Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2019 Mar;22(2):107-121. 10.5223/pghn.2019.22.2.107.
Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children: from Guidelines to Clinical Practice
- Affiliations
-
- 1KidZ Health Castle, UZ Brussel, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussels, Belgium. Yvan.Vandenplas@uzbrussel.be
- 2Department of Pediatrics, University of Insubria, Varese, Italy.
- KMID: 2440585
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2019.22.2.107
Abstract
- The diagnosis and management of gastro-esophageal reflux (GER) and GER disease (GERD) in infants and children remains a challenge. Published guidelines and position papers, along with Embase, MEDLINE, and the Cochrane Database were reviewed and summarized with the intent to propose a practical approach and management of GER and GERD for healthcare providers and to standardize and improve the quality of care for infants and children. For this purpose, 2 algorithms were developed, 1 for infants < 12 months of age and the other for older children. None of the signs and symptoms of GER and GERD are specific and there is no gold standard diagnostic test or tool. Nutritional management is recommended as a first-line approach in infants, while in children, a therapeutic trial with antacid medication is advised for early management. The practical recommendations from this review are intended to optimize the management of GER in infants and older children and reduce the number of investigations and inappropriate use of medication.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
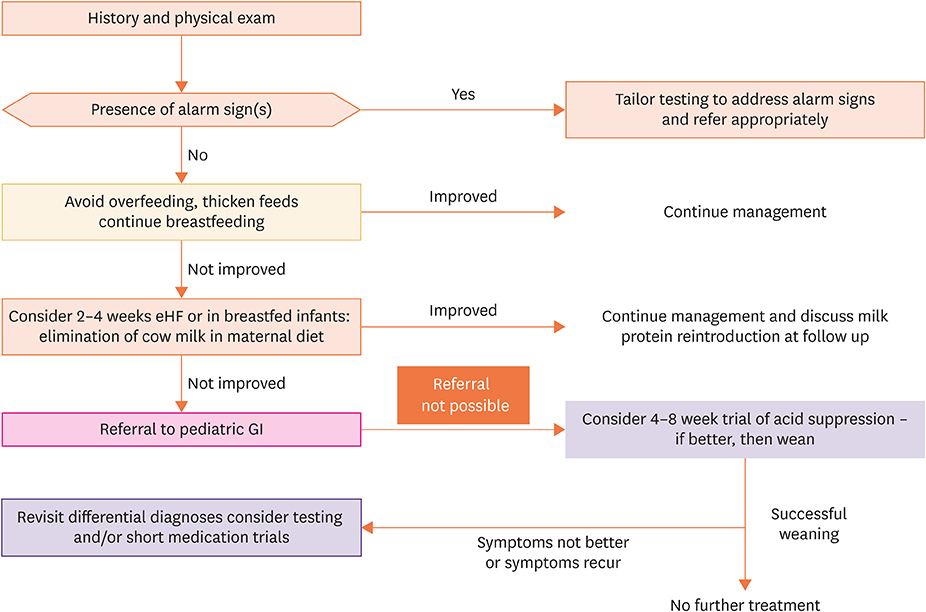
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Is the Diagnostic Trial with Proton Pump Inhibitors Reasonable for School Age Children with Gastroesophageal Reflux Symptoms?
Jaeeun Yang, Jieon Lee, Hyunju Lee, Juyeon Lee, Young Mi Yoon, Jae Hong Choi, Yoon-Joo Kim, Hyun Sik Kang, Kyoung Hee Han, Seung Hyo Kim, Ki-Soo Kang
Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2019;22(6):511-517. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2019.22.6.511.
Reference
-
1. Vandenplas Y, Rudolph CD, Di Lorenzo C, Hassall E, Liptak G, Mazur L, et al. Pediatric gastroesophageal reflux clinical practice guidelines: joint recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (NASPGHAN) and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2009; 49:498–547.
Article2. Rosen R, Vandenplas Y, Singendonk M, Cabana M, DiLorenzo C, Gottrand F, et al. Pediatric gastroesophageal reflux clinical practice guidelines: joint recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018; 66:516–554.
Article3. Gupta SK, Hassall E, Chiu YL, Amer F, Heyman MB. Presenting symptoms of nonerosive and erosive esophagitis in pediatric patients. Dig Dis Sci. 2006; 51:858–863.
