Clinical Features of Atopic Dermatitis in Adults Are Different according to Onset
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dermap@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2439472
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.8.1360
Abstract
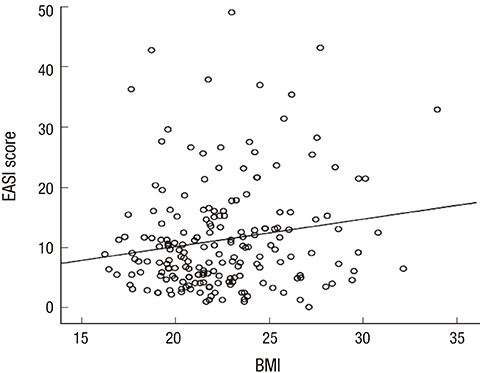
- Few studies of atopic dermatitis (AD) in adult patients have evaluated differences in clinical features of AD according to onset age. We aimed to characterize the clinical features of AD in adult patients according to age of onset. Subjects with AD outpatient visiting the Department of Dermatology at Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital were recruited for this study. A dermatologist conducted clinical evaluation, a survey of demographics, and onset of AD-associated signs and symptoms for each participant. Total immunoglobulin E (IgE) was also tested. A total of 280 adult AD patients were enrolled, among which 232 patients (82.86%) showed pre-adult-onset (age < 18 years) and 48 patients (17.14%) had adult-onset (age ≥ 18 years) of AD. There were significant differences between the 2 groups in the area of initial involvement (P = 0.017) and in treatment history (P = 0.010). Interestingly, patients with body mass index (BMI) ≥ 25 showed significantly higher Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) scores than did patients with BMI < 25 in the pre-adult-onset adult AD group (P = 0.048). On the other hand, there were no significant differences in sex, family history, BMI, EASI, and total IgE between patients with pre-adult-onset AD and patients with adult-onset AD. Our findings suggest that, even though many common features exist, there are significant differences between the clinical characteristics of pre-adult-onset and adult-onset AD subgroups, in adult patients with AD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Influence of Weight Loss on Severity of Atopic Dermatitis in a 20-Year-Old Female with Atopic Dermatitis
Jee Hee Son, Bo Young Chung, Min Je Jung, Yong Won Choi, Hye One Kim, Chun Wook Park
Ann Dermatol. 2018;30(5):626-628. doi: 10.5021/ad.2018.30.5.626.Clinical Characteristics of Atopic Dermatitis in Korean School-Aged Children and Adolescents According to Onset Age and Severity
You Hoon Jeon, Kangmo Ahn, Jihyun Kim, Meeyong Shin, Soo-Jong Hong, So-Yeon Lee, Bok Yang Pyun, Taek Ki Min, Minyoung Jung, Jeongmin Lee, Tae Won Song, Hye-Young Kim, Sooyoung Lee, Kyunguk Jeong, Yoonha Hwang, Minji Kim, Yong Ju Lee, Min Jung Kim, Ji Young Lee, Hye Yung Yum, Gwang Cheon Jang, Young A Park, Jeong Hee Kim,
J Korean Med Sci. 2022;37(4):e30. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e30.
Reference
-
1. Williams HC. Epidemiology of atopic dermatitis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2000; 25:522–529.2. Hunter JA, Herd RM. Recent advances in atopic dermatitis. Q J Med. 1994; 87:323–327.3. Tay YK, Khoo BP, Goh CL. The profile of atopic dermatitis in a tertiary dermatology outpatient clinic in Singapore. Int J Dermatol. 1999; 38:689–692.4. Kim HO, Cho SI, Kim JH, Chung BY, Cho HJ, Park CW, Lee CH. Food hypersensitivity in patients with childhood atopic dermatitis in Korea. Ann Dermatol. 2013; 25:196–202.5. Silverberg JI, Kleiman E, Lev-Tov H, Silverberg NB, Durkin HG, Joks R, Smith-Norowitz TA. Association between obesity and atopic dermatitis in childhood: a case-control study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 127:1180–1186.e1.6. Kim JH, Kim H, Park CW, Lee CH. Quality of life in adults with atopic dermatitis. Korean J Dermatol. 2011; 49:983–992.7. Garmhausen D, Hagemann T, Bieber T, Dimitriou I, Fimmers R, Diepgen T, Novak N. Characterization of different courses of atopic dermatitis in adolescent and adult patients. Allergy. 2013; 68:498–506.8. Rajka G. Essential Aspects of Atopic Dermatitis. [place unknown]: Springer;2012.9. Sandström Falk MH, Faergemann J. Atopic dermatitis in adults: does it disappear with age? Acta Derm Venereol. 2006; 86:135–139.10. Pyun BY. Natural history and risk factors of atopic dermatitis in children. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2015; 7:101–105.11. Sandström MH, Faergemann J. Prognosis and prognostic factors in adult patients with atopic dermatitis: a long-term follow-up questionnaire study. Br J Dermatol. 2004; 150:103–110.12. Wüthrich B. Clinical aspects, epidemiology, and prognosis of atopic dermatitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1999; 83:464–470.13. Mortz CG, Andersen KE, Dellgren C, Barington T, Bindslev-Jensen C. Atopic dermatitis from adolescence to adulthood in the TOACS cohort: prevalence, persistence and comorbidities. Allergy. 2015; 70:836–845.14. Bannister MJ, Freeman S. Adult-onset atopic dermatitis. Australas J Dermatol. 