al. Impact of breast reconstruction on time to definitive surgical treatment, adjuvant therapy, and breast cancer outcomes. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018; 25:3096–3105.
Article30. Xavier Harmeling J, Kouwenberg CA, Bijlard E, Burger KN, Jager A, Mureau MA. The effect of immediate breast reconstruction on the timing of adjuvant chemotherapy: a systematic review. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015; 153:241–251.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Immediate Breast Reconstruction Following Mastectomy for the Treatment of Advanced Breast Cancer Patients
- Reliability of Reconstructed Breast Flap after Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy in Immediate Breast Reconstruction
- Delay of Treatment Initiation Does Not Adversely Affect Survival Outcome in Breast Cancer
- Analysis of the Effects of Breast Reconstruction in Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Radiotherapy after Mastectomy
- Does Immediate Breast Reconstruction after Mastectomy affect the Initiation of Adjuvant Chemotherapy?