Article4. Martigne L, Delaage PH, Thomas-Delecourt F, Bonnelye G, Barthélémy P, Gottrand F. Prevalence and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease in children and adolescents: a nationwide cross-sectional observational study. Eur J Pediatr. 2012; 171:1767–1773.
Article5. Rasquin A, Di Lorenzo C, Forbes D, Guiraldes E, Hyams JS, Staiano A, et al. Childhood functional gastrointestinal disorders: child/adolescent. Gastroenterology. 2006; 130:1527–1537.
Article6. Hyman PE, Milla PJ, Benninga MA, Davidson GP, Fleisher DF, Taminiau J. Childhood functional gastrointestinal disorders: neonate/toddler. Gastroenterology. 2006; 130:1519–1526.
Article7. Dalla Vecchia LK, Grosfeld JL, West KW, Rescorla FJ, Scherer LR 3rd, Engum SA. Reoperation after Nissen fundoplication in children with gastroesophageal reflux: experience with 130 patients. Ann Surg. 1997; 226:315–321.8. Schneider A, Gottrand F, Sfeir R, Duhamel A, Bonnevalle M, Guimber D, et al. Postoperative lower esophageal dilation in children following the performance of Nissen fundoplication. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2012; 22:399–403.
Article9. Westra SJ, Wolf BH, Staalman CR. Ultrasound diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux and hiatal hernia in infants and young children. J Clin Ultrasound. 1990; 18:477–485.
Article10. Jang HS, Lee JS, Lim GY, Choi BG, Choi GH, Park SH. Correlation of color Doppler sonographic findings with pH measurements in gastroesophageal reflux in children. J Clin Ultrasound. 2001; 29:212–217.
Article11. Patra S, Singh V, Chandra J, Kumar P, Tripathi M. Diagnostic modalities for gastro-esophageal reflux in infantile wheezers. J Trop Pediatr. 2011; 57:99–103.
Article12. Ravelli AM, Panarotto MB, Verdoni L, Consolati V, Bolognini S. Pulmonary aspiration shown by scintigraphy in gastroesophageal reflux-related respiratory disease. Chest. 2006; 130:1520–1526.
Article13. Ravelli AM, Villanacci V, Ruzzenenti N, Grigolato P, Tobanelli P, Klersy C, et al. Dilated intercellular spaces: a major morphological feature of esophagitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006; 42:510–515.14. Cucchiara S, Minella R, D'Armiento F, Franco M, Lervolino C, Campanozzi A, et al. Histologic grading of reflux oesophagitis and its relationship with intra-oesophageal and intragastric pH variables. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1993; 5:621–626.
Article15. Arasu TS, Wyllie R, Fitzgerald JF, Franken EA, Siddiqui AR, Lehman GA, et al. Gastroesophageal reflux in infants and children comparative accuracy of diagnostic methods. J Pediatr. 1980; 96:798–803.
Article16. Vandenplas Y, Franckx-Goossens A, Pipeleers-Marichal M, Derde MP, Sacré-Smits L. Area under pH 4: advantages of a new parameter in the interpretation of esophageal pH monitoring data in infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1989; 9:34–39.17. Farhath S, He Z, Saslow J, Soundar S, Amendolia B, Bhat V, et al. Detection of pepsin in mouth swab: correlation with clinical gastroesophageal reflux in preterm infants. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013; 26:819–824.
Article18. Rosen R, Johnston N, Hart K, Khatwa U, Nurko S. The presence of pepsin in the lung and its relationship to pathologic gastro-esophageal reflux. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012; 24:129–133. e84–125.
Article19. Farrell S, McMaster C, Gibson D, Shields MD, McCallion WA. Pepsin in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid: a specific and sensitive method of diagnosing gastro-oesophageal reflux-related pulmonary aspiration. J Pediatr Surg. 2006; 41:289–293.
Article20. Krishnan U, Mitchell JD, Messina I, Day AS, Bohane TD. Assay of tracheal pepsin as a marker of reflux aspiration. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2002; 35:303–308.
Article21. Dy F, Amirault J, Mitchell PD, Rosen R. Salivary pepsin lacks sensitivity as a diagnostic tool to evaluate extraesophageal reflux disease. J Pediatr. 2016; 177:53–58.