2000; 41:225–228.15. Roth HL, Kierland RR. The natural history of atopic dermatitis. A 20-year follow-up study. Arch Dermatol. 1964; 89:209–214.16. Lammintausta K, Kalimo K, Raitala R, Forsten Y. Prognosis of atopic dermatitis. A prospective study in early adulthood. Int J Dermatol. 1991; 30:563–568.17. Hanifin JM, Thurston M, Omoto M, Cherill R, Tofte SJ, Graeber M. The eczema area and severity index (EASI): assessment of reliability in atopic dermatitis. EASI Evaluator Group. Exp Dermatol. 2001; 10:11–18.18. Kanwar AJ, Narang T. Adult onset atopic dermatitis: under-recognized or under-reported? Indian Dermatol Online J. 2013; 4:167–171.19. Ozkaya E. Adult-onset atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005; 52:579–582.20. Lee JH, Han KD, Jung HM, Youn YH, Lee JY, Park YG, Lee SH, Park YM. Association between obesity, abdominal obesity, and adiposity and the prevalence of atopic dermatitis in young Korean adults: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008–2010. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2016; 8:107–114.21. Kwon JA, Roh KY, Koh BK, Kim JW. Clinical characteristics of adolescence and adult atopic dermatitis in Korea. Korean J Dermatol. 2004; 42:949–954.22. Kim KH, Park KC. Clinical characteristics of adult atopic dermatitis. Ann Dermatol. 1998; 10:229–232.23. Chu H, Shin JU, Park CO, Lee H, Lee J, Lee KH. Clinical diversity of atopic dermatitis: a review of 5,000 patients at a single institute. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017; 9:158–168.24. Kim KH, Park AY, Kim JS. Factors associated with atopic dermatitis in Korean adults: the Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey 2008. Korean J Rehabil Nurs. 2012; 15:83–90.25. Chung Y, Kwon JH, Kim J, Han Y, Lee SI, Ahn K. Retrospective analysis of the natural history of atopic dermatitis occurring in the first year of life in Korean children. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27:723–728.26. Nnoruka EN. Current epidemiology of atopic dermatitis in south-eastern Nigeria. Int J Dermatol. 2004; 43:739–744.27. Haeck IM, Knol MJ, Ten Berge O, van Velsen SG, de Bruin-Weller MS, Bruijnzeel-Koomen CA. Enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium versus cyclosporin A as long-term treatment in adult patients with severe atopic dermatitis: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011; 64:1074–1084.28. Beck LA, Thaçi D, Hamilton JD, Graham NM, Bieber T, Rocklin R, Ming JE, Ren H, Kao R, Simpson E, et al. Dupilumab treatment in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2014; 371:130–139.29. Gutgesell C, Heise S, Seubert S, Seubert A, Domhof S, Brunner E, Neumann C. Double-blind placebo-controlled house dust mite control measures in adult patients with atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2001; 145:70–74.30. Koutroulis I, Magnelli L, Gaughan J, Weiner E, Kratimenos P. Atopic dermatitis is more severe in children over the age of two who have an increased body mass index. Acta Paediatr. 2015; 104:713–717.31. Silverberg JI, Silverberg NB, Lee-Wong M. Association between atopic dermatitis and obesity in adulthood. Br J Dermatol. 2012; 166:498–504.32. Boulet LP. Obesity and atopy. Clin Exp Allergy. 2015; 45:75–86.33. Hersoug LG, Linneberg A. The link between the epidemics of obesity and allergic diseases: does obesity induce decreased immune tolerance? Allergy. 2007; 62:1205–1213.34. Martín-Romero C, Santos-Alvarez J, Goberna R, Sánchez-Margalet V. Human leptin enhances activation and proliferation of human circulating T lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 2000; 199:15–24.35. Nagel G, Koenig W, Rapp K, Wabitsch M, Zoellner I, Weiland SK. Associations of adipokines with asthma, rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in German schoolchildren. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2009; 20:81–88.36. Salam MT, Wenten M, Gilliland FD. Endogenous and exogenous sex steroid hormones and asthma and wheeze in young women. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 117:1001–1007.37. Luo X, Xiang J, Dong X, Cai F, Suo J, Wang Z, Liu M. Association between obesity and atopic disorders in Chinese adults: an individually matched case-control study. BMC Public Health. 2013; 13:12.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Measurement of Atopic Dermatitis Disability
- Clinical Characteristics of Lichen Amyloidosis Associated with Atopic Dermatitis: A Single Center, Retrospective Study
- Serum IgE Level in Patients of Atopic Dermatitis and Atopic Dermatitis with Molluscum Contagiosum
- Difference of Malassezia Species and Pityrosporum ovale Specific IgE in Head and Neck Lesions of Atopic Dermatitis Related to Ages and Severity
- Nipple Involvement in Atopic Dermatitis: Report of 3 cases