Article22. Fortunato JE, D'Agostino RB Jr, Lively MO. Pepsin in saliva as a biomarker for oropharyngeal reflux compared with 24-hour esophageal impedance/pH monitoring in pediatric patients. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017; 29:e12936.
Article23. O'Reilly RC, He Z, Bloedon E, Papsin B, Lundy L, Bolling L, et al. The role of extraesophageal reflux in otitis media in infants and children. Laryngoscope. 2008; 118:Suppl 116. 1–9.24. Kelly EA, Parakininkas DE, Werlin SL, Southern JF, Johnston N, Kerschner JE. Prevalence of pediatric aspiration-associated extraesophageal reflux disease. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013; 139:996–1001.
Article25. Rosen R, Fritz J, Nurko A, Simon D, Nurko S. Lipid-laden macrophage index is not an indicator of gastroesophageal reflux-related respiratory disease in children. Pediatrics. 2008; 121:e879–e884.
Article26. Tucker E, Knowles K, Wright J, Fox MR. Rumination variations: aetiology and classification of abnormal behavioural responses to digestive symptoms based on high-resolution manometry studies. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013; 37:263–274.
Article27. Kessing BF, Bredenoord AJ, Smout AJ. Objective manometric criteria for the rumination syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014; 109:52–59.
Article28. van der Pol RJ, Smits MJ, van Wijk MP, Omari TI, Tabbers MM, Benninga MA. Efficacy of proton-pump inhibitors in children with gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review. Pediatrics. 2011; 127:925–935.
Article29. Haddad I, Kierkus J, Tron E, Ulmer A, Hu P, Sloan S, et al. Efficacy and safety of rabeprazole in children (1–11 years) with gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2013; 57:798–807.
Article30. Fiedorek S, Tolia V, Gold BD, Huang B, Stolle J, Lee C, et al. Efficacy and safety of lansoprazole in adolescents with symptomatic erosive and non-erosive gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005; 40:319–327.
Article31. Baker R, Tsou VM, Tung J, Baker SS, Li H, Wang W, et al. Clinical results from a randomized, double-blind, dose-ranging study of pantoprazole in children aged 1 through 5 years with symptomatic histologic or erosive esophagitis. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2010; 49:852–865.
Article32. Tolia V, Ferry G, Gunasekaran T, Huang B, Keith R, Book L. Efficacy of lansoprazole in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2002; 35:Suppl 4. S308–S318.
Article33. Croffie JM, Fitzgerald JF, Molleston JP, Gupta SK, Corkins MR, Pfefferkorn MD, et al. Accuracy and tolerability of the Bravo catheter-free pH capsule in patients between the ages of 4 and 18 years. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007; 45:559–563.
Article34. Rao NM, Campbell DI, Rao P. Two years' experience of using the Bravo wireless oesophageal pH monitoring system at a single UK tertiary centre. Acta Paediatr. 2017; 106:312–315.
Article35. Cabrera J, Davis M, Horn D, Pfefferkorn M, Croffie JM. Esophageal pH monitoring with the BRAVO capsule: experience in a single tertiary medical center. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011; 53:404–408.36. Moon RY. Task Force on Sudden Infant Death Syndrome. SIDS and other sleep-related infant deaths: expansion of recommendations for a safe infant sleeping environment. Pediatrics. 2011; 128:1030–1039.
Article37. Salvatore S, Savino F, Singendonk M, Tabbers M, Benninga MA, Staiano A, et al. Thickened infant formula: what to know. Nutrition. 2018; 49:51–56.
Article38. Koebnick C, Getahun D, Smith N, Porter AH, Der-Sarkissian JK, Jacobsen SJ. Extreme childhood obesity is associated with increased risk for gastroesophageal reflux disease in a large population-based study. Int J Pediatr Obes. 2011; 6:e257–63.
Article39. Pashankar DS, Corbin Z, Shah SK, Caprio S. Increased prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux symptoms in obese children evaluated in an academic medical center. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2009; 43:410–413.
Article40. Ummarino D, Miele E, Martinelli M, Scarpato E, Crocetto F, Sciorio E, et al. Effect of magnesium alginate plus simethicone on gastroesophageal reflux in infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015; 60:230–235.
Article41. Miller S. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of a new aluminium-free paediatric alginate preparation and placebo in infants with recurrent gastro-oesophageal reflux. Curr Med Res Opin. 1999; 15:160–168.
Article42. Salvatore S, Ripepi A, Huysentruyt K, van de Maele K, Nosetti L, Agosti M, et al. The effect of alginate in gastroesophageal reflux in infants. Paediatr Drugs. 2018; 20:575–583.
Article43. Davies I, Burman-Roy S, Murphy MS. Guideline Development Group. Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in children: NICE guidance. BMJ. 2015; 350:g7703.
Article44. Orenstein SR, Hassall E, Furmaga-Jablonska W, Atkinson S, Raanan M. Multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial assessing the efficacy and safety of proton pump inhibitor lansoprazole in infants with symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Pediatr. 2009; 154:514–520.e4.
Article45. Yadlapati R, Kahrilas PJ. The “dangers” of chronic proton pump inhibitor use. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018; 141:79–81.
Article46. Katz PO, Gerson LB, Vela MF. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108:308–328.
Article47. Rosen R, Amirault J, Liu H, Mitchell P, Hu L, Khatwa U, et al. Changes in gastric and lung microflora with acid suppression: acid suppression and bacterial growth. JAMA Pediatr. 2014; 168:932–937.
Article48. Trikha A, Baillargeon JG, Kuo YF, Tan A, Pierson K, Sharma G, et al. Development of food allergies in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease treated with gastric acid suppressive medications. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2013; 24:582–588.
Article49. Khoshoo V, Dhume P. Clinical response to 2 dosing regimens of lansoprazole in infants with gastroesophageal reflux. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008; 46:352–354.
Article50. Omari TI, Benninga MA, Sansom L, Butler RN, Dent J, Davidson GP. Effect of baclofen on esophagogastric motility and gastroesophageal reflux in children with gastroesophageal reflux disease: a randomized controlled trial. J Pediatr. 2006; 149:468–474.
Article51. Li S, Shi S, Chen F, Lin J. The effects of baclofen for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2014; 2014:307805.
Article52. De Loore I, Van Ravensteyn H, Ameryckx L. Domperidone drops in the symptomatic treatment of chronic paediatric vomiting and regurgitation. A comparison with metoclopramide. Postgrad Med J. 1979; 55:Suppl 1. 40–42.53. Carroccio A, Iacono G, Montalto G, Cavataio F, Soresi M, Notarbartolo A. Domperidone plus magnesium hydroxide and aluminum hydroxide: a valid therapy in children with gastroesophageal reflux. A double-blind randomized study versus placebo. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1994; 29:300–304.
Article54. Lau Moon Lin M, Robinson PD, Flank J, Sung L, Dupuis LL. The Safety of metoclopramide in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Drug Saf. 2016; 39:675–687.
Article55. Morris AD, Chen J, Lau E, Poh J. Domperidone-associated QT interval prolongation in non-oncologic pediatric patients: a review of the literature. Can J Hosp Pharm. 2016; 69:224–230.
Article56. Levi P, Marmo F, Saluzzo C, Dell'Olio D, Ansaldi N, Giuliani L, et al. Bethanechol versus antiacids in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1985; 40:349–359.57. Euler AR. Use of bethanechol for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux. J Pediatr. 1980; 96:321–324.
Article58. Rohof WO, Bennink RJ, de Ruigh AA, Hirsch DP, Zwinderman AH, Boeckxstaens GE. Effect of azithromycin on acid reflux, hiatus hernia and proximal acid pocket in the postprandial period. Gut. 2012; 61:1670–1677.
Article59. Rothenberg SS. Two decades of experience with laparoscopic nissen fundoplication in infants and children: a critical evaluation of indications, technique, and results. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2013; 23:791–794.
Article60. Hambraeus M, Arnbjörnsson E, Anderberg M. A literature review of the outcomes after robot-assisted laparoscopic and conventional laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication for gastro-esophageal reflux disease in children. Int J Med Robot. 2013; 9:428–432.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
- Letter to the Editor: Guidelines for the Treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
- Clinical Practice Guidelines on Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systematic Quality Appraisal of International Guidelines
- Is Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Achalasia Coincident or Not?
- Esophageal pH and Combined Impedance-pH Monitoring in